Disposable test strips with integrated reagent/blood separation layer
A one-time, isolation-layer technology that can be used in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biological testing, instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as adverse effects on accuracy, increased cost, and reduced effective electrode area.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
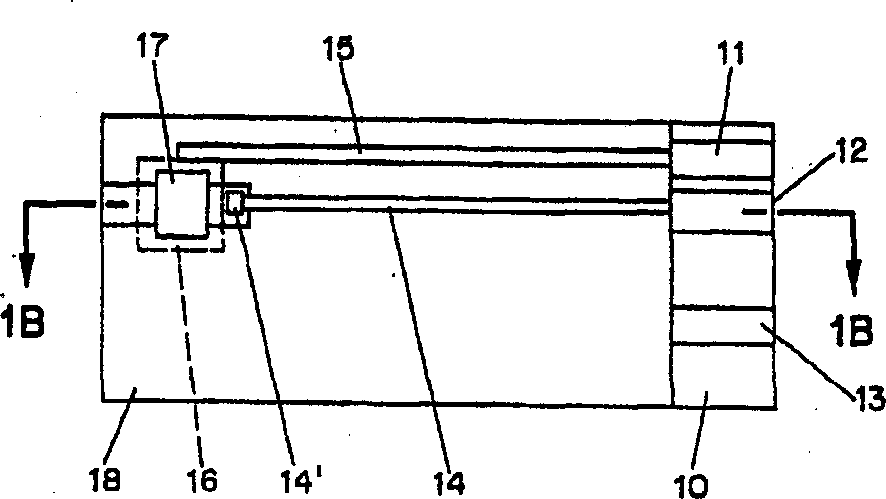
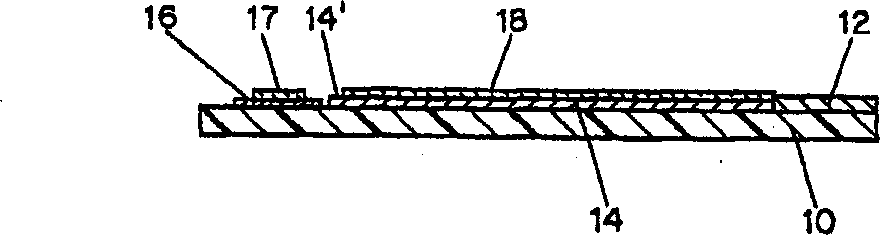
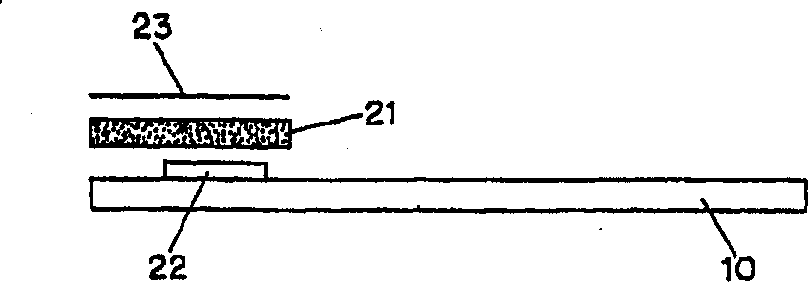
[0052] A non-conductive formulation for the preparation of the monolithic reagent / blood separation layer 17 was prepared as follows. 100 mL of the aqueous phase was adjusted to pH 6 with 20 mM trisodium citrate in water by adding 0.1 M citric acid. Add 6g of hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), and homogenize and mix. The mixture was left overnight and allowed to air bubble to disperse before being used as a storage solution for the coating composition.
[0053] 2 grams of Cab-o-Sil silica and 0.1 grams of DowCorning antifoam compound were added gradually by hand to 50 grams of the HEC solution until 4 / 5 of the total was added. While homogenizing to mix, add the rest. The mixture was then cooled in the refrigerator for 10 minutes. Then 8 g of potassium hexacyanoferrate (III) was added and mixed until completely dissolved. Finally, 0.8 g of glucose oxidase preparation (250 units / mg) was added and mixed thoroughly until dissolved. The resulting formulation can be used for printing...
Embodiment 2
[0055]To prepare glucose test strips using the slurry formulation of Example 1, screen printing was performed in a series of patterns on a 330 micron polyester substrate (Melinex 329). The first step is to print the carbon pad. The polyester substrate was printed with EC2 carbon (Ercon) to form a 10 x 50 array of carbon pads on its surface. The printed substrate is then passed through a heated dryer, and may also be cured at a high temperature (eg, 70° C.) for 1-3 weeks.
[0056] Next, an array of silver / silver chloride connecting tracks and contacts was printed on the substrate with ERCON R-414 (DPM-68) 1.25 bioelectrode sensor coating material and dried. For each carbon pad in the array, a working rail and a reference rail are printed in contact with the carbon pad.
[0057] The dielectric layer was then printed with ERCON R488-B(HV)-B2 blue. The pattern imprinted with the dielectric layer covered nearly the entirety of each device, exposing only the contacts, the tip of ...
Embodiment 3
[0061] With the slurry of embodiment 1, the test strip manufactured in the manner of embodiment 2 is placed in the meter, and a voltage of 500mV is added for testing blood with different glucose concentrations and hematocrit between 40%-60%. sample. Figures 3A-3C shows the measured current versus glucose concentration after applying the voltage for 25 seconds, while Figure 4 is the slope of the glucose response plotted as a function of hematocrit. As can be seen, the results are very reproducible currents, essentially independent of hematocrit.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com