Rotor blade for a wind energy turbine
A technology of rotor blades and turbines, applied in wind power generation, wind engines, wind turbine components, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in combining the internal structure of rotor blades, complex structure of the buffer system, etc., and achieve low additional mass, firm structure, and easy manufacturing and the effect of installing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
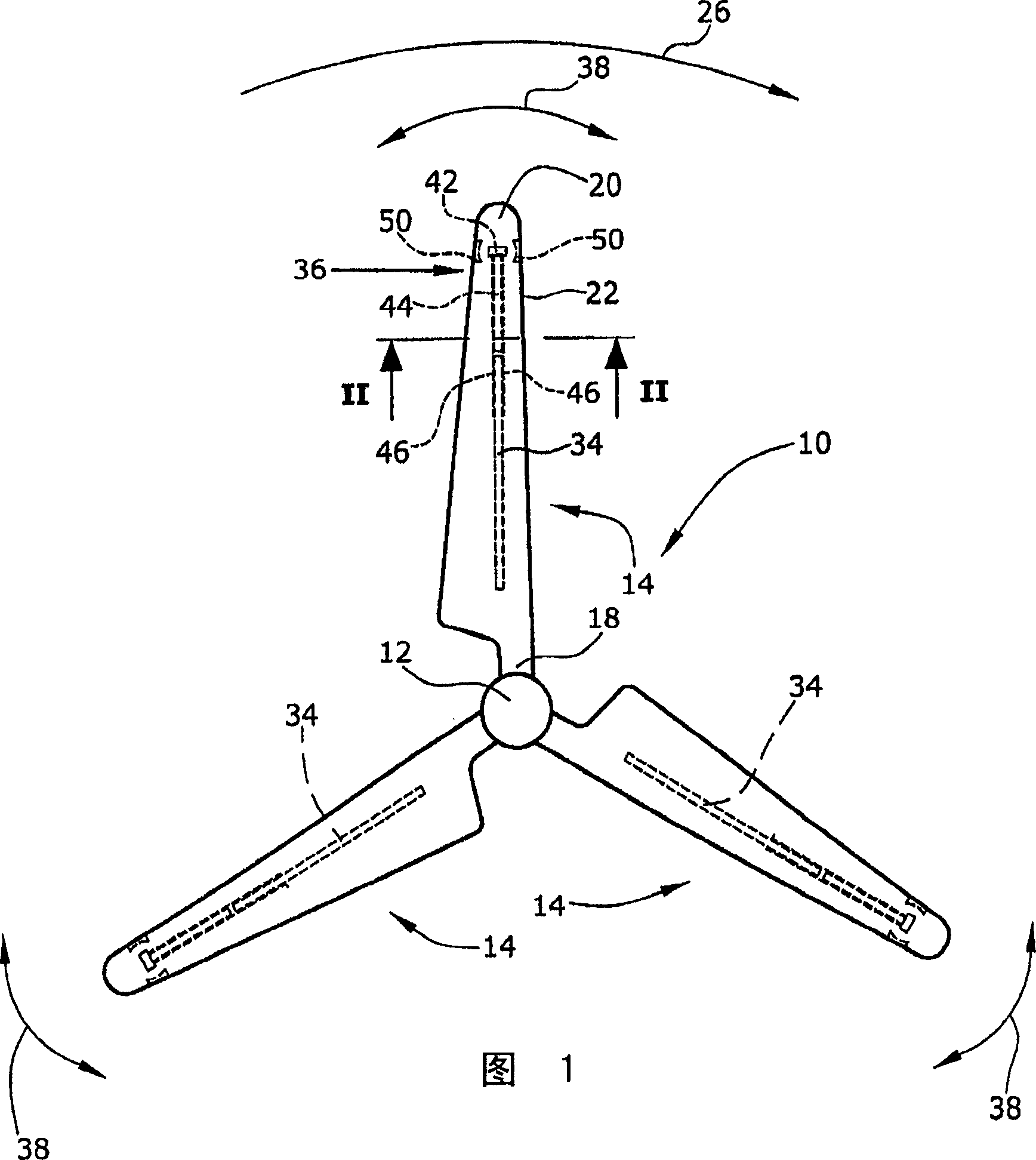
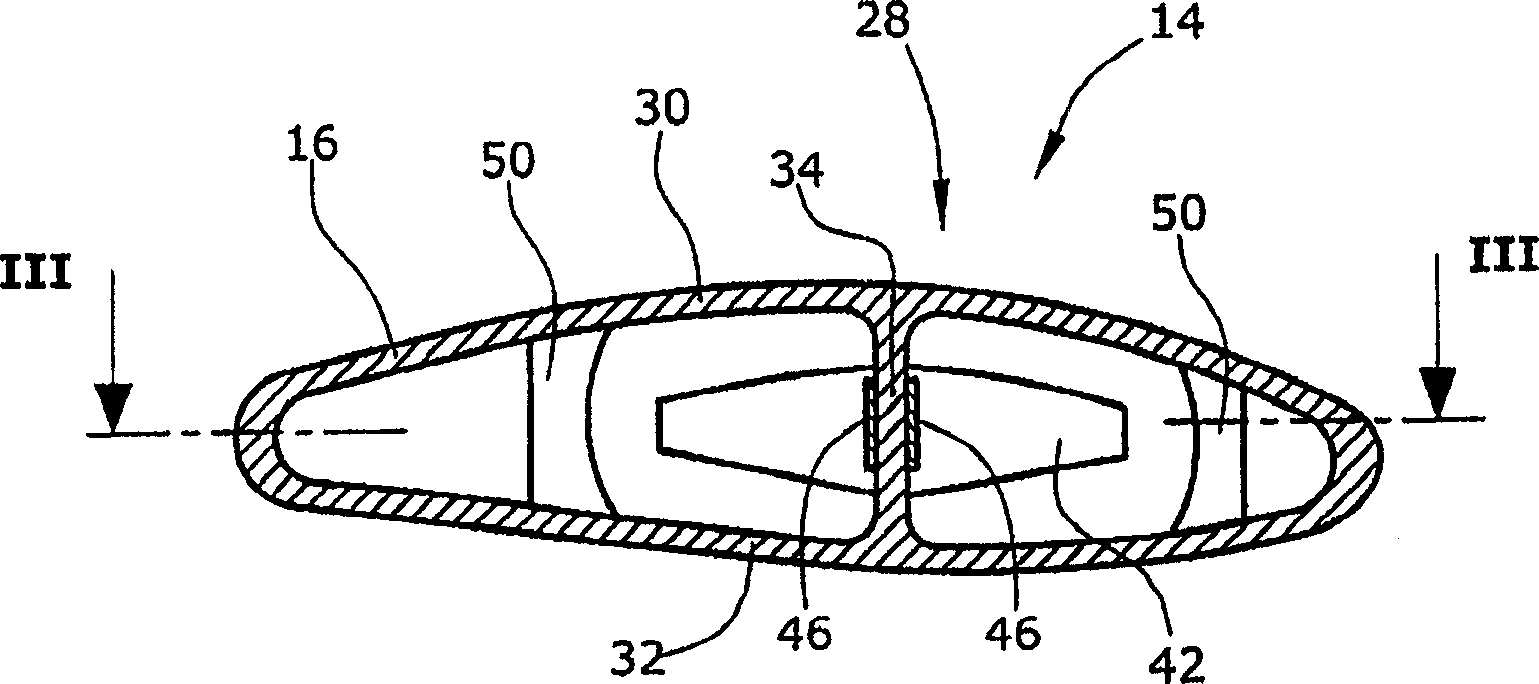
[0021] FIG. 1 shows a front view of a rotor 10 for a wind energy turbine, the rotor 10 comprising a hub 12 and three rotor blades 14 extending radially from the hub 12 . Each rotor blade 14 includes a shell 16 defining a root 18 and a tip 20 that limit the longitudinal dimension of the rotor blade 14 (see also figure 2 ). The casing 16 of each rotor blade 14 also defines a leading or forward edge 22 and a trailing or rearward edge 24 relative to the direction of rotation of the rotor 10 (see arrow 26 in FIG. 1 ). The configuration of the casing 16 of each rotor blade 14 also includes a spar 28 having two spar caps 30 , 32 disposed within the casing 16 and extending and connecting the spar caps 30 , 32 within the casing 16 . At least one shear web 34 of . The individual parts of the casing 16 and its spars 28 comprise sandwich and laminate structures that are basically known to those of ordinary skill in the art of manufacturing rotor blades.
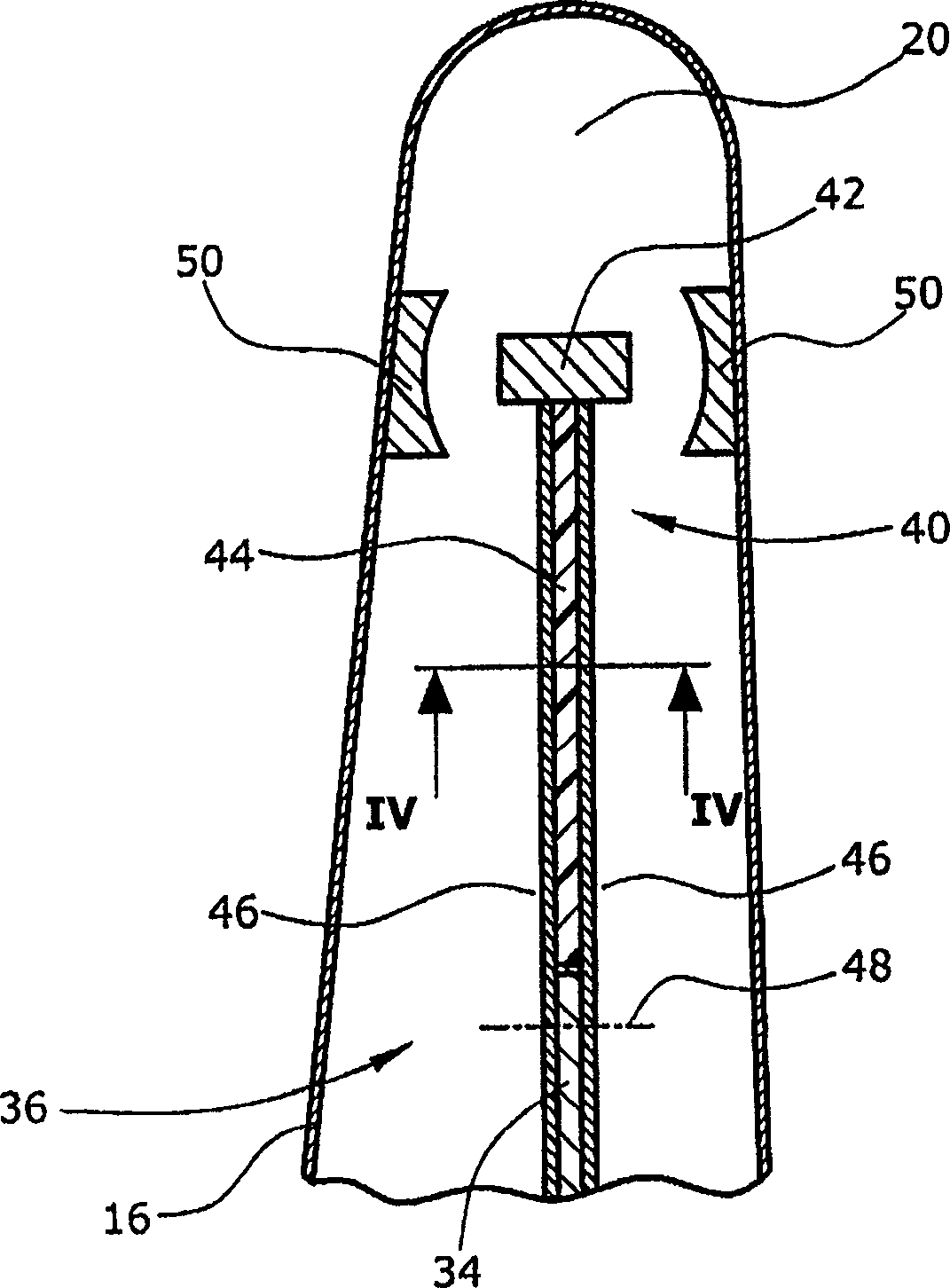
[0022] Figures 1 and 2 and i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com