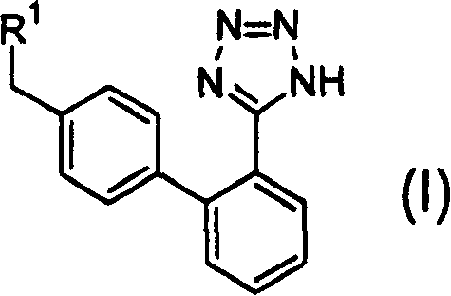
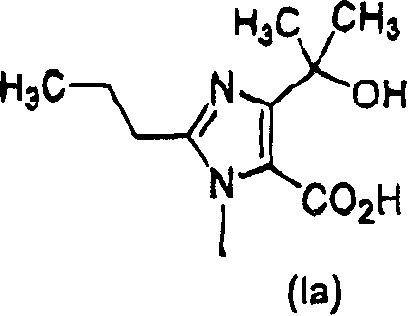
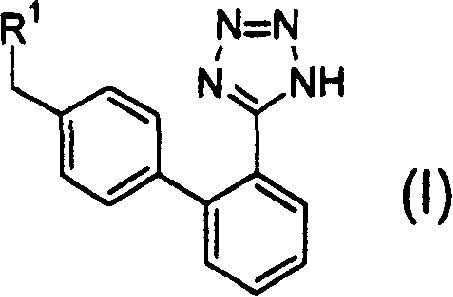
Combined agents for treatment of glaucoma
A glaucoma and therapeutic agent technology, applied in the field of glaucoma preventive or therapeutic agent, capable of solving problems such as insufficient glaucoma effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] New Zealand white rabbits weighing 2 to 3 kg were used to create an elevated intraocular pressure model according to the method of Kurihara et al. (Ophthalmic Pharmacology, pp. 62-64, Vol. 4, 1990), and the intraocular pressure-lowering effect of the test compound was examined.
[0072] That is, rabbits were general anesthetized with urethane, and intraocular pressure was measured with a tonometer (Alcon Applanation Pneumatonography: manufactured by Alcon Corporation). Then, after instilling the eyes of the rabbit with a local anesthetic, 0.1 ml of 5% sodium chloride water was injected into the vitreous through a 30 gauge injection needle. 30 minutes after the injection, after confirming the increase in intraocular pressure, 50 μl of the drug to be tested was instilled in the eye. Thereafter, intraocular pressure was measured at intervals of 30 minutes for 2 hours (single administration test).
[0073] In the combined drug administration test, after confirming the incr...
Embodiment 2
[0082] [Embodiment 2] Reduce intraocular pressure effect (2)
[0083] After the intraocular pressure was measured in New Zealand white rabbits (without anesthesia) weighing 2 to 3 kg using a tonometer (Alcon Applanation Pneumatonography: manufactured by Alcon Corporation), 50 μl of the test drug was instilled in the eyes. Thereafter, the intraocular pressure was measured at intervals of 1 hour for 4 hours (single administration test).
[0084] In the combined administration test, after confirming the intraocular pressure before instillation, instill 50 μl of the first test drug in the eye, 5 minutes later, instill the same amount of the second test drug, and then at intervals of 1 hour Measure intraocular pressure for 4 hours.
[0085] In addition, the same test drug as described in Example 1 was also used in this example.
[0086] When Compound A, which is an angiotensin II antagonist, is administered in combination with any of Compounds B, C, D, and E, an intraocular press...
Embodiment 3
[0087] [embodiment 3] reduce intraocular pressure test (3)
[0088] After the intraocular pressure was measured in the same manner as in Example 2, 150 μl of the test drug was instilled in the eyes, and 5 minutes later, 2 eye drops of the same amount of the test drug were used. From this time, the intraocular pressure was measured 4 hours later, and the eye pressure was calculated using the following calculation formula: rate of change in pressure.
[0089] Intraocular pressure change rate (%) = [(intraocular pressure after instillation - intraocular pressure before instillation) / intraocular pressure before instillation] × 100
[0090] In addition, the same test drug as described in Example 1 was also used in the examples. The results are shown in Table 1 and Table 2 below.
[0091] Tested drug 1
[0092] Tested drug 1
[0093] As shown in Tables 1 and 2 above, a synergistic intraocular pressure-lowering effect was observed when the angiotensin II antagon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com