The primers specific to cervus elaphus, c. nippon, c. canadensis and rangifer tarandus gene and the method to identify cervi parvum cornu species
An identification method, a technology of sika deer, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbe determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problem of no introduction of velvet antler
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] (Example 1) Preparation of velvet antler sample
[0058] The blood and tissues of red deer, sika deer, red deer, and reindeer raised in Seoul Grand Park were used as the standard sample of antler. As other blood, the blood and blood of red deer, sika deer, and red deer raised on domestic individual farms and domestic The circulating dried velvet antler is used in experiments. Use QIAamp DNA microkit (QIAGEN Germany) to extract all the DNA isolated from the blood or tissue of deer antler according to the user's instructions.
Embodiment 2
[0059] (Example 2) Confirming the partial base sequence of the D-loop of velvet antler and determining the standard D-loop base sequence
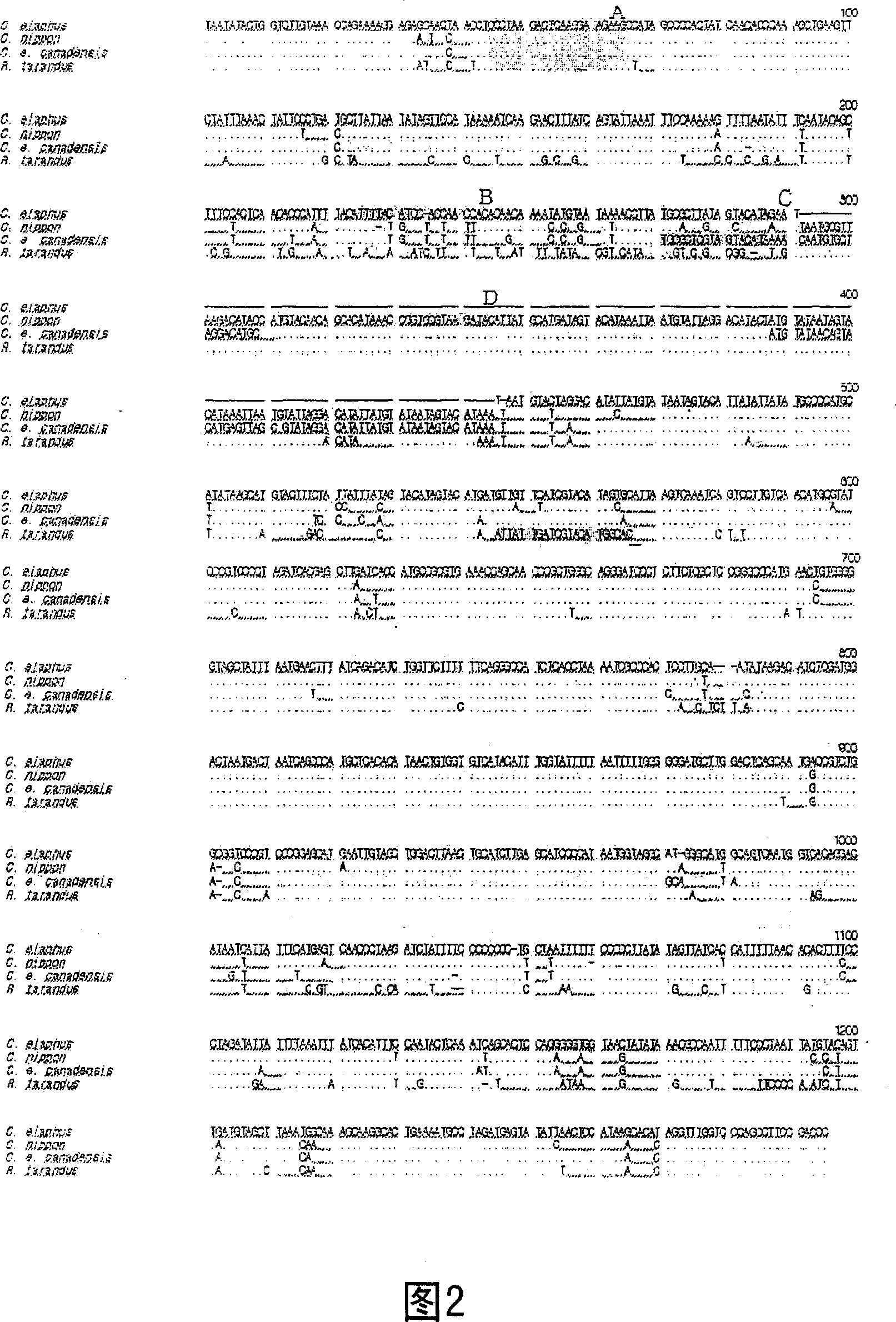
[0060] In order to amplify the D-loop region of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) of red deer (Cervus elaphus), sika deer (Cervus nippon), red deer (Cervuselaphus canadensis) and reindeer (Rangiger tarandus) for base sequence analysis, three primers were used. The CST2 primers and CST39 primers described in sequence numbers 1 and 2 use the primers published in Polziehn et al. (1998), because the SeqR primer described in sequence number 3 cannot base the entire D-loop in one experiment. Sequence analysis is based on the result of base sequence analysis with CST39 primers for re-synthesis, and then completes the remaining base sequence analysis to obtain all base sequences.
[0061] The base sequence analysis of the D-loop region was performed with Perkin-Elmer DNA terminator Cycle Sequencing Ready Reaction Kit, DNA amplifier (GeneAmp PCR System 9700, Ap...
Embodiment 3
[0065] (Example 3) Preparation and confirmation of specific primers
[0066] After determining the standard D-loop base sequence of red deer, sika deer, red deer, and reindeer, FOR primer (sense; Tm value 58°C) (SEQ ID NO: 4) was used as the forward primer, and the Sika deer, red deer and reindeer specific reaction primers (serial number 5 to 8), each primer is called RED (Tmvalue 53℃), NIP (Tm value 53℃), ELK (Tm value 53℃), REIN (Tm value) 54°C). To make primers, use http: / / www.bioneer.co.kr / tools website.
[0067] In order to obtain the specific D-loop mtDNA section of the antler species, 2 pmole of FOR, RED, NIP, ELK, REIN primers and 40 pmole of L14724 (Masudaet.al., 1996) primers, 10X reaction buffer (Applied biosystems) as internal control , USA), 1.5mMMgCl2, 0.2mM dNTP Mixture, 1.25unit of AmpliTaq Gold polymerase (Applied biosystems, USA) and 1ng of DNA were added to 25μl of reaction solution.
[0068] After DNA amplification was performed at 95°C for 12 minutes in the pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com