Reversible vapor compression system
A technology for compressing system and steam, applied in irreversible cycle compressors, compressors with reversible cycle, compressors, etc., can solve the problem of no gas cooler and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
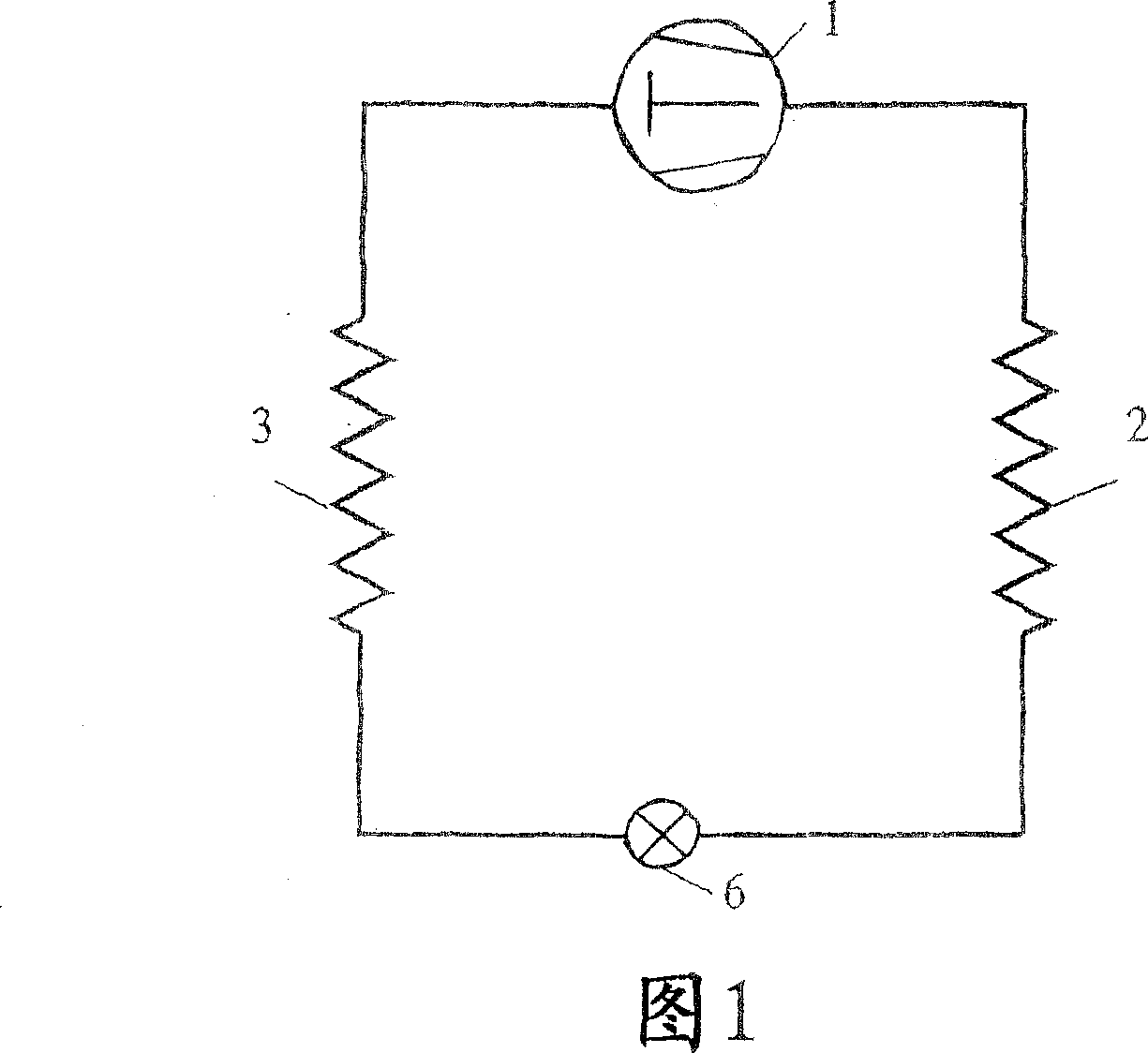
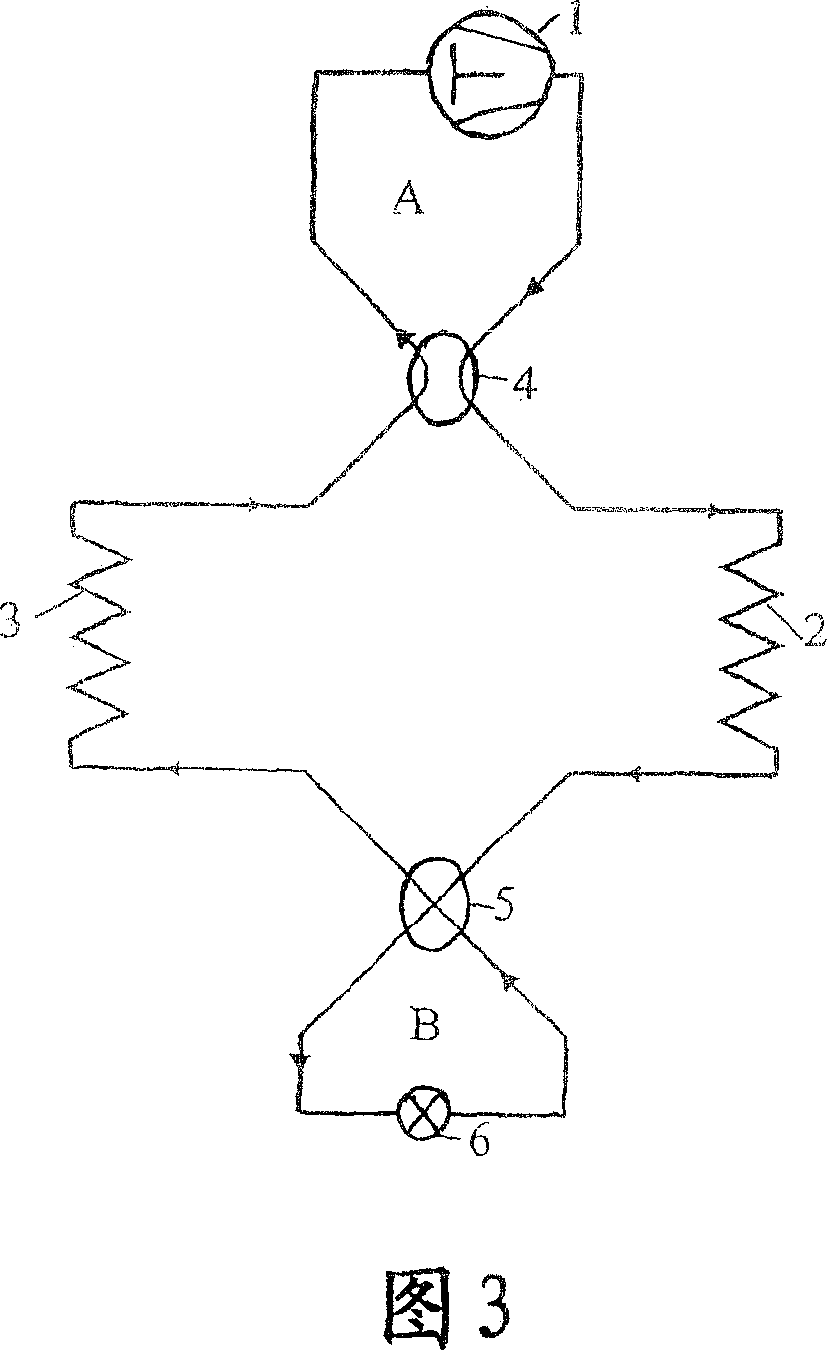
[0062] The first (basic) embodiment of the invention is for a single stage reversible vapor compression cycle, shown in FIG. 3 in heating mode operation and in FIG. 4 in cooling mode operation. According to the invention, the system comprises a compressor 1 , an internal heat exchanger 2 , an expansion device 6 (such as a throttle valve) and an external heat exchanger 3 , like known systems. It should be understood that the complete system has connecting lines in which a refrigerant circulates in order to form a closed main flow path. The first embodiment of the present invention is characterized in that two sub-routes are used, the first route A and the second route B are respectively connected to the main flow circuit through a first flow reversing device 4 and a second flow reversing device 5, and the reversing The device can be, for example, a four-way shutter. The compressor 1 and the expansion device 6 are arranged in the first sub-route A and in the second sub-route B ...
no. 2 example
[0070] Figures 5 and 6 respectively show schematic views of the second embodiment in heating and cooling mode operation. Compared to the first embodiment, it has a supplementary line circuit C comprising a heat desiccant exchanger 25 , an expansion device 23 and a valve 24 . The heat exchanger 25 has a dehumidifying function in the heating mode and works as a common evaporator in the cooling mode. In heating mode, some of the high pressure refrigerant is deflated through the expansion device 23 after reversing the device 5, where the refrigerant pressure is reduced to the evaporation pressure in the heat exchanger described above. The above-mentioned refrigerant is then evaporated by heat absorption in the heat exchanger 25 before it passes through the valve 24 . In this way, the interior air moves through this desiccant heat exchanger 25 before it is reheated by the interior heat exchanger 2, so as to provide dry air into the interior space for demisting purposes, such as in...
no. 3 example
[0072] Figures 7 and 8 show schematic views of a third embodiment operating in heating and cooling modes, respectively. Compared with the second embodiment, the pipeline circuit C relative to the main circuit is arranged in such a way that the internal heat exchangers 2 of the desiccant heat exchanger 25 are connected in series in the cooling mode, at this time by means of setting the flow changing devices 26 and 26 ' (eg inspection valve), which is contrary to the second embodiment, wherein the above-mentioned heat exchangers are connected in parallel, regardless of the working mode. The reversing of the system is the same as in the first embodiment, by changing the position of the two flow reversing devices 4 and 5, from heating mode to cooling mode and vice versa.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com