Method and system for distributing multimedia contents through a wireless communications network, particularly a mobile telephony network
A wireless communication network and wireless communication network technology, applied in the field of telecommunications, can solve the problems of indistinguishable network equipment, impossibility of sending address information to a specific mobile station, advance timing of mobile stations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
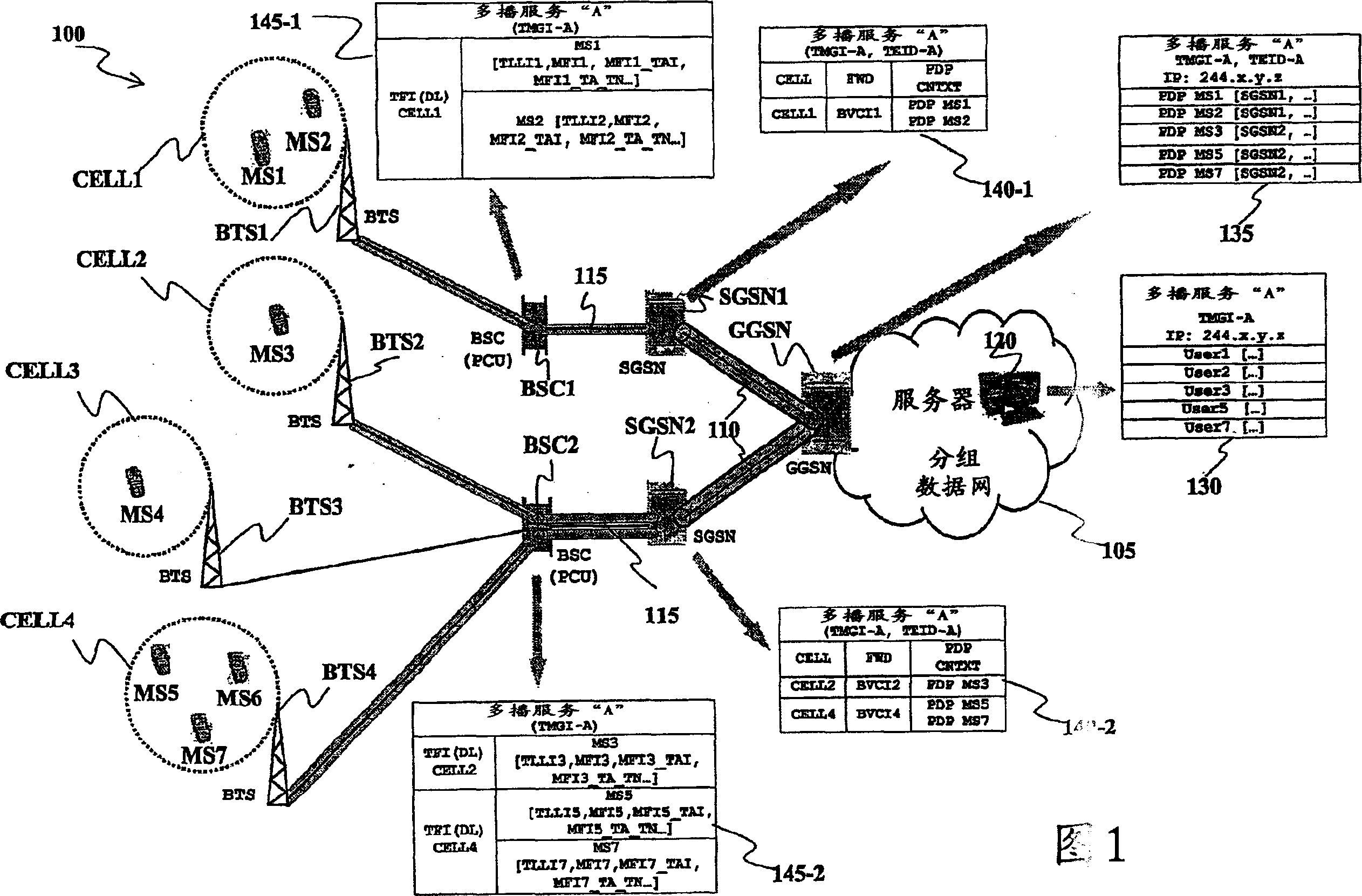
[0076] Reference is made to the figures, in particular to Fig. 1, which schematically shows a cellular mobile communication network 100, in particular a GSM network.
[0077] Mobile communication network 100 includes a number of base station subsystems (BSS), each providing signal coverage for cellular communications within a respective geographic area.
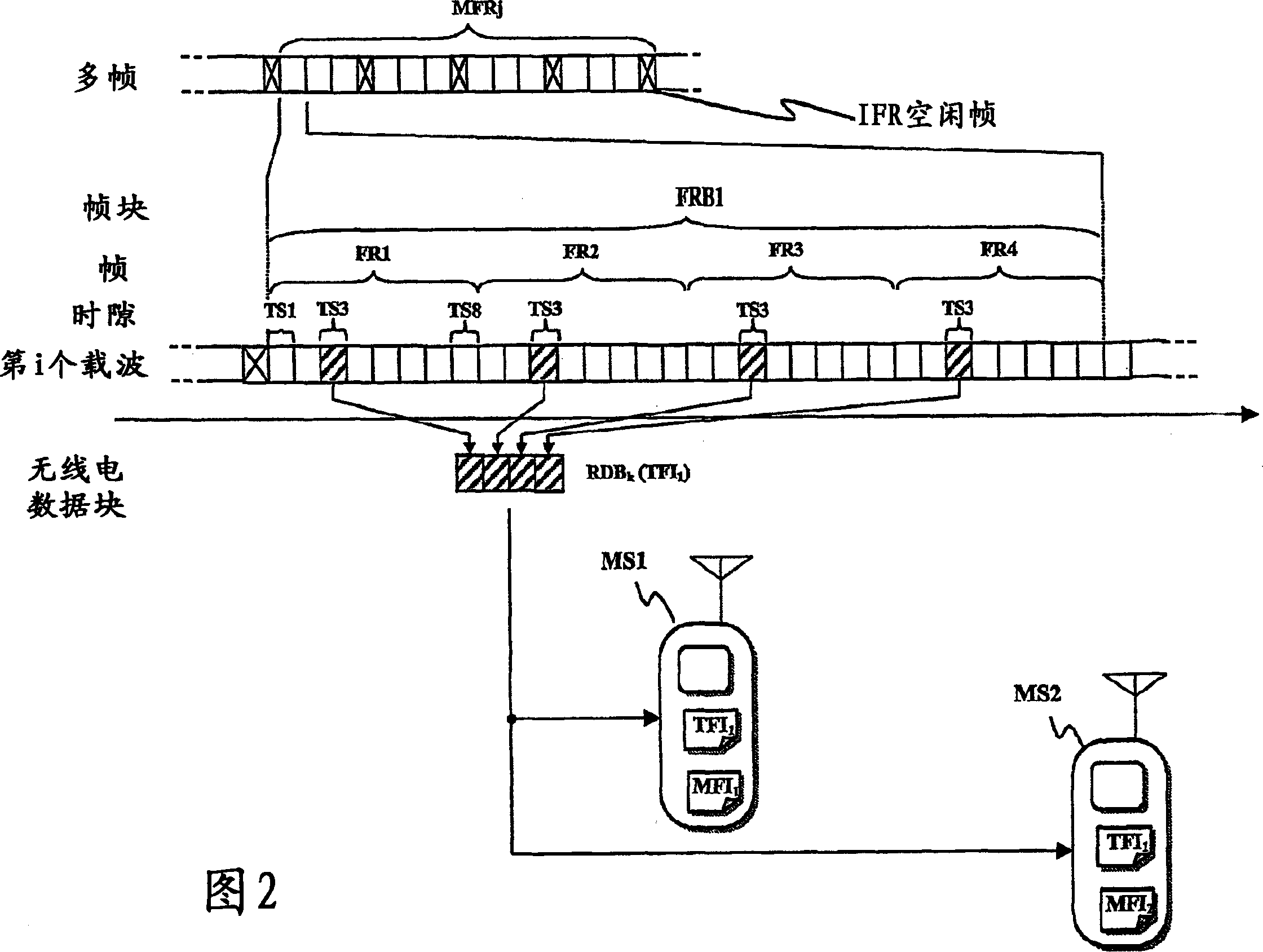
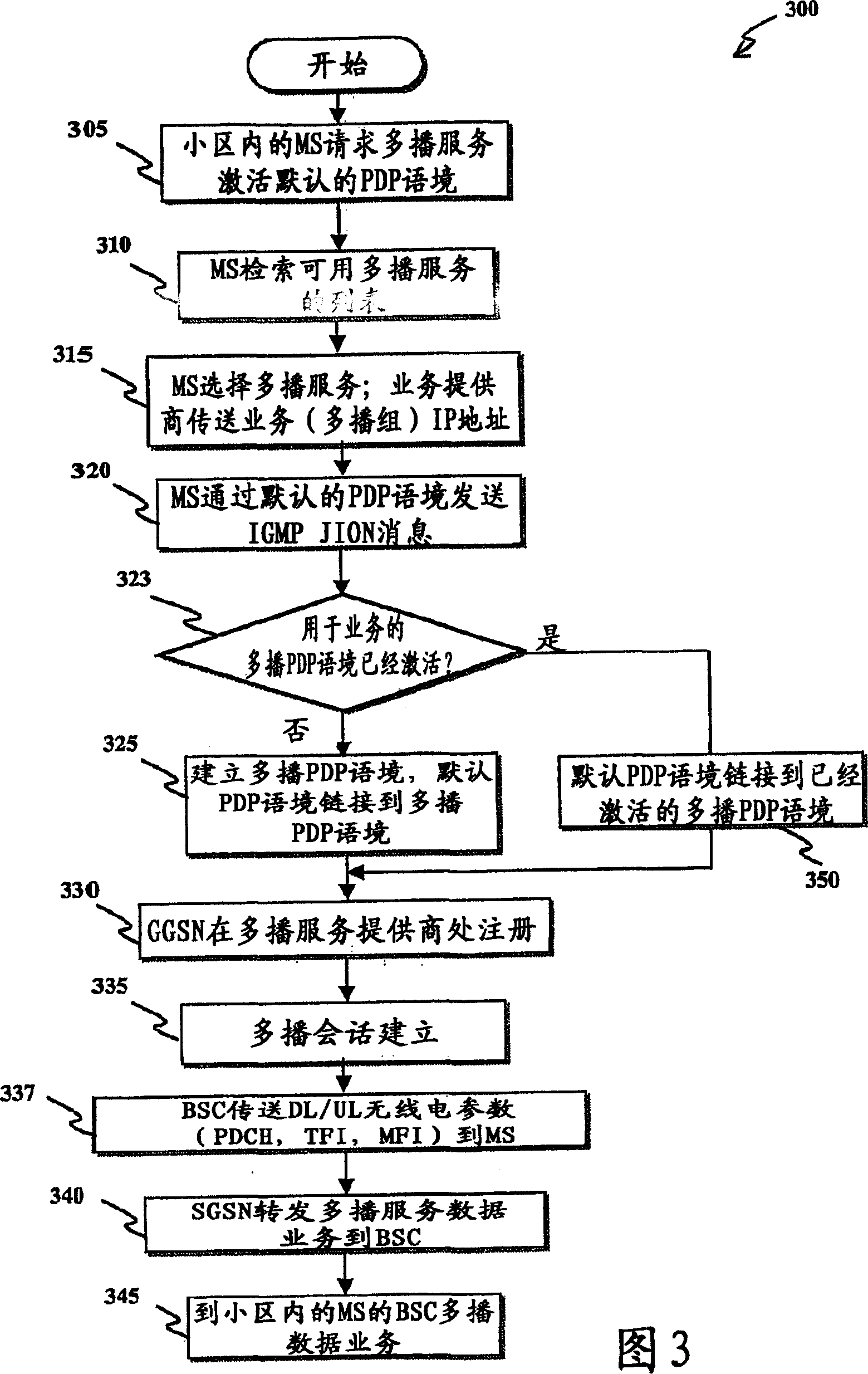
[0078] A typical BSS includes many Base Transceiver Stations (BTS), each covering its own geographic area within the area covered by the BSS; the number of BTSs in a BSS may actually be higher, however, to simplify the illustration, only the Four BTSs BTS1, BTS2, BTS3, and BTS4 (illustrated schematically with antennas) are shown with associated cells CELL1, CELL2, CELL3, and CELL4 (illustrated as areas surrounded by dashed circles). A normal BTS communicates with a user's mobile station (MS), usually a cellular phone, located within the cell of the BTS, such as MSs MS1 and MS2 in cell CELL1, MS MS3 in cell CELL2, MS MS4 in ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com