Transcutaneous sedative release control in autonomous imaging
A sedative, automatic release technology, applied in the direction of drugs or prescriptions, can solve problems such as danger and abruptness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
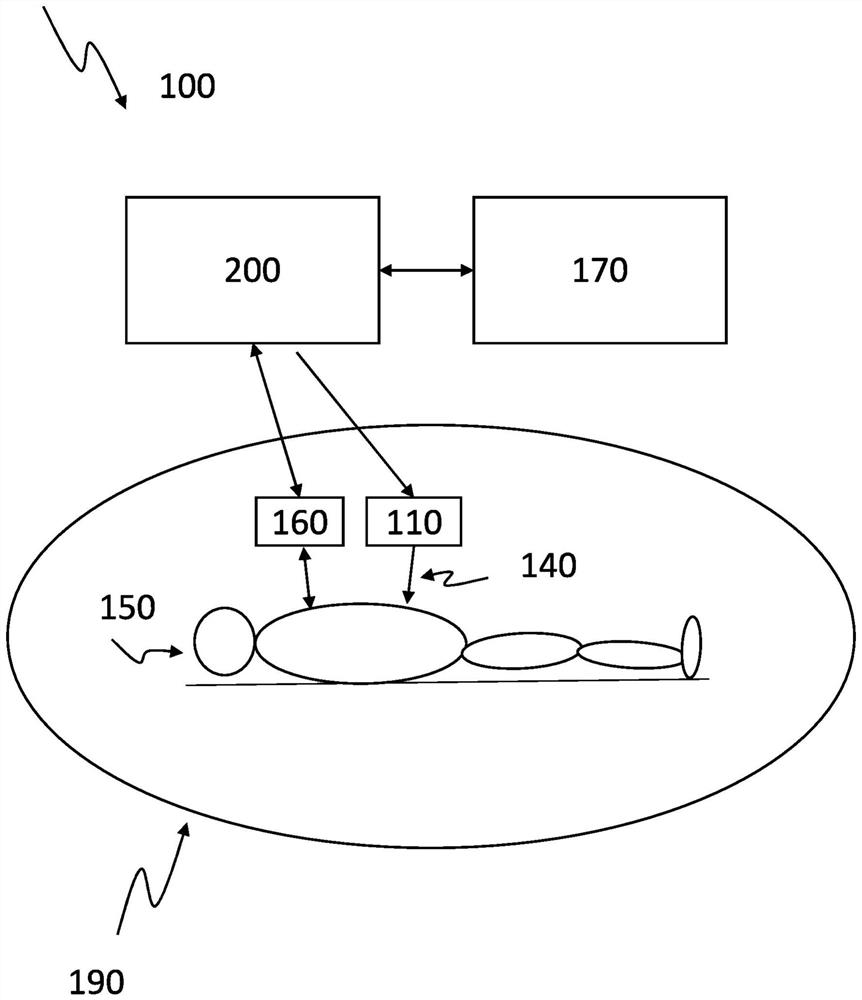
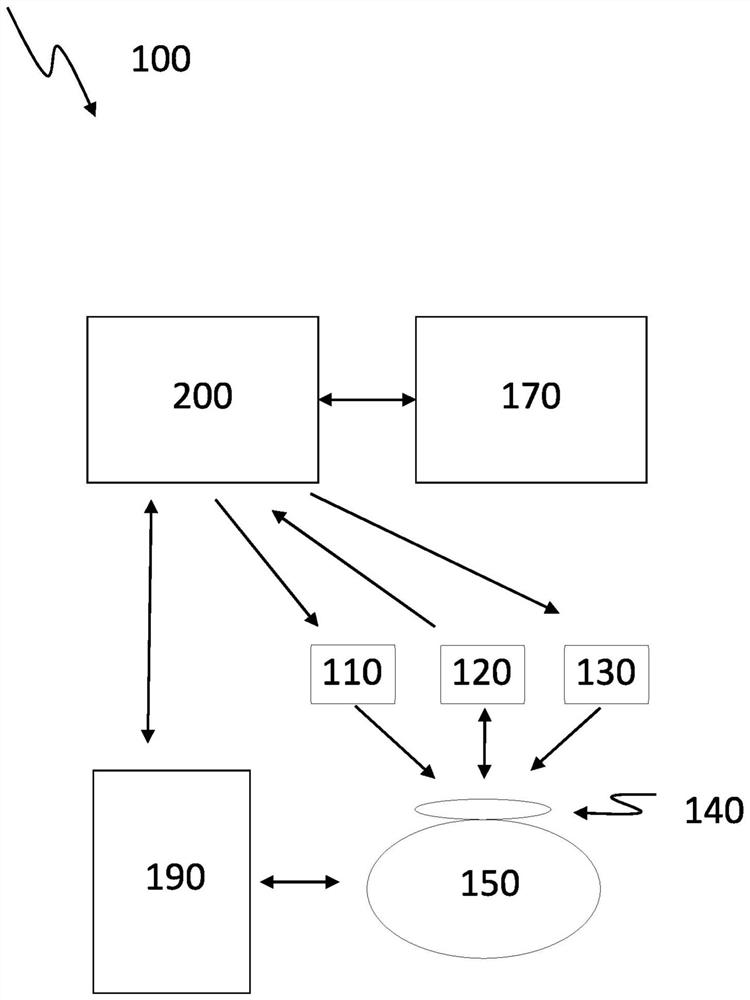
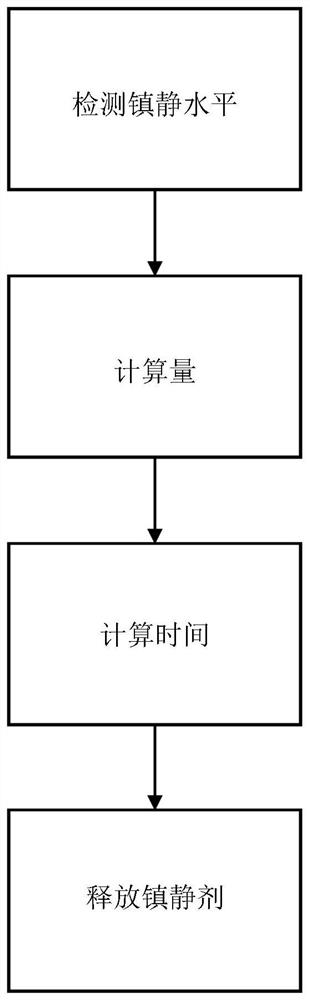
[0083] figure 1 A schematic setup of a system 100 for controlling the transdermal and automatic release of a sedative 140 during imaging of a subject 150 in accordance with the present invention is shown. Object 150 is positioned within medical imaging device 190 . The sedation level monitoring system 160 detects and determines the sedation level of the subject 150 . The processing unit 200 is communicatively connected to the sedation level monitoring system 160 and receives data regarding the sedation level. The amount of sedative 140 to be released to subject 150 is calculated by comparing the sedation level to the set value for the sedation level. Additionally, the time at which the amount of sedative 140 will be released to subject 150 is calculated. These calculations may be performed by the processing unit 200 or by the artificial intelligence module 170 communicatively coupled to the processing unit 200 . The amount of sedative 140 is released to the subject at a de...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com