Method of manufacturing head suspension
一种制造方法、磁头的技术,应用在记录头的配置/安装、支持头、臂部件的结构等方向,能够解决冲击特性下降等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
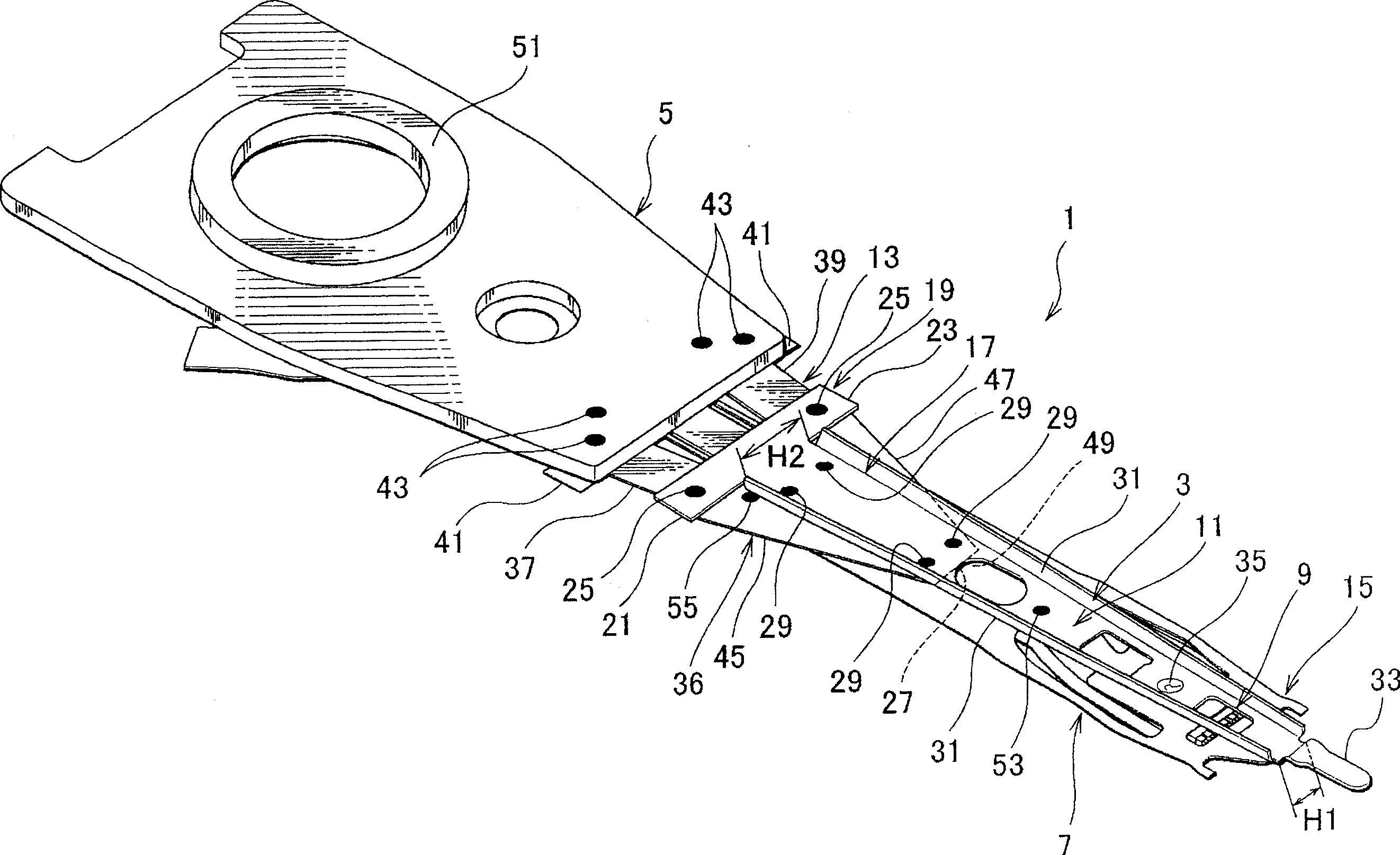
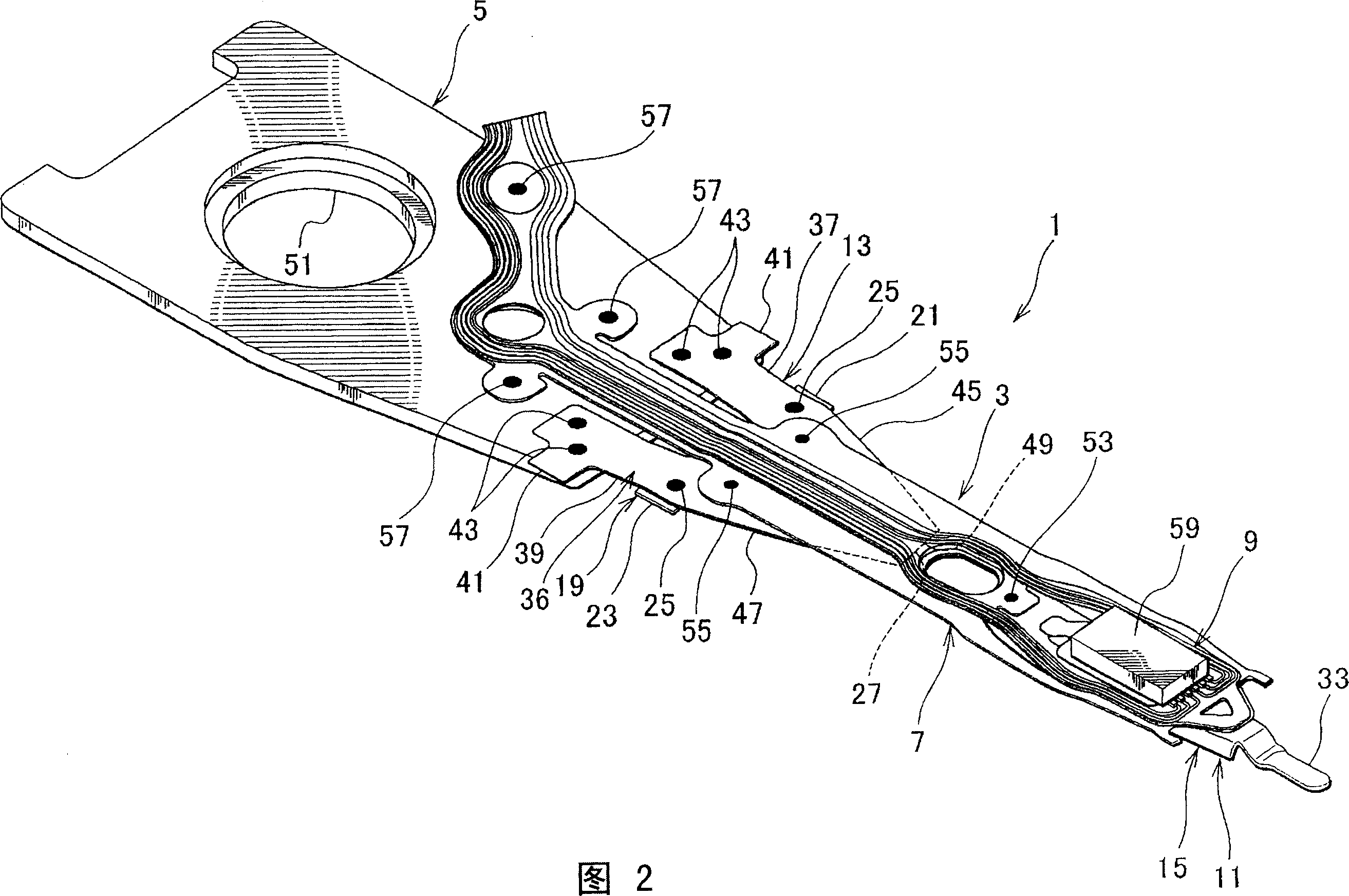
[0072] The following will refer to figure 1 and 2 to illustrate the structure of the head suspension.
[0073] figure 1 is a perspective view showing the head suspension according to the first embodiment of the present invention on the side facing away from the disk, and FIG. 2 shows figure 1 Perspective view of the middle head suspension on the disk side. In this specification, a "disk" is a storage medium mounted in a hard disk drive to which data is written and from which data is read by a magnetic head supported by a head suspension. The side facing away from the magnetic disk is the side where the direction of the head suspension 1 faces away from the magnetic disk. On the other hand, the disk side is the other side of the head suspension 1 facing the disk.
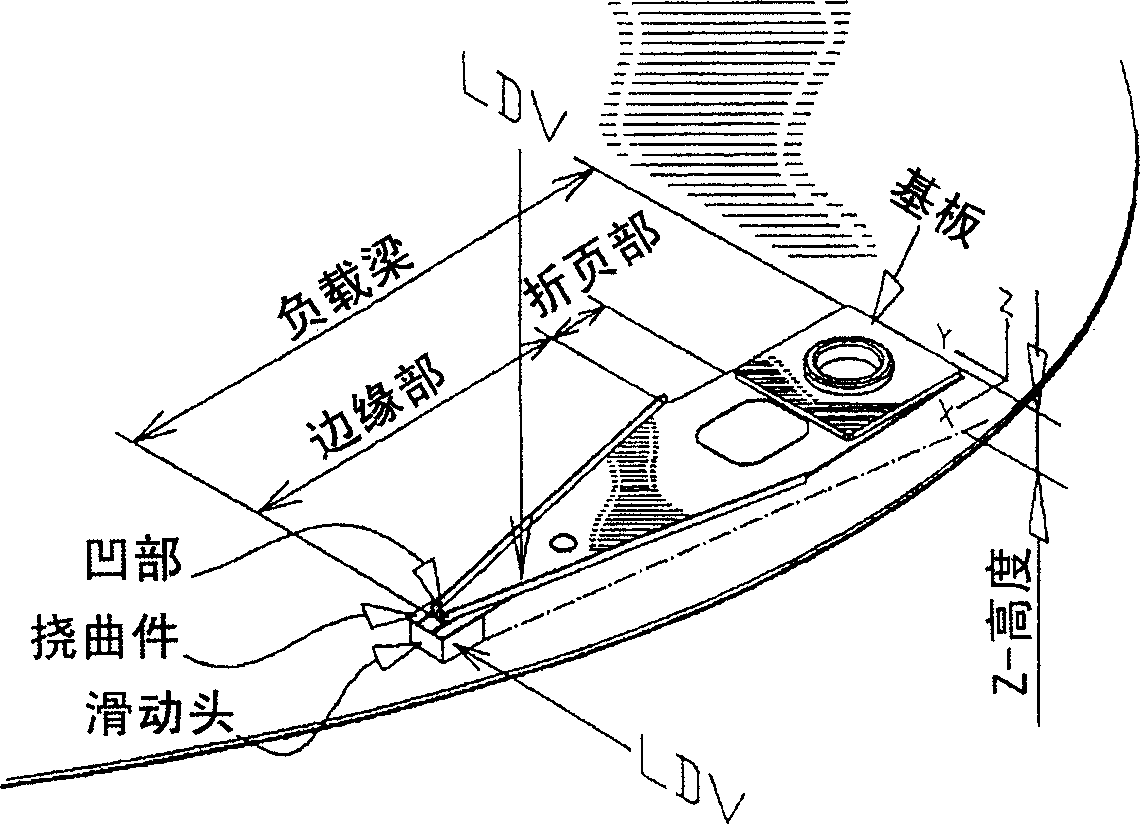
[0074] The shock characteristic of the load beam is represented by the magnitude of the shock by which the slider of the load beam is lifted from the disk surface. The phenomenon that the slider of the load b...
example 1
[0142] The B1 frequencies of Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 are not much different from each other, they are 5.99 kHz and 6.08 kHz because both have high longitudinal stiffness and are light in weight. However, Comparative Example 2 was thick and heavy, so its B1 frequency dropped to 5.61 kHz.
[0143] The T1 frequencies of Example 1 and Comparative Example 1 are not much different from each other, they are 9.09 kHz and 9.18 kHz because both have high longitudinal stiffness and are light in weight. However, Comparative Example 2 is thick and has a large inertia, so its T1 frequency drops to 7.76 kHz.
[0144] The rocking frequencies of Example 1 and Comparative Example 2 are not much different from each other, they are 14.54 kHz and 14.89 kHz because both have high stiffness in the rocking direction. On the other hand, Comparative Example 1 has low stiffness in the shaking direction, so its shaking frequency is reduced to 12.27 kHz.
[0145] The STA of Example 1 and Com...
no. 2 example
[0174] will refer to Figure 44 A second embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figure 44 is a plan view corresponding to manufacturing steps for realizing the method of manufacturing the head suspension according to the second embodiment. The manufacturing steps of the second embodiment are basically the same as those of the first embodiment, and therefore, the same or corresponding parts are denoted by the same reference numerals in FIG. 35 .
[0175] In the manufacturing method of the second embodiment, the lamination and bonding steps E1 and F1 are employed instead of the lamination and bonding steps E and F of the first embodiment. exist Figure 44 Among them, step (5) corresponds to lamination step E1, and step (6) corresponds to welding step F1.
[0176] In the lamination step E1 shown in step (5), the rigid member chain 71 , the elastic member chain 73 , each substrate, and each flexure 7 are laminated and arranged in an appropriate relationship. T...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| resonance frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com