Current transfer logic
一种逻辑电路、电流的技术,应用在逻辑信号领域,能够解决电压偏移、检测电路操作不利影响等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
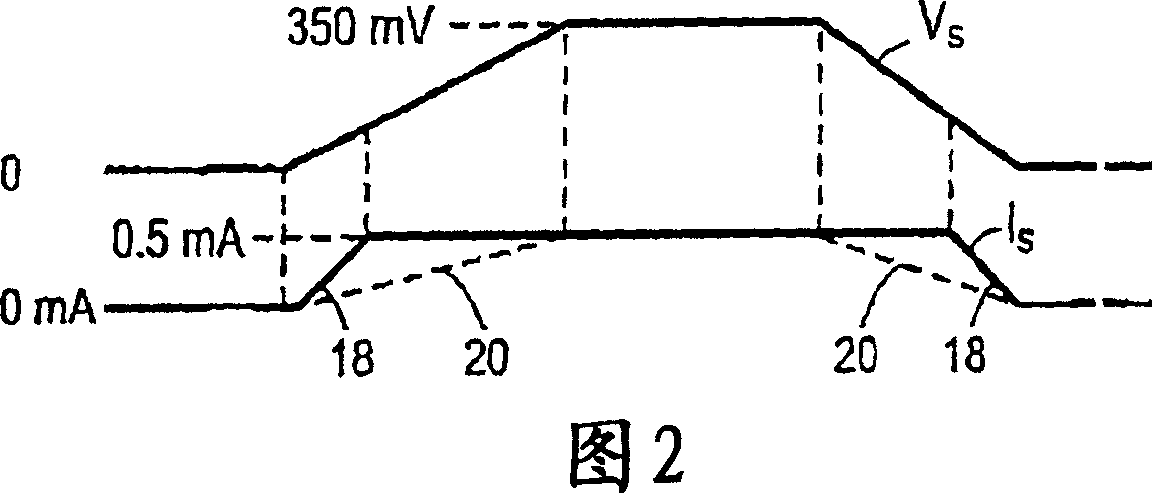
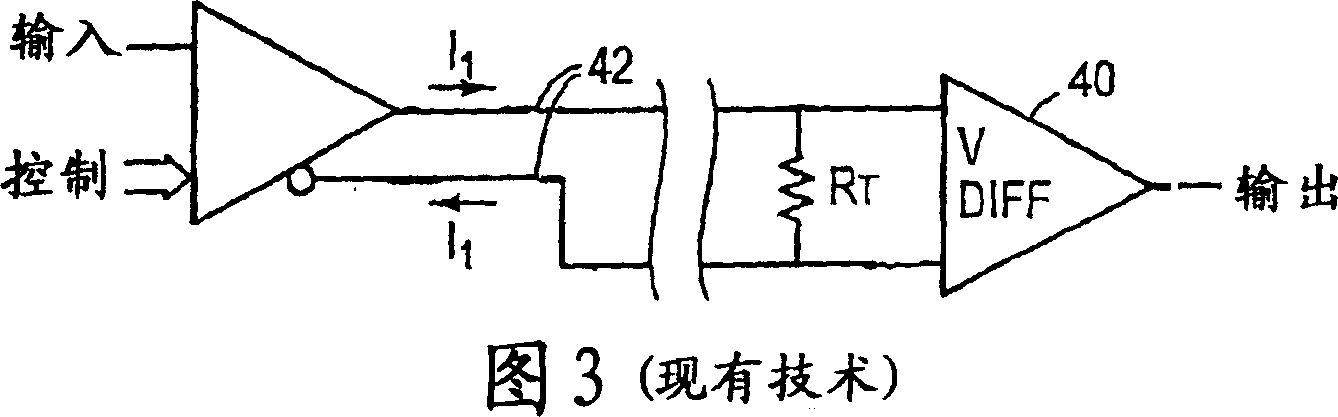
[0025] Figure 4A shows a diagram of a preferred embodiment of the invention. The input signal Vin controls and selects the output current signals Ia and Ib that are driven into the transmission lines 50 and 52 . In one logic state, Ia is a positive current output into the first transmission line 50 and Ib is a negative current input from the second transmission line 52 . In the opposite logic state, Ia is a negative current entering from the first transmission line 50 and Ib is a positive current entering the second transmission line 52 . In another preferred embodiment, it is also possible that no current is driven into any of the transmission lines.
[0026] If each transmission line has a characteristic impedance of 50 ohms, an Rt of 100 ohms is placed between the ends of the signal wires and used to terminate the two transmission lines. It is important that Ia and Ib are not equal to each other so that there is a return current through the shield. Also, since Rt is conn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com