Pipe hoop stress tensility testing method
A technique of hoop stretching, a testing method applied in directions such as testing material strength using applied stable tension/compression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
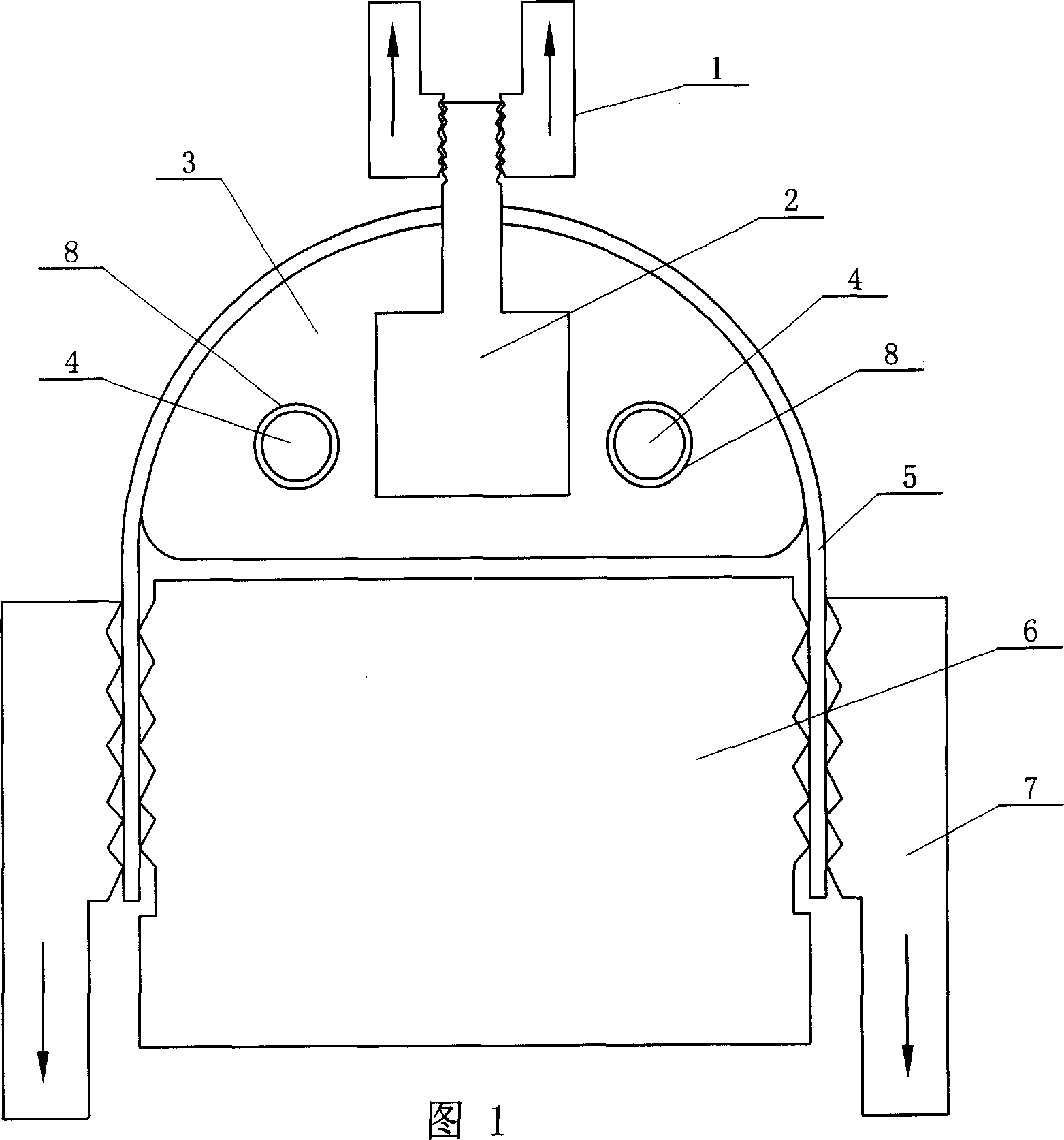
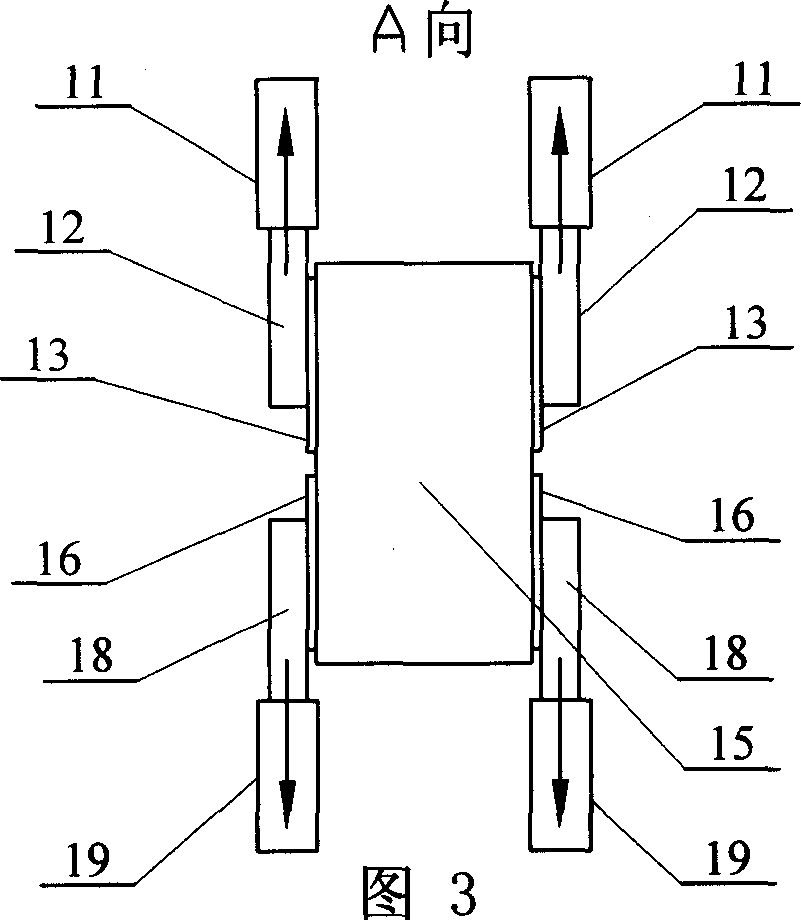
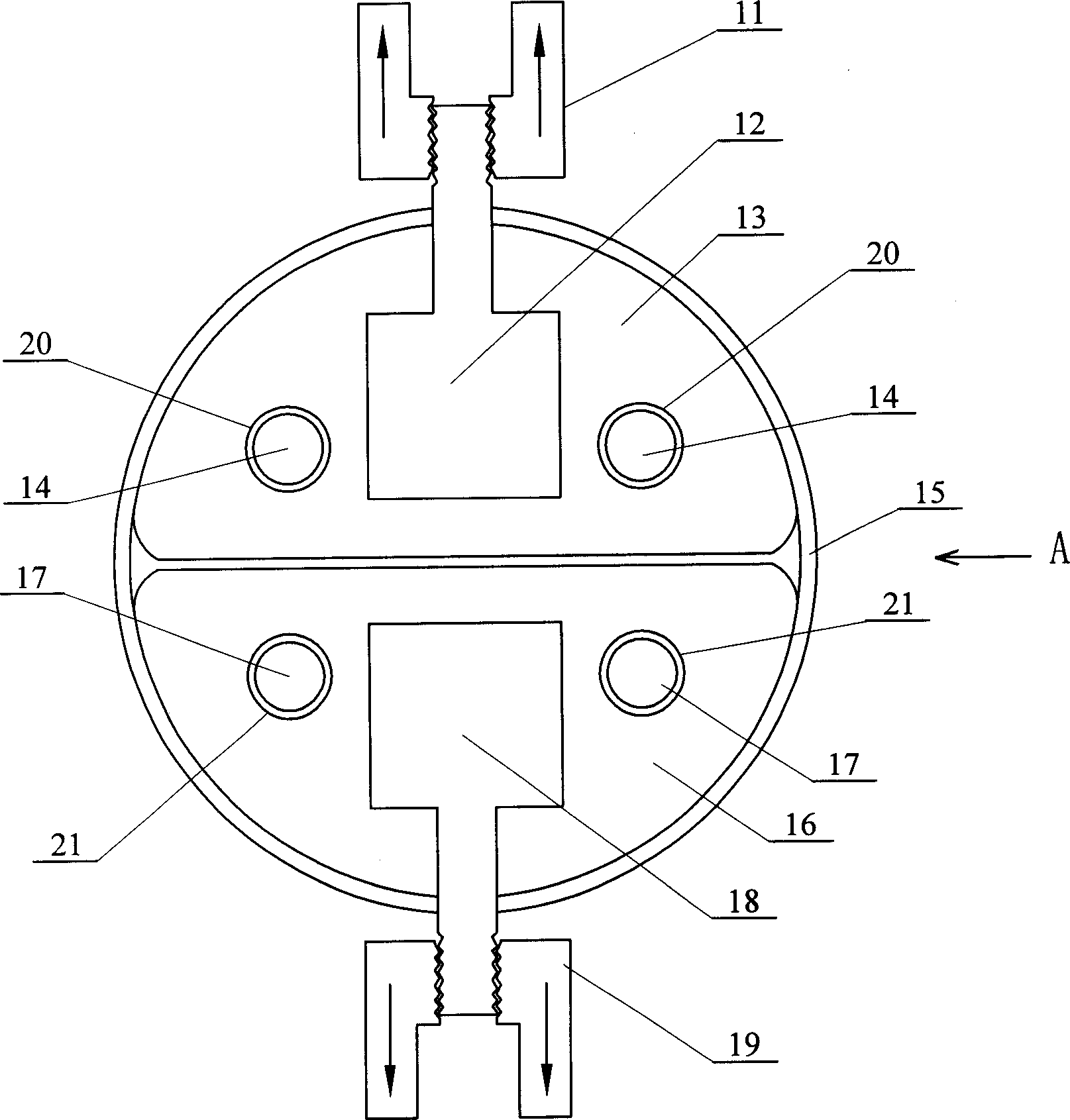
[0005] Specific embodiment one: (referring to Fig. 1) the technical scheme of the present embodiment is realized according to the following steps: one, will have the side of pipe material 5 of certain length axially incise, each 1 / 4 circle of otch both sides The long pipe is flattened, and the remaining pipes are kept in an arc shape; 2. Pass the semicircular rod 3 with the same diameter as the pipe inner diameter through the inner wall of the pipe 5, and the two ends of the semicircular rod 3 pass through the connecting body 2. Connect with the upper fixture 1 of the material tensile testing machine; 3. Place the clamping mandrel 6 with a width equal to the inner diameter of the pipe 5 between the two ends of the flattened pipe 5, and use the lower clamp of the material tensile testing machine to The clamp 7 clamps the two ends of the flattened pipe 5 on the clamping mandrel 6; 4. Start the material tensile testing machine to pull the upper clamp 1 and the lower clamp 7, so th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0006] Specific embodiment two: (referring to Fig. 1) the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that a round hole 8 is provided in the rod body of the semicircular rod 3, and an electric heating rod 4 is provided in the round hole 8 for use. When heating the pipe material 5, the heating temperature of the pipe material 5 is 20-800°C. The hoop tensile properties of the pipe 5 at different temperatures can be measured by heating the pipe 5 to a certain temperature and then stretching. Other process conditions and process steps are the same as the specific embodiment one.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0007] Embodiment 3: (see FIG. 1 ) The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the lubricant molybdenum disulfide is placed between the semicircular rod 3 and the pipe 5 . Good lubrication is maintained between the semicircular rod 3 and the pipe 5 to reduce the influence of friction on the deformation of the pipe, so that the deformation of the pipe is closer to the state of unidirectional tensile stress. Other process conditions and process steps are the same as the specific embodiment one.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com