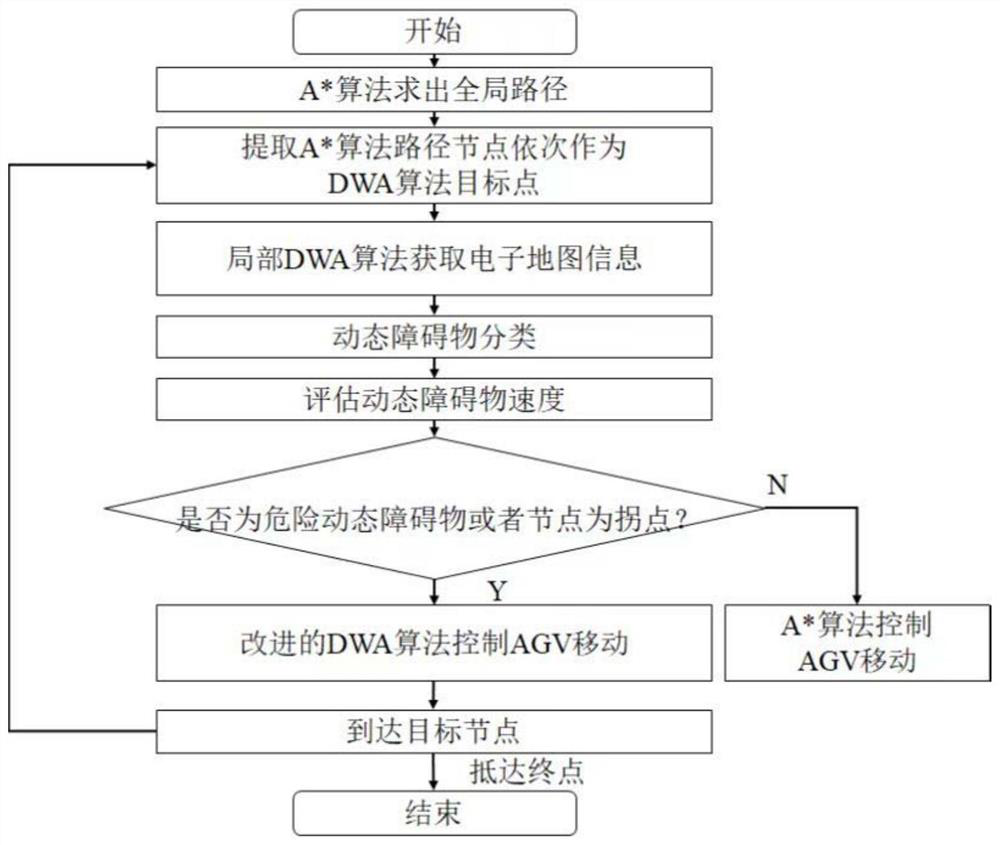
AGV path planning method based on improved DWA algorithm in dynamic environment
A dynamic environment and path planning technology, applied in manufacturing computing systems, electric/hybrid power, two-dimensional position/channel control, etc., can solve the problem of less research on efficient obstacle avoidance methods for dynamic obstacles, and achieve shortened AGV Exercise time, improve the effect of obstacle avoidance judgment ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] Example 1: Build a grid map
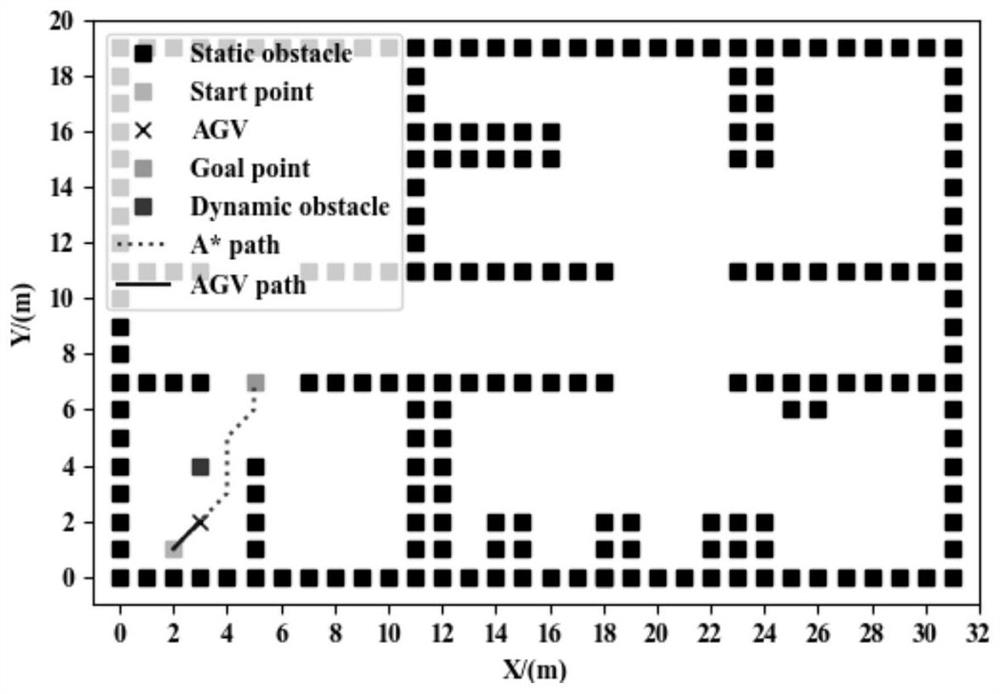
[0086] The invention takes the semi-automatic production workshop of gyro products as the research object, extracts and simplifies the layout of the workshop, performs two-dimensional grid processing on the internal environment of the production workshop where the AGV is located, and constructs a grid map of the production workshop, such as figure 2 shown.
[0087] The production workshop in the figure is about 32m long and 20m wide. The AGV is placed in a plane rectangular coordinate system, with the X axis in the horizontal direction and the Y axis in the vertical direction. Referring to the actual situation of the objects in the production workshop, the number of black squares in the figure is the largest, indicating Walls, workstations and other static obstacles, while scattered in the space surrounded by static obstacles, a small number of dark squares represent people or other dynamic obstacles; there are two light-colored squares, w...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2: Principle of A* Algorithm
[0089] Specifically, the A* algorithm is used for global path planning. The A* algorithm is mainly used for path planning in a two-dimensional plane, and is the most effective direct search method for finding the shortest path in a static map. The A* algorithm is a kind of heuristic algorithm, which uses the heuristic function to guide the search direction of the path. The heuristic search path planning algorithm is used, and the evaluation function is used to guide the search and expansion of nodes. Therefore, the evaluation function affects the size of the search space and the speed of the algorithm. The evaluation function expression of the traditional A* algorithm is shown in the following formula.
[0090] f(n)=g(n)+h(n)
[0091] Among them, n represents the current node, f(n) represents the evaluation function from the starting point to the target point via node n; g(n) represents the actual cost of reaching the node n from...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Embodiment 3: Principle of DWA Algorithm
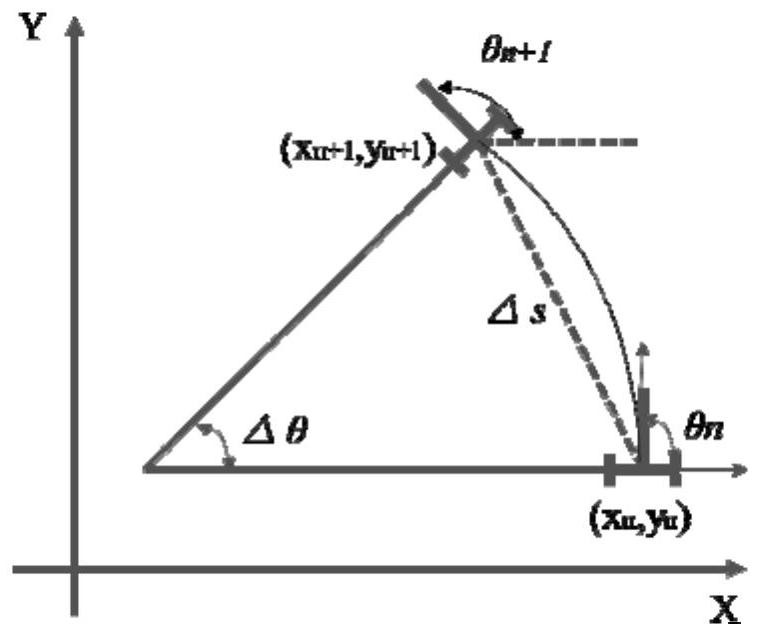
[0098] The DWA algorithm converts position control into speed control, so it is necessary to analyze the motion model of the AGV. The kinematic model of the AGV of the present invention is as follows image 3 shown.
[0099] The AGV kinematics model of the present invention adopts a two-wheel differential motion model. It is assumed that within the sampling time, the AGV displacement is very small, and the movement trajectory is regarded as straight line processing. At this time, the mathematical expression of the motion model is:
[0100] x n+1 =x n +Δs*cosΔθ
[0101] y n+1 =y n +Δs*sinΔθ
[0102] θ n+1 =θ n +Δθ
[0103] where, (x n ,y n ,θ n ) is the position information of the AGV at the current moment, (x n+1 ,y n+1 ,θ n+1 ) is the position information of the AGV at the next moment.
[0104] The DWA algorithm samples the speed and angular speed according to the current speed and angular speed of the AGV, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com