Method of regulating degradation rate of porous collagen-based cradle with amino acid
A degradation rate, porous scaffold technology, used in medical science, prosthesis, surgery, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in regulating cross-linking degree, cytotoxicity, and inability to meet the requirements of various tissues and organs with different regeneration rates. To achieve the effect of simple and easy preparation process, low cost, good biocompatibility and degradation performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
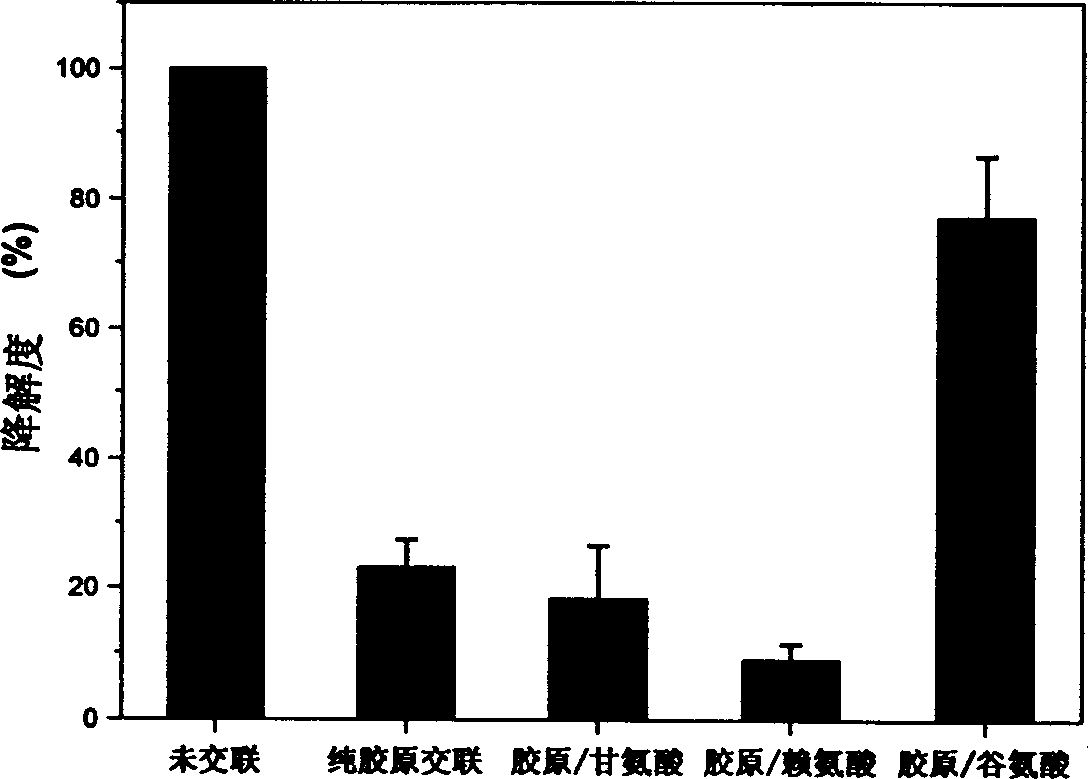
[0019] Effects of different kinds of amino acids on the degree of degradation of collagen-based porous scaffolds.
[0020] Type I collagen scaffolds (2.5 mg / block) derived from bovine tendon were placed in 24-well culture plates, and 1 ml of glycine (Gly), glutamic acid (Glu) or lysine (Lys) containing 2.5 μM 2-N-Morpholine ethanesulfonic acid (MES) solution (50 mM, pH 5.5), soaked for 1 hour; at the same time, three distilled water was added for soaking as a control. Then add 1ml of 1-ethyl-3-(dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide (EDAC) containing 40mM, MES solution of 40mM N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) respectively, so that the final The concentrations of EDAC and NHS were 20 mM and 10 mM, respectively. Cross-link at room temperature for 24 hours, rinse with triple distilled water for 6 times, 10 minutes each time after cross-linking. After freeze-drying, the cross-linked collagen-based porous scaffold is obtained.
[0021] Add 3ml of 0.1mg / ml type I collagenase solution (PBS, ...
Embodiment 2
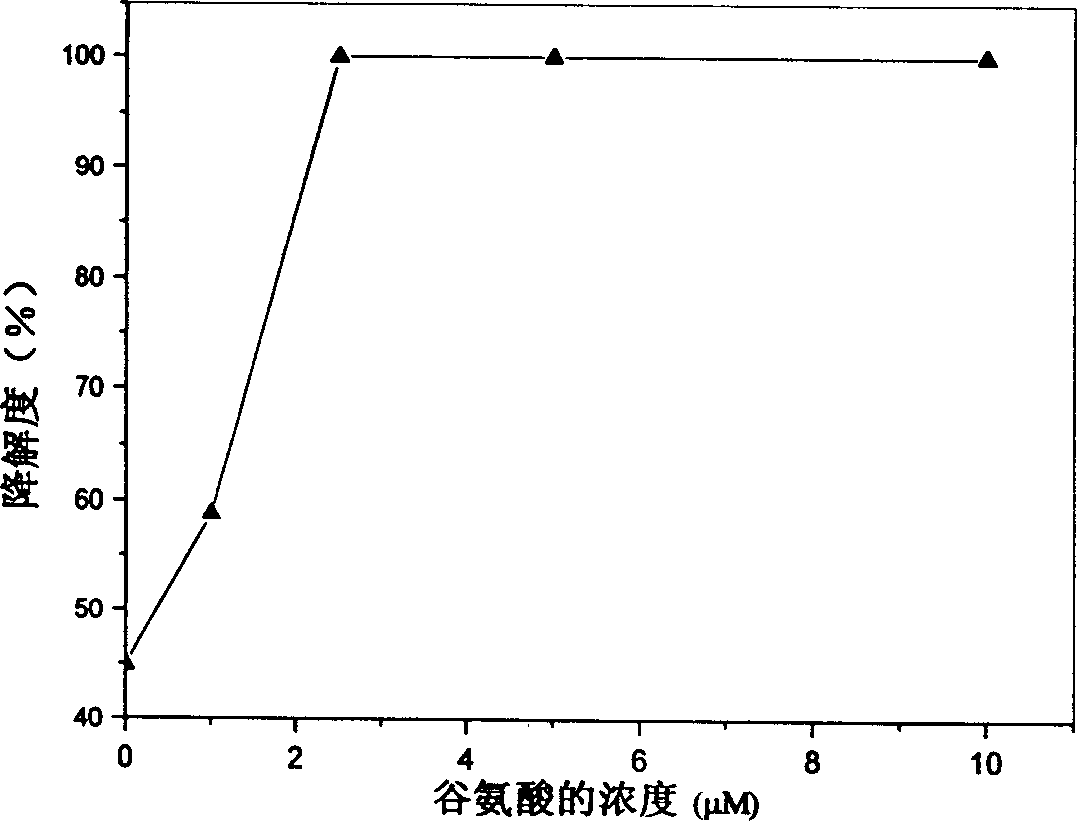
[0023] Effect of glutamic acid concentration on the degradation rate of collagen-based porous scaffolds.
[0024] Place the type I collagen scaffolds (2.5mg / block) derived from bovine tendon in a 24-well culture plate, add 1ml of 1-10μM glutamic acid MES solution (50mM, pH 5.5), soak for 1 hour; then Add 1 ml of MES solution containing 40 mM EDAC and 40 mM NHS respectively, so that the final concentrations of EDAC and NHS are 20 mM and 10 mM, respectively. Cross-link at room temperature for 24 hours, rinse with triple distilled water for 6 times, 10 minutes each time after cross-linking. After freeze-drying, the cross-linked collagen-based porous scaffold is obtained.
[0025] Take the cross-linked porous scaffolds added with different concentrations of glutamic acid, add 3ml of 0.5mg / ml type I collagenase solution (PBS, pH7.4), and digest in a constant temperature water bath at 37°C for 12h. Aspirate 1ml of the digested supernatant, put it in a polymerization tube, add 2ml ...
Embodiment 3
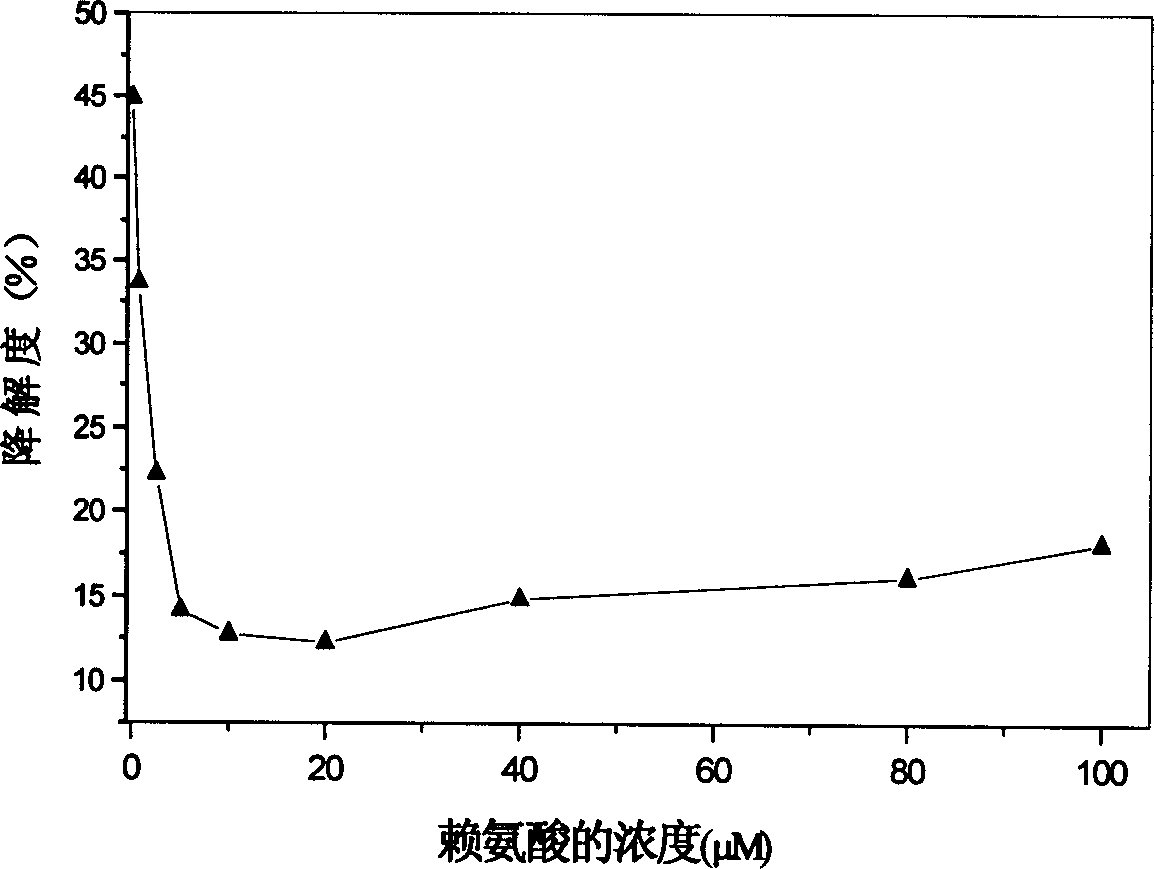
[0027] The effect of lysine concentration on the degradation rate of collagen-based porous scaffolds.
[0028] Place the type I collagen scaffolds (2.5mg / piece) derived from bovine tendon in a 24-well culture plate, add 1ml of 0.67-100μM lysine MES solution (50mM, pH 5.5), soak for 1 hour; then Add 1 ml of MES solution containing 40 mM EDAC and 40 mM NHS respectively, so that the final concentrations of EDAC and NHS are 20 mM and 10 mM, respectively. Cross-link at room temperature for 24 hours, rinse with triple distilled water for 6 times, 10 minutes each time after cross-linking. After freeze-drying, a cross-linked collagen-based porous scaffold is obtained.
[0029] Take the cross-linked porous scaffolds added with different concentrations of lysine, add 3ml of 0.5mg / ml type I collagenase solution (PBS, pH7.4), and digest in a constant temperature water tank at 37°C for 12h. Aspirate 1ml of the digested supernatant, put it in a polymerization tube, add 2ml of 6M hydrochlo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com