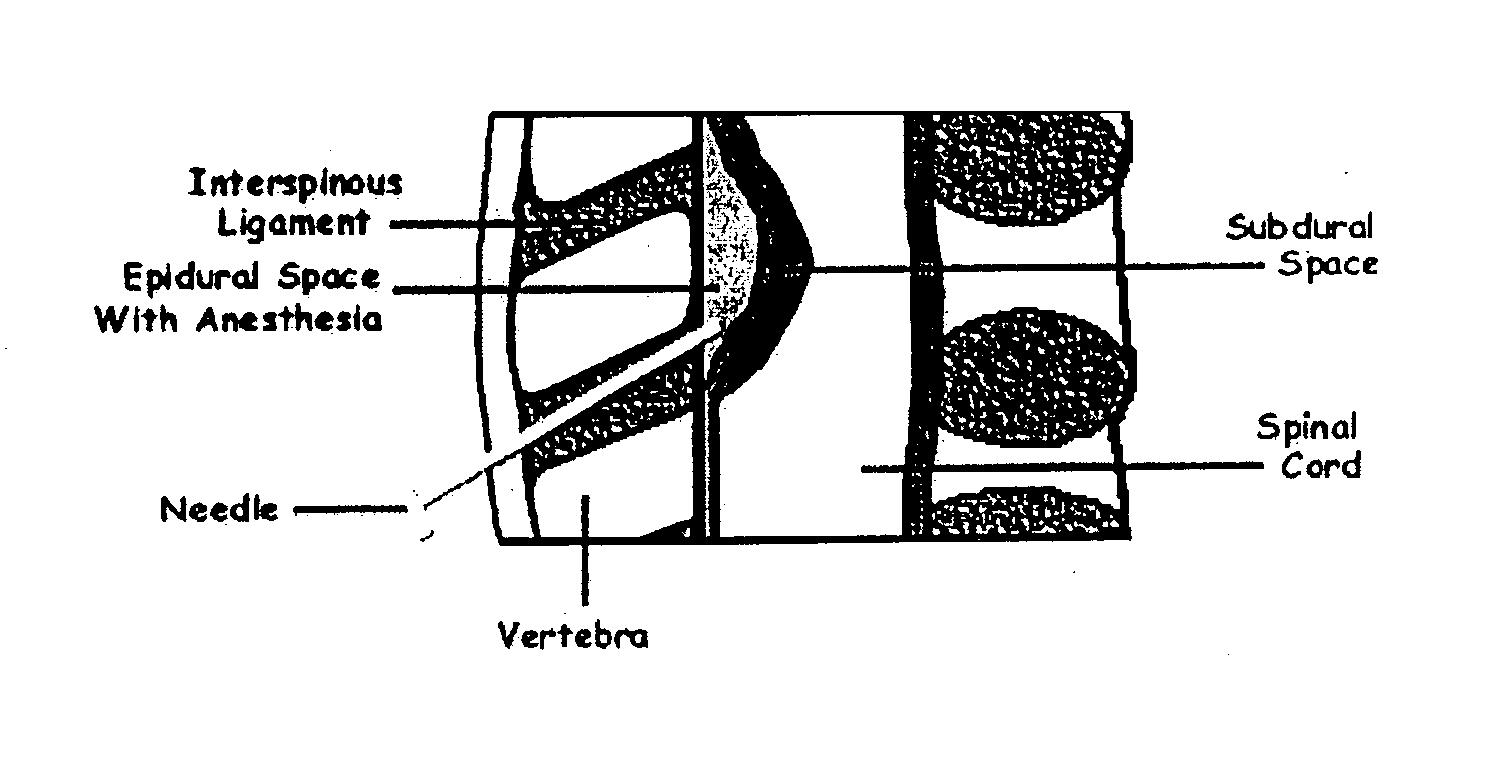
Methods and kits for detecting cerebrospinal fluid in a sample
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 2
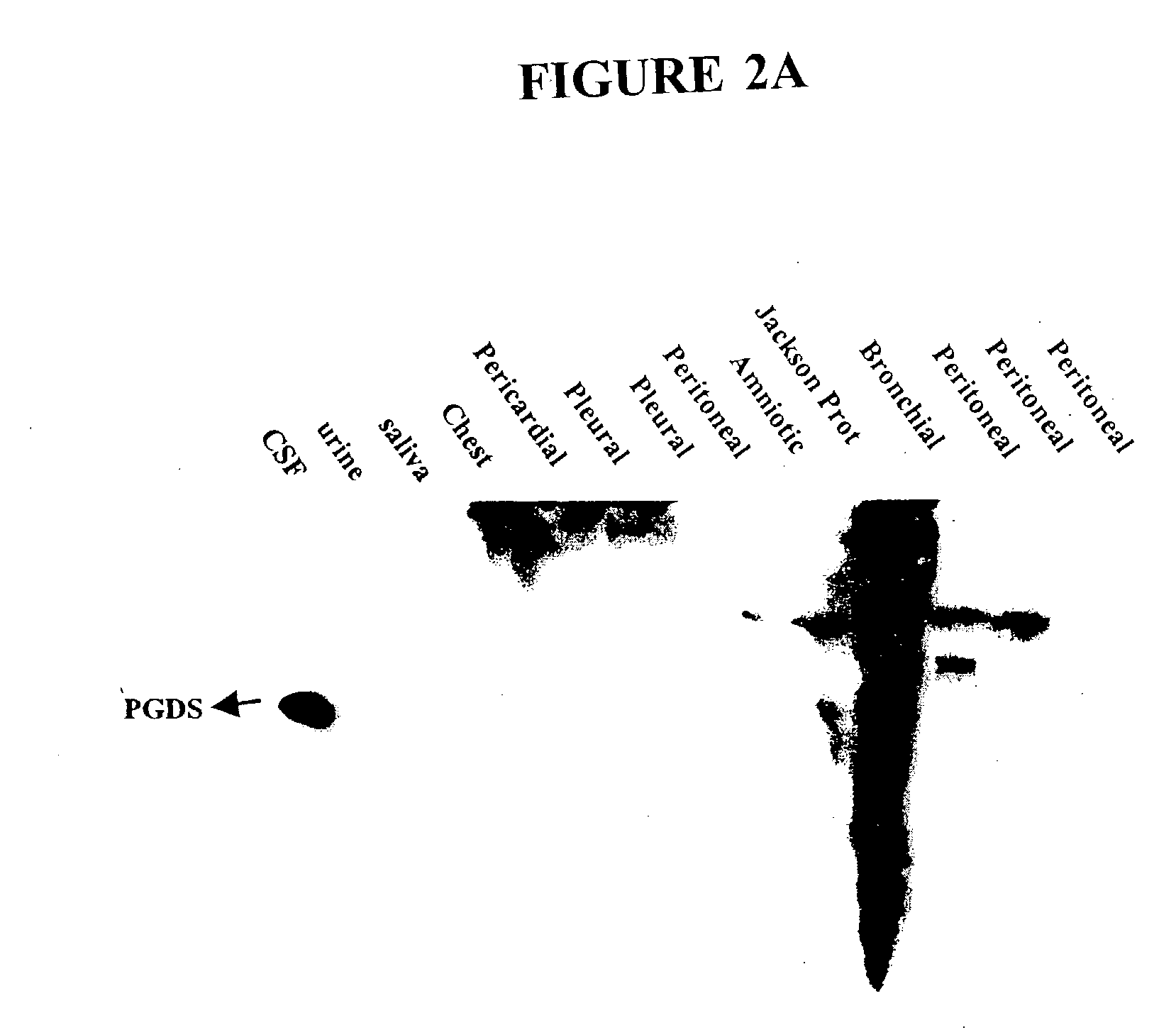
[0094] Polyclonal anti-PGDS antibody reliably detects PGDS in CSF samples from 12 distinct human sources, indicating the antibody-mediated detection of PGDS in CSF is antigen-specific but not patient-specific (FIG. 2B).
example 3
[0095] Polyclonal anti-PGDS antibody reliably discriminates aspirates of fluid from different body compartments. Strong anti-PGDS binding is observed in fluid samples from spinal sources, whereas no PGDS binding is seen in eluates from catheters in the epidural space (FIG. 2C).
[0096] These results indicate that the presence or absence of PGDS in body fluid samples reliably and specifically predicts the source of the fluid, and thereby discriminates between spinal, epidural and other body fluid compartment origins.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com