RFID scheme in harsh environments
a technology of harsh environments and rfid sensors, applied in the field of rfid sensors in harsh environments, can solve problems such as limit the use of rfid sensors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
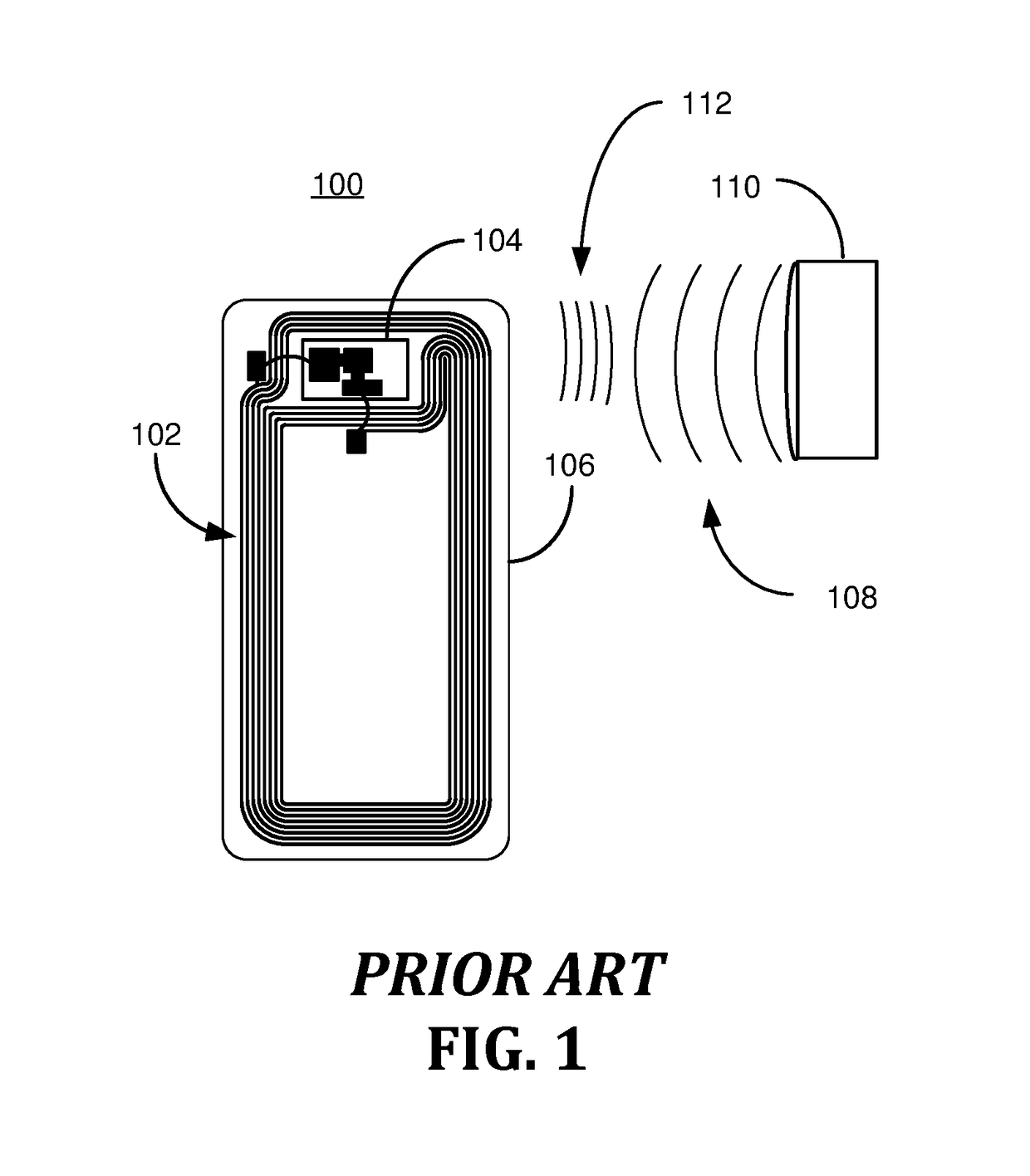
[0017]Initially, this disclosure is by way of example only, not by limitation. Thus, although the instrumentalities described herein are for the convenience of explanation, shown and described with respect to exemplary embodiments, it will be appreciated that the principles herein may be applied equally to various RFID tags exposed to a variety of environments that exceed operability of RFID tags. In what follows, similar or identical structures may be identified using identical callouts.
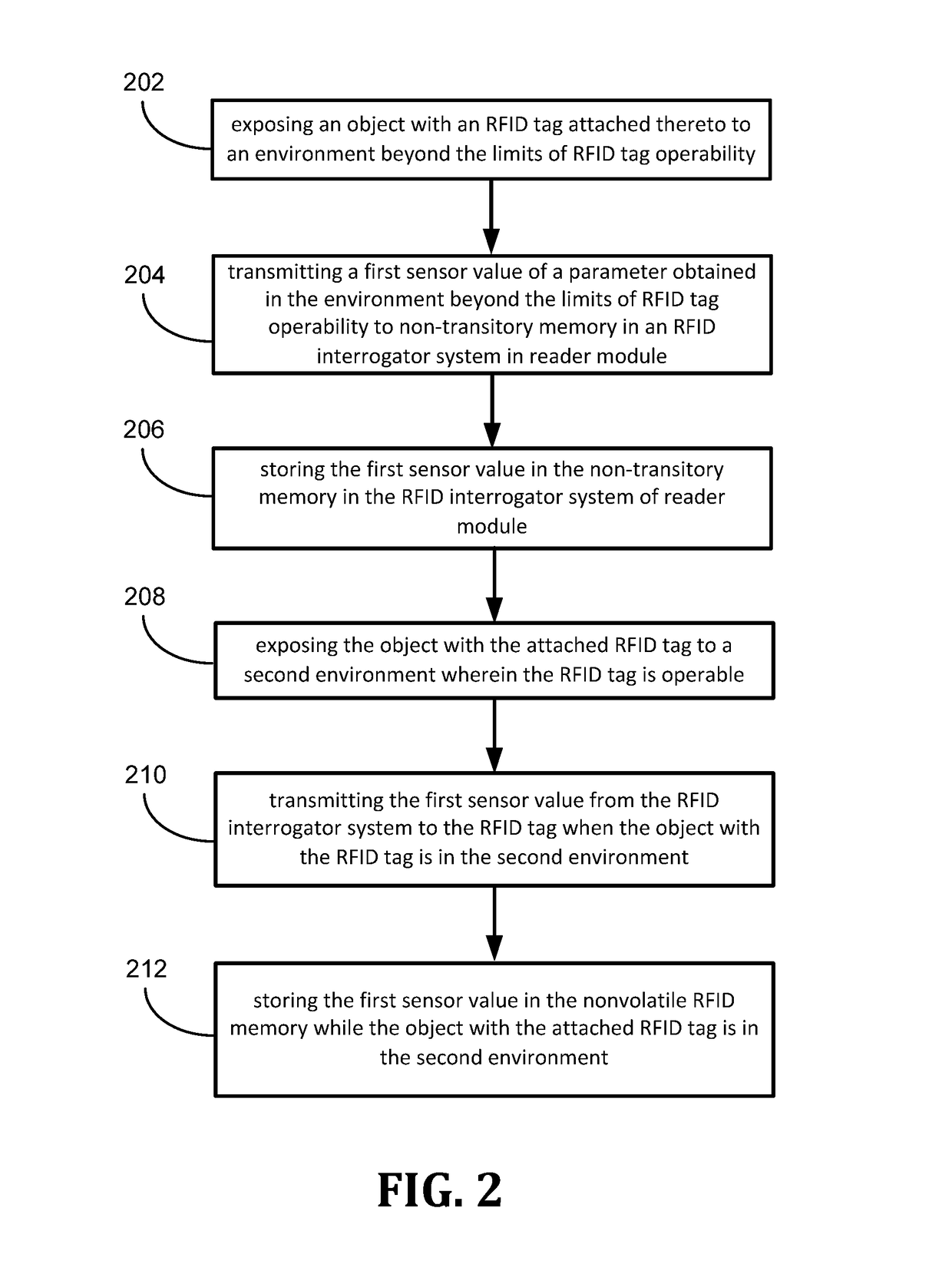
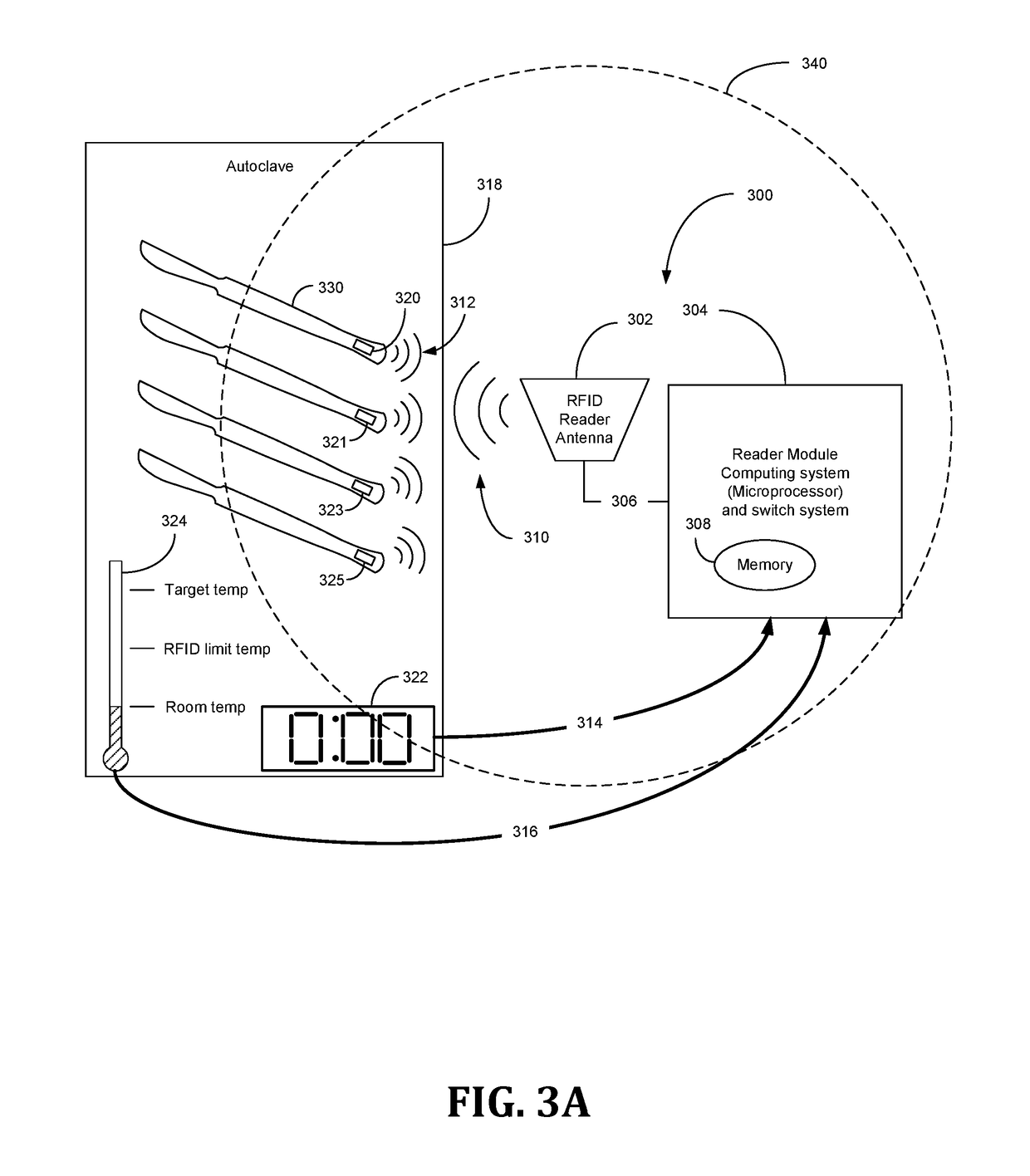
[0018]In certain instances, object / s, such as a tool, may intentionally or unintentionally be exposed to extreme environments momentarily or for prolonged periods of time. For purposes of record keeping, it may be desirable to record data associated with the object / s in the extreme environment. An extreme environment can be an elevated temperature or extreme cold or something undergoing high pressure or accelerations, just to name several examples. Extreme environments as used in this disclosure is ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com