Impingement air dry process for making absorbent sheet
a technology of absorbent cells and absorbent sheets, applied in papermaking, non-fibrous pulp addition, coatings, etc., can solve the problems of fiber, wet press operations, fiber, and energy-intensive conventional thermal dewatering with hot air, and achieve the effect of reducing the cost of fibers, and increasing the cost of square
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
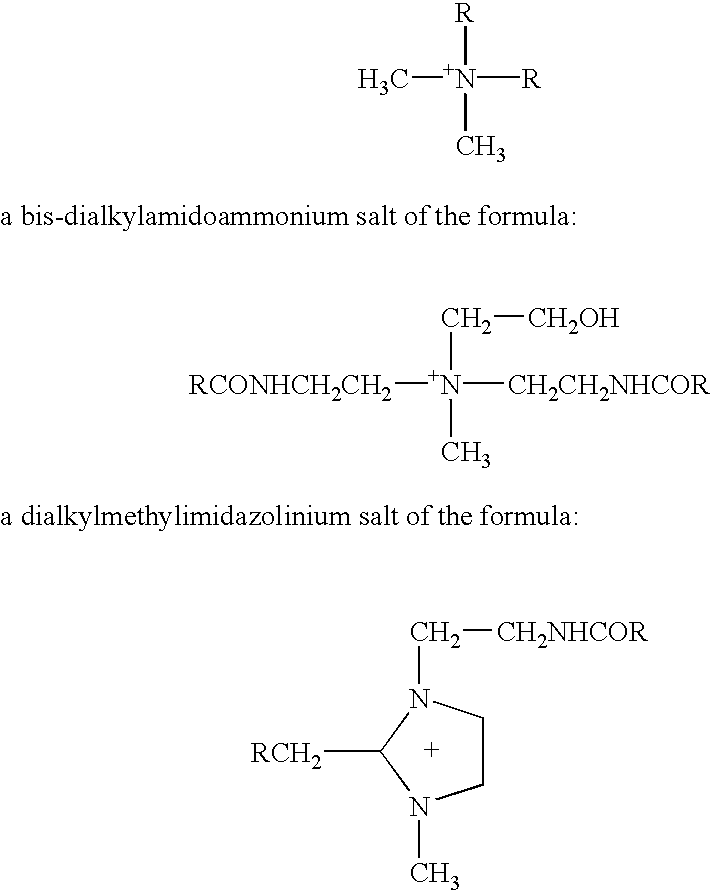
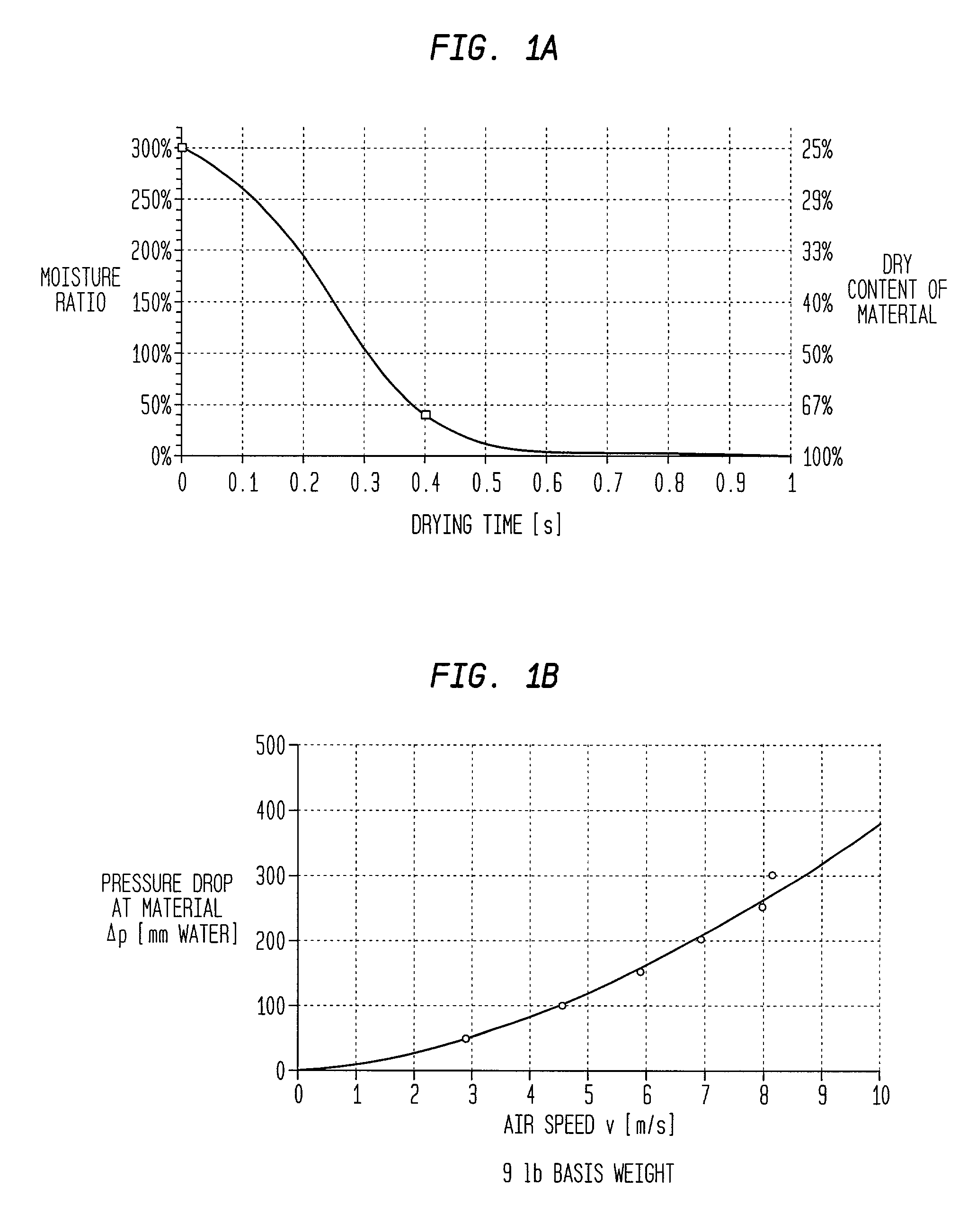
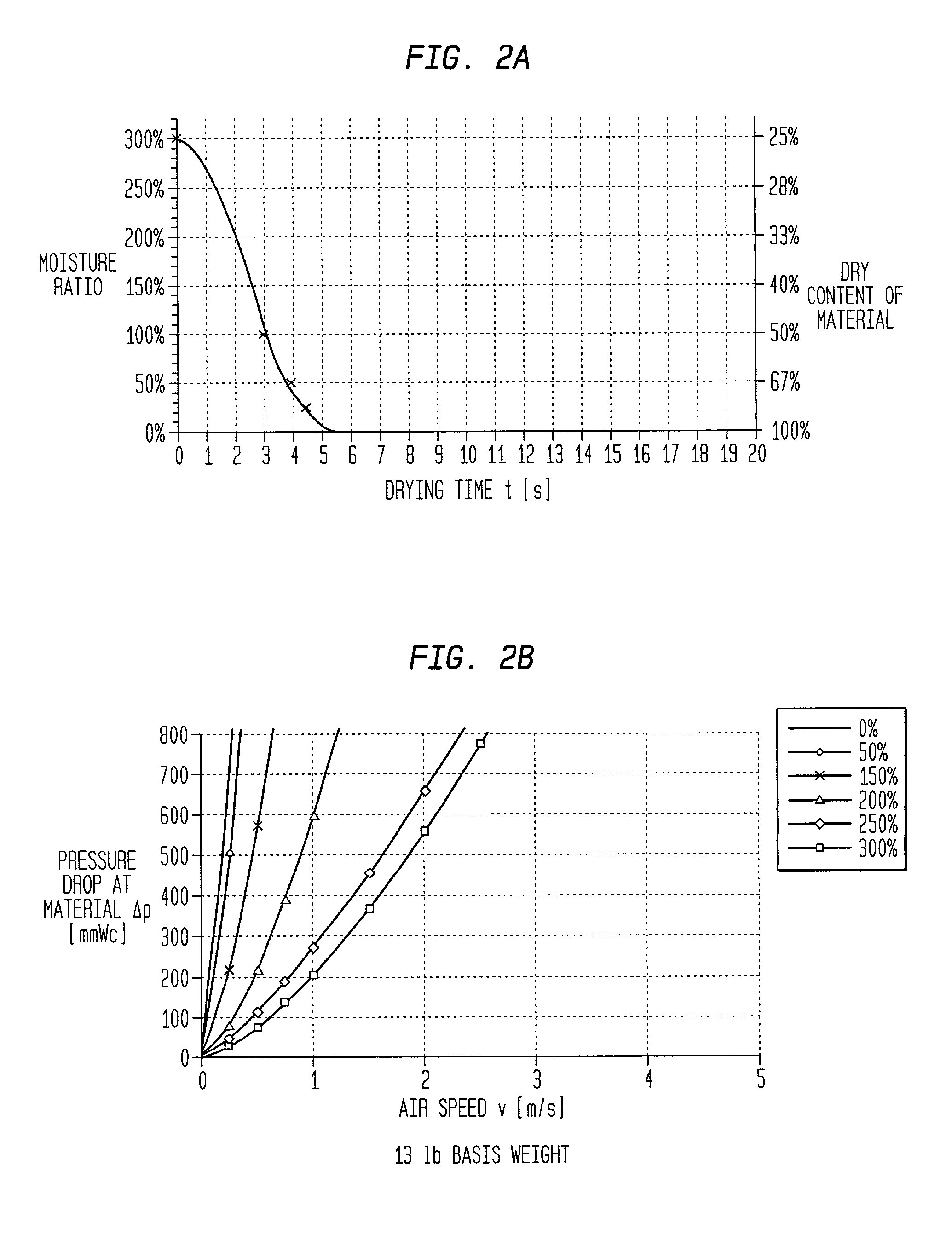
[0033] The present invention is described in detail below for purposes of exemplification only. Various modifications within the spirit and scope of the present invention, set forth in the appended claims, will be readily apparent to those of skill in the art. According to the present invention, an absorbent paper web can be made by dispersing fibers into aqueous slurry and depositing the aqueous slurry onto the forming wire of a papermaking machine. Any art recognized forming technique might be used. For example, an extensive but non-exhaustive list includes a crescent former, a C-wrap twin wire former, an S-wrap twin wire former, a suction breast roll former, or a Fourdrinier former. The particular forming apparatus is not critical to the success of the present invention. The forming fabric can be any suitable foraminous member including single layer fabrics, double layer fabrics, triple layer fabrics, photopolymer fabrics, and the like. Non-exhaustive background art in the formin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com