Method and apparatus for testing hollow pieces for impermeability
a technology of impermeability and hollow pieces, applied in the direction of fluid-tightness measurement, structural/machine measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the test time, unable to conduct useful measurements, and unable to achieve useful measurements, so as to accelerate the achieving of temperature equilibrium and reduce the test time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
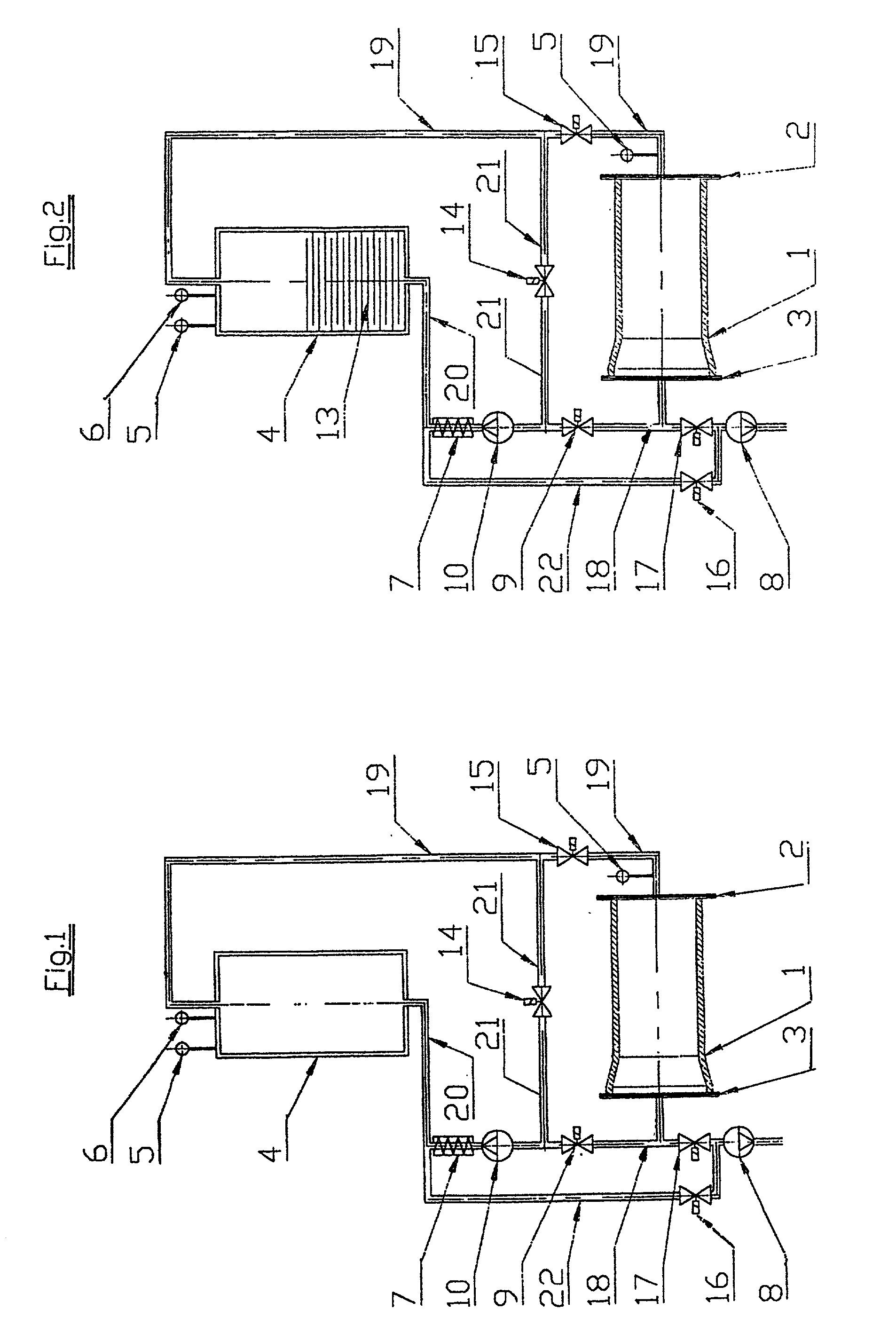
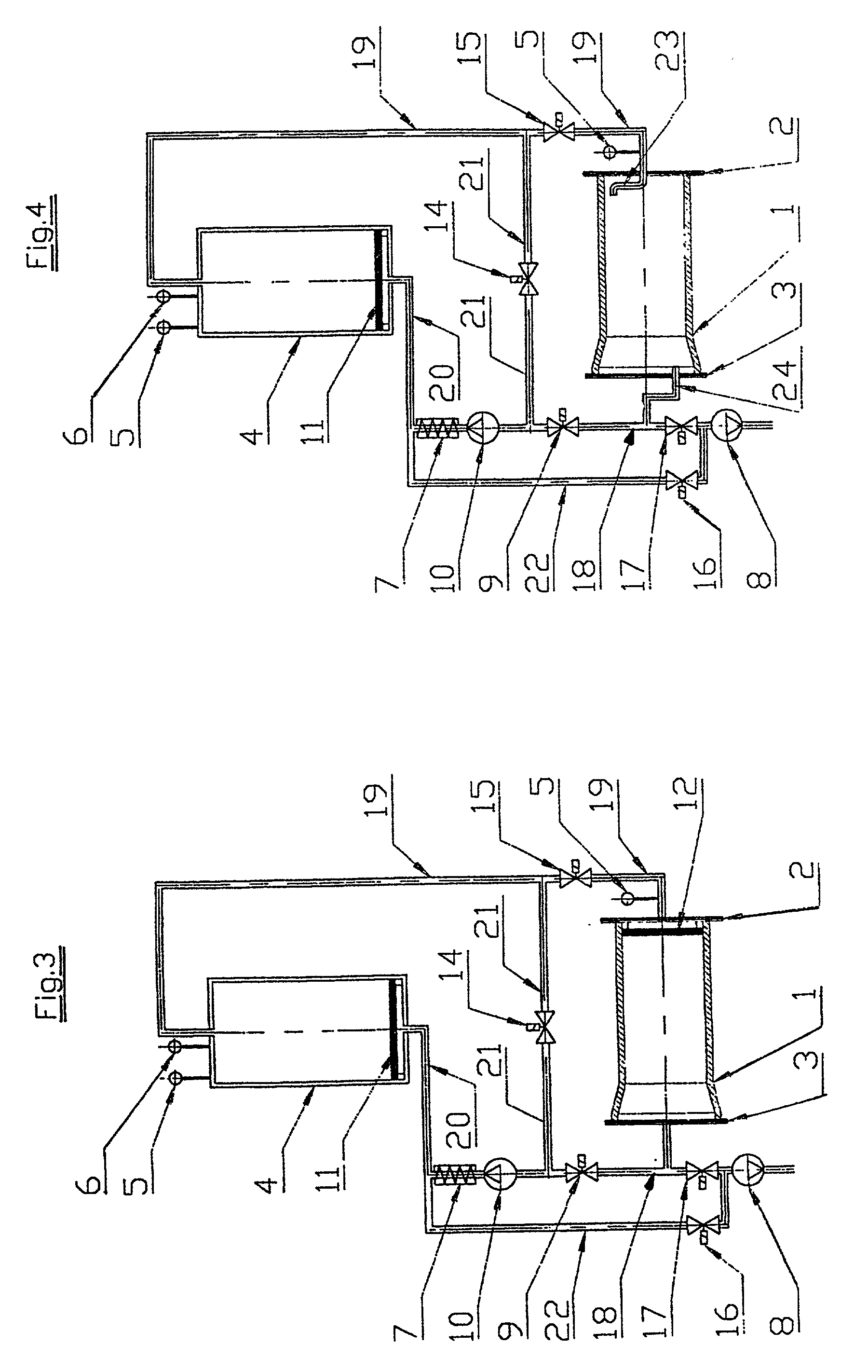
[0032] FIG. 1 shows the test piece 1, in particular a concrete pipe, that is clamped between the end plates 2 and 3 for the purpose of an impermeability test. It goes without saying that these end plates 2 and 3 are part of a whole testing construct (which is not shown here in more detail). The testing construct can also be set up to provide for examination of the test pieces 1 at fixed cycles, with the test pieces resting on a transport device and being transported through the testing construct that is designed as a testing station and as a part of the manufacturing process. The front plate 3 can be attached to a vacuum pump 8 via a tab line that is inserted into the connecting line 18. The vacuum pump 8 is suitable for adjusting the desired or required testing pressure inside the test piece 1. After the desired or required vacuum has been reached, a valve 17 is closed, thereby interrupting the connection between test piece 1 and vacuum pump 8. Any permeability in the walls of the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| impermeability | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com