Detection and treatment of cancer
A technology of biological samples and antibodies, applied in the field of cancer detection and/or treatment, which can solve the problems of disappearance of staining and low availability of extracellular proteins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
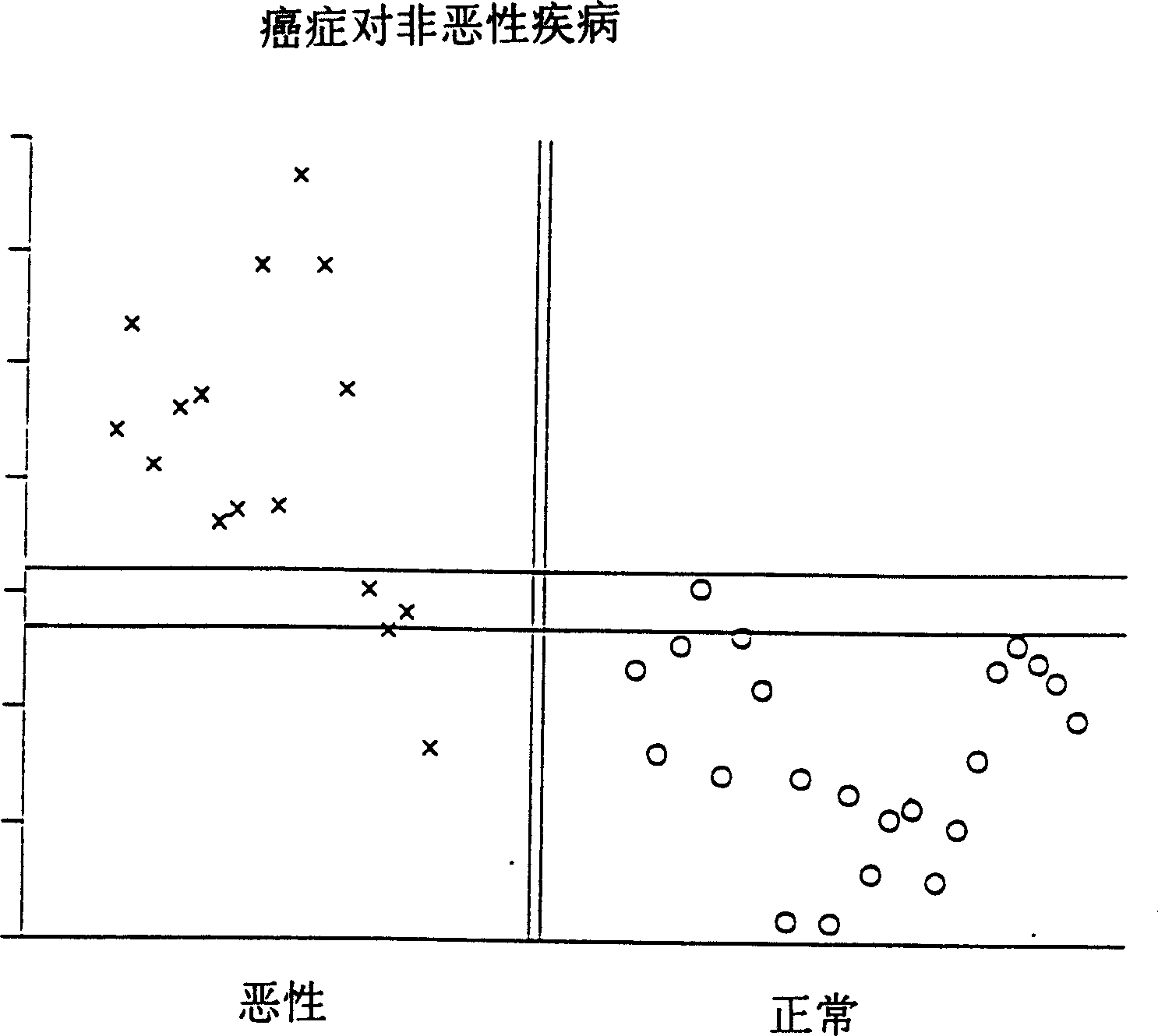
[0064] In this example, 22 serum samples from non-cancer patients and 17 samples from cancer patients were tested for AFP receptor concentrations by enzyme immunoassay (EIA) using the following technique: in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (0.05MPO 4Serum samples from the above groups diluted 1 / 16384 in , 0.15M NaCl, pH 7.5) were coated on EIA 96-well plates for 1 hour to overnight. In a similar manner wells were coated with pleural effusion from a patient with lung metastases from breast cancer at a dilution of 1 / 256. Due to its availability in large quantities, this material, called P89, was used as a standard, which allowed P89 to be used as the same standard to compare all samples with all other samples in all experiments. After washing 3 times with PBS, non-specific binding sites were blocked with 1% ovalbumin or gelatin in PBS for 1 hour. After washing 3 times, 100 μl of ascitic fluid (as described in [Moro, R., Tamaoki, T., Wegmann, T.G., Longenecker.B.M., and Ladera...
Embodiment 2
[0101] In another embodiment, an appropriate plastic or glass substrate (EIA plate or test tube) is coated with AFP receptor monoclonal antibody (Mab) at an appropriate concentration. After washing away excess Mab, the substrate is blocked with an irrelevant protein or amino acid to prevent non-specific binding, and the coated substrate is incubated with an appropriate sample dilution of the patient's bodily fluids (serum, saliva, urine, etc.) After a period of time, after washing to remove unbound sample material, a secondary antibody of the polyclonal type (polyclonal antibody produced by immunizing an animal and using its serum as a reactive antibody source, as opposed to Mab, which is obtained by culturing produced by individual cloning or transplantation of immortal splenocytes into a suitable host), this antibody can be coupled to a suitable marker or enzyme for color development, or, by adding an anti-secondary antibody labeled with said marker or enzyme The secondary a...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Same as Example 2 but using two different polyclonal antibodies instead of monoclonal antibody and antibody as primary and secondary antibodies respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com