Distributing realizing method for radio sensor network no-anchor point location
A wireless sensor and sensor network technology, applied in the transmission system, electrical components, data exchange through path configuration, etc., can solve the problems of interruption of information exchange, power consumption, high communication overhead, etc., and achieve the effect of high positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
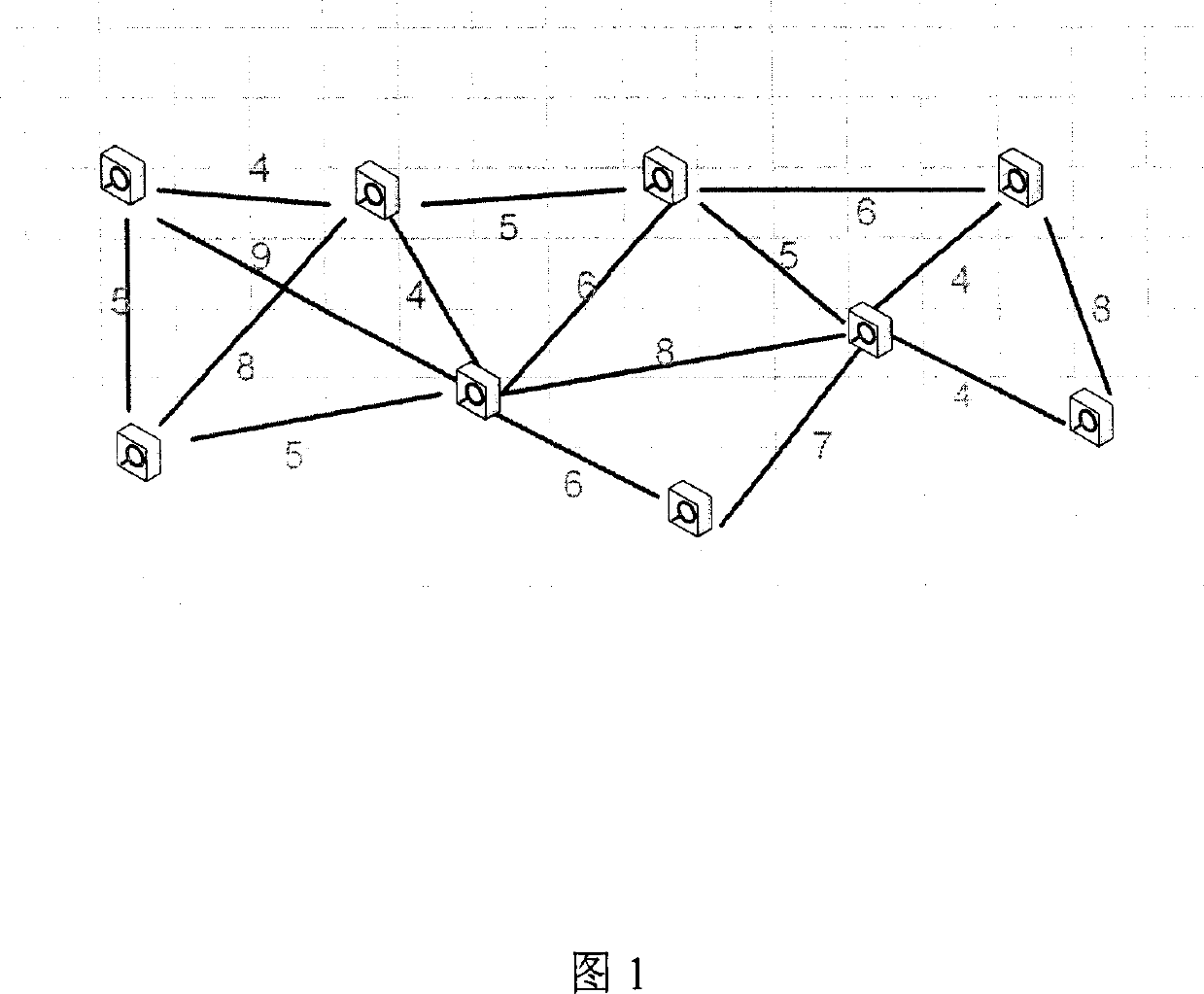
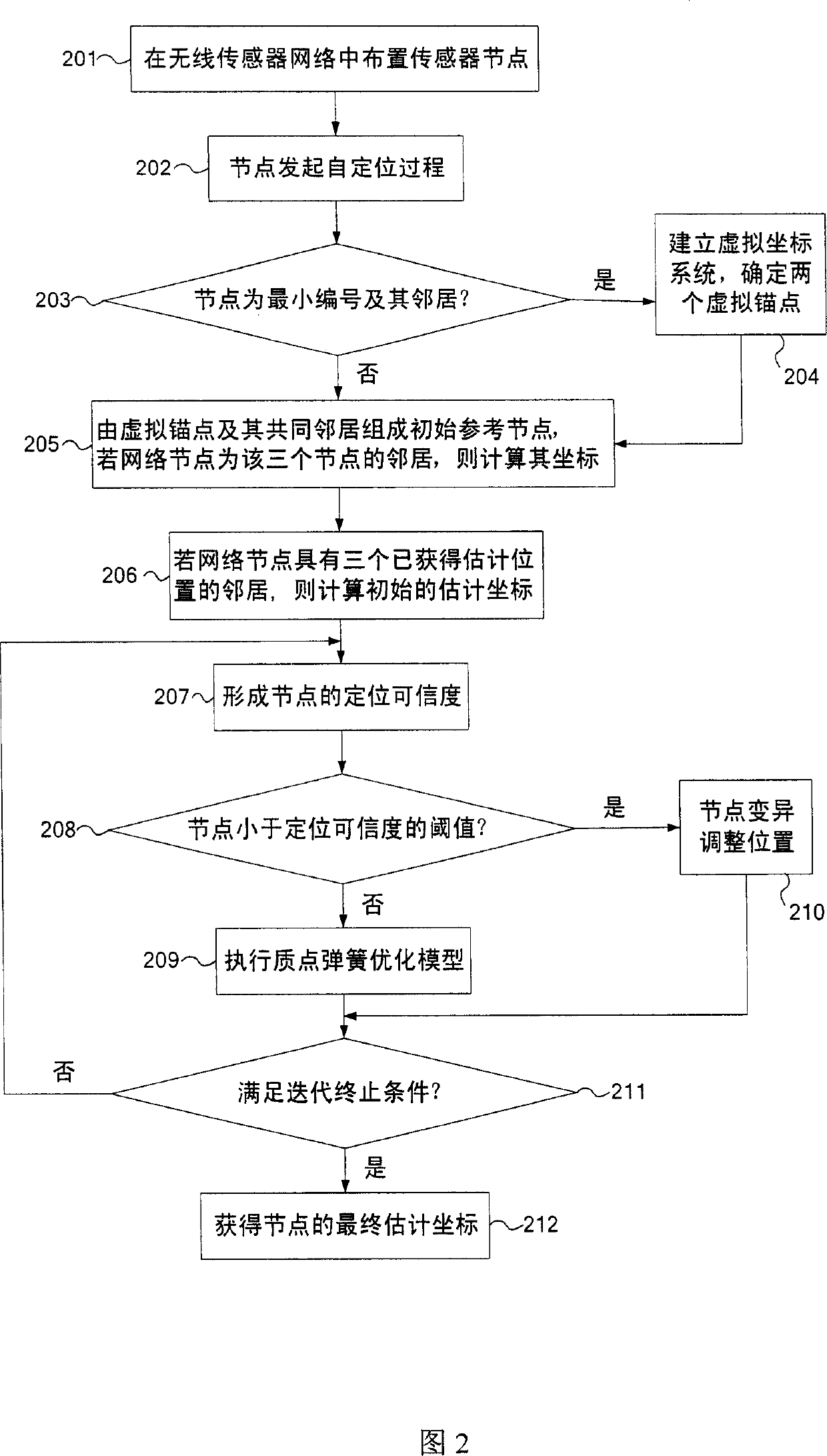
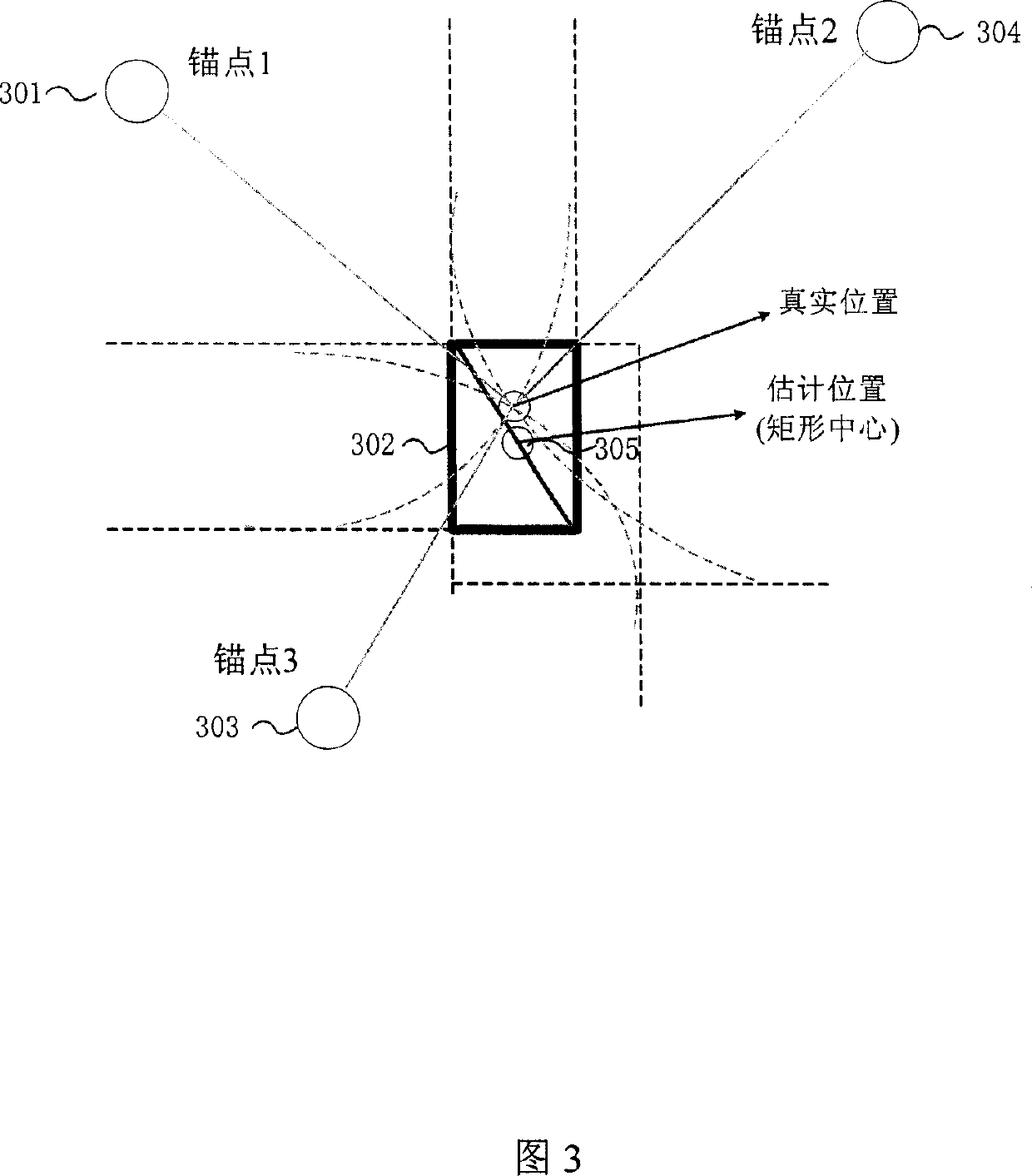
[0054] Certain embodiments of the invention are described in more detail with reference to the accompanying drawings. The present invention provides a practical distributed anchor-free positioning algorithm based on computational geometry theory, as long as the distance between adjacent nodes can be measured. The positioning process uses distributed operations to establish a set of virtual coordinate systems. First, the approximate position of the node is estimated, and then the coordinate position is iteratively solved by using the particle spring optimization model and combining the adjacency information of the node. This scheme overcomes the defect that existing positioning schemes require anchor points, and the calculation process is implemented in a distributed manner at each node, avoiding a large amount of communication overhead caused by centralized operations.
[0055] Fig. 2 is a flow chart showing the positioning steps and details of the method of the present invent...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com