Method for quickly detecting hepatitis B virus drug-resistant gene variation
A technology of hepatitis B virus and drug-resistant genes, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, etc., can solve the problems of mixed mutation detection, cumbersome experiments, and restrictions on wide application, so as to facilitate monitoring Efficacy, adjustment of treatment plan, effect of high amplification efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1 preparation kit
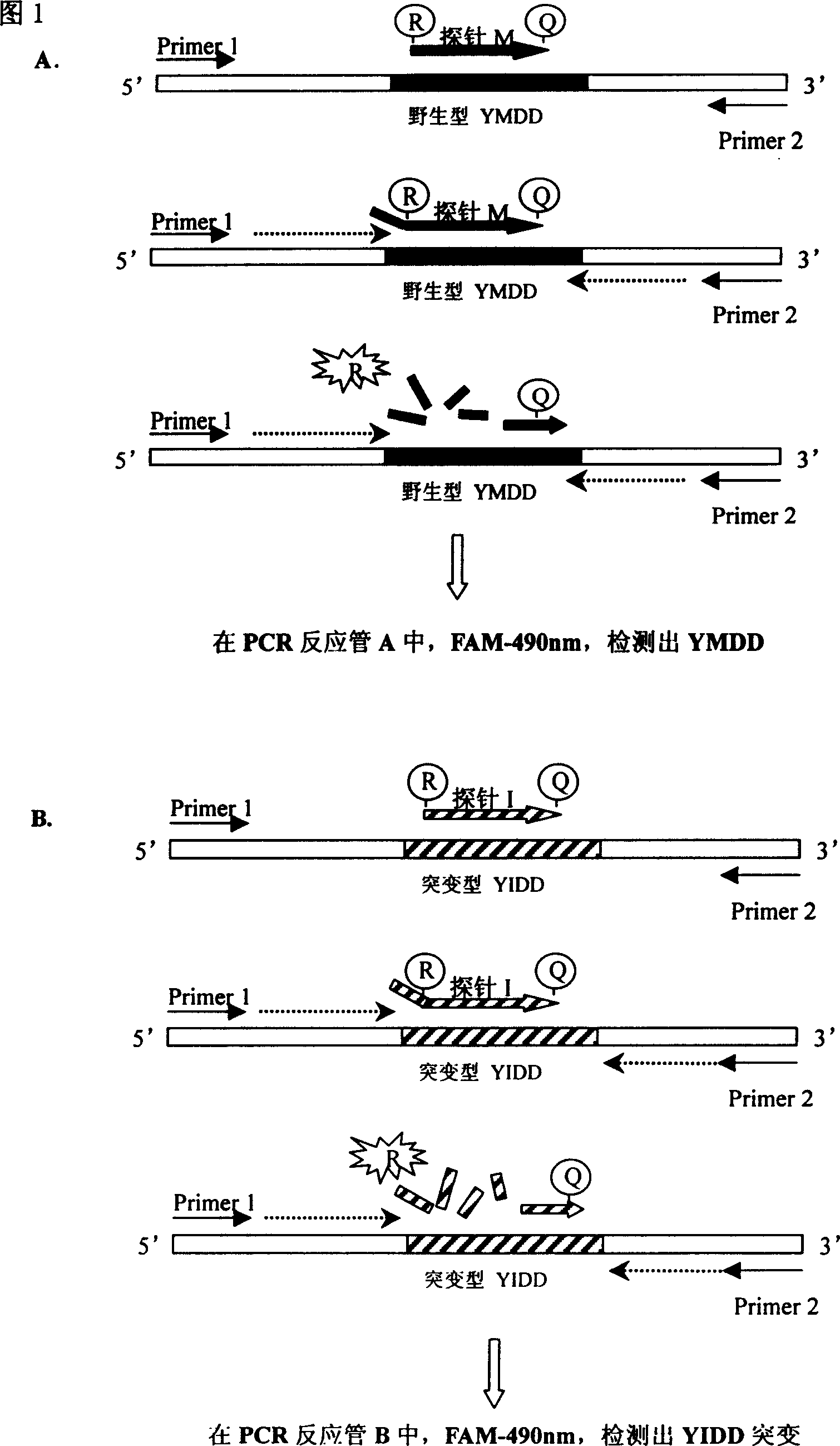
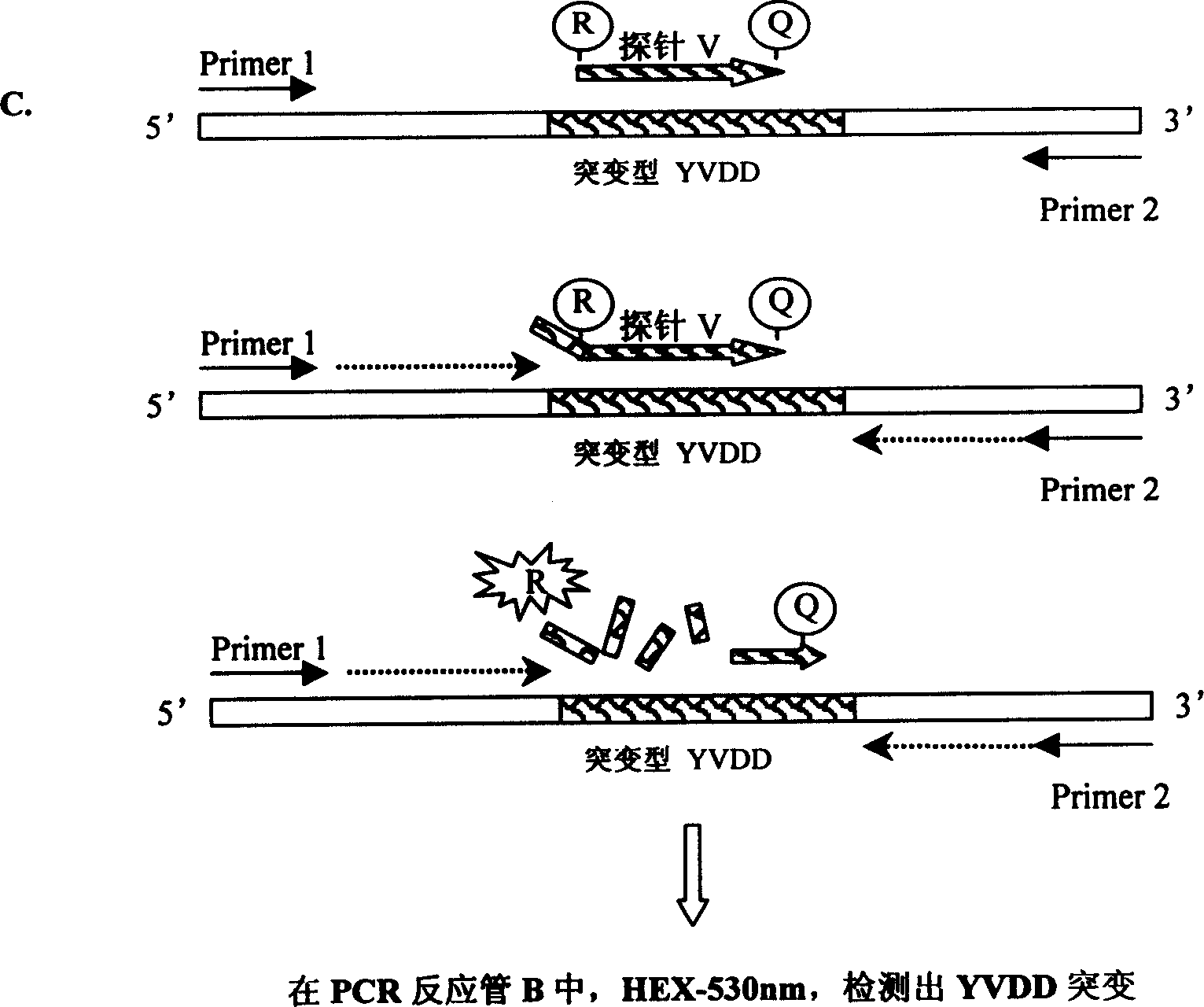
[0045] The main components of the kit are PCR reaction mixture A (which also contains primers 1, 2 and fluorescent probe M), PCR reaction mixture B (which also contains primers 1, 2 and fluorescent probes I and V), Taq enzyme, HBV DNA Extraction Reagent, Negative Quality Control and ddH 2 O.
[0046] The primers and fluorescent probes are designed near the 552nd amino acid encoded in the P gene region of the hepatitis B virus, are only specific to the hepatitis B virus, and have no cross-reaction with other species. Primers were designed near the YMDD region of the HBV-encoded polymerase DNA sequence of EMBL, with a full length of 92 bps and a single-copy gene sequence. The fluorescent probe design site is located between the two primers.
[0047] The primer sequences are:
[0048] Primer 1: 5′GTA GGG CTT TCC CCC ACT G 3′19bps
[0049] Primer 2: 5′GGT AAA AAG GGA YTC AMG ATG 3′21bps The fluorescent probe sequences for YMDD, YIDD, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2 Using the Hepatitis B Virus Gene Drug Resistance Mutation Detection Kit for Mutation Detection
[0076] Take 50 μl of the serum sample to be tested, add 50 μl of HBV DNA extraction solution I, shake and mix for 15 seconds, centrifuge at 12,000 rpm for 10 minutes, and discard the supernatant. Add 50 μl of HBV DNA Extraction II solution, shake and mix well, and bathe in water at 100°C for 10 minutes. Centrifuge at 12000rpm for 2min, and take the supernatant for PCR amplification, or store it at -20°C for future use.
[0077] Negative quality control products were treated the same as above.
[0078] PCR amplification:
[0079] 2 μl of the HBV DNA-containing supernatant extracted by the above method was added to the PCR reaction mixture A and B, mixed evenly and placed in a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR instrument (Bio-Rad, iCycler), and the amplification reaction was carried out according to the following cycles: 94 Pre-denaturation at ℃ for 5 minutes...
Embodiment 3
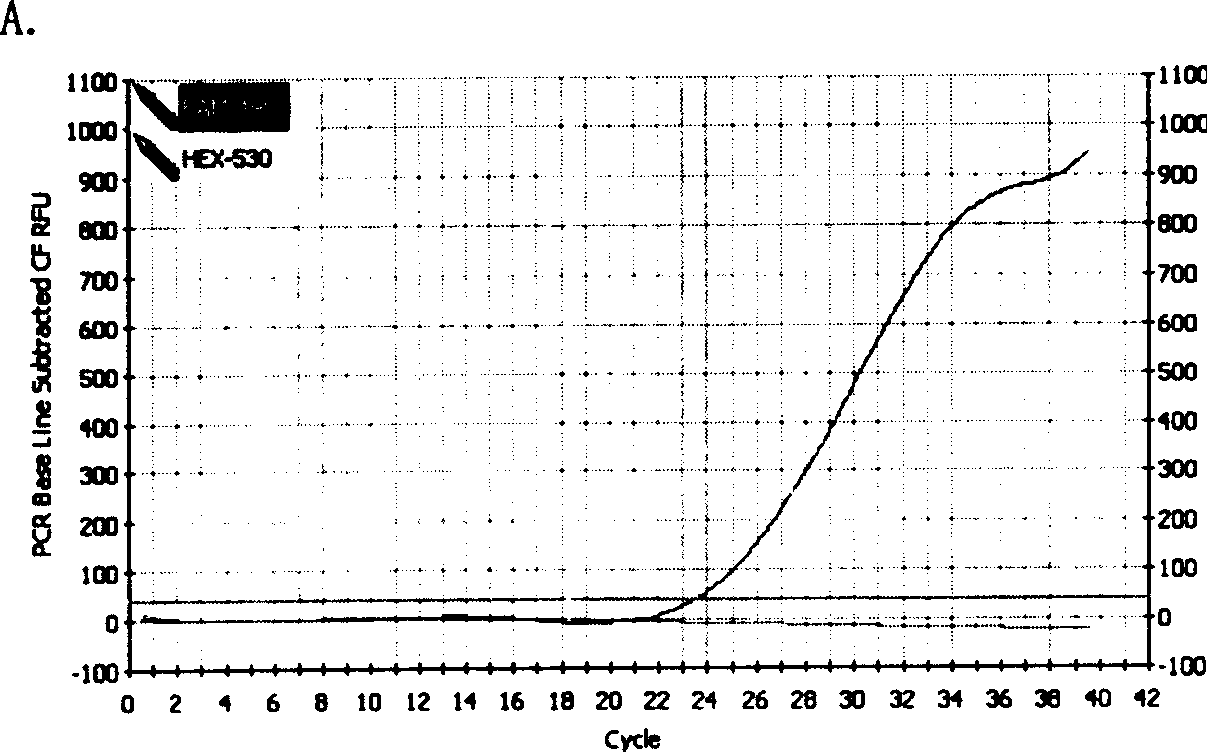
[0087]Configure the PCR reaction solution as in Example 1, put the PCR tube into a fluorescence detector that can read the fluorescence, read the value, record the fluorescence value A0, transfer the PCR tube to an ordinary PCR instrument, and perform the amplification reaction according to the following cycle : 94°C pre-denaturation for 5 minutes → (94°C denaturation for 20 seconds → 60°C annealing for 40 seconds → 72°C extension for 30 seconds) × 40 cycles → 72°C extension for 2 minutes, then move the PCR product to a fluorescence detector to read the fluorescence Value Ax.
[0088] Analyzing the end-point fluorescence value, the following results can be judged:
[0089] 1. If the value of tube A (Ax-A0) of the PCR reaction mixture is higher than 10 times the standard deviation of the negative control, it is considered that the HBV DNA position 552 in the sample is wild-type YMDD;
[0090] 2. Tube B of the PCR reaction mixture has a fluorescent signal at the wavelength of F...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com