Camera pose estimation method and system based on semantics
A pose estimation and camera technology, applied in computing, computer components, image analysis, etc., can solve the problem that the effect depends on the accuracy of semantic segmentation and has no advantages, so as to reduce the occlusion of dynamic objects, improve the effect, and improve the correlation. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
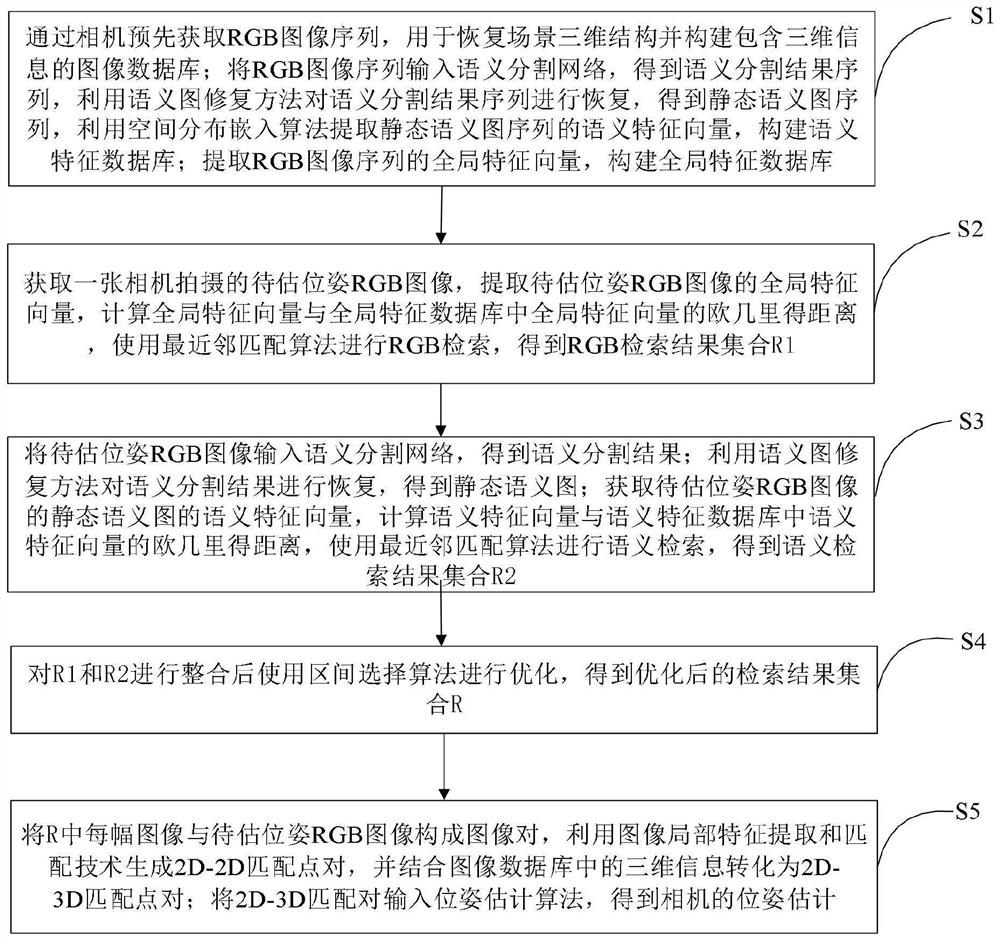
[0022] like figure 1 As shown, a semantic-based camera pose estimation method provided by an embodiment of the present invention includes the following steps:
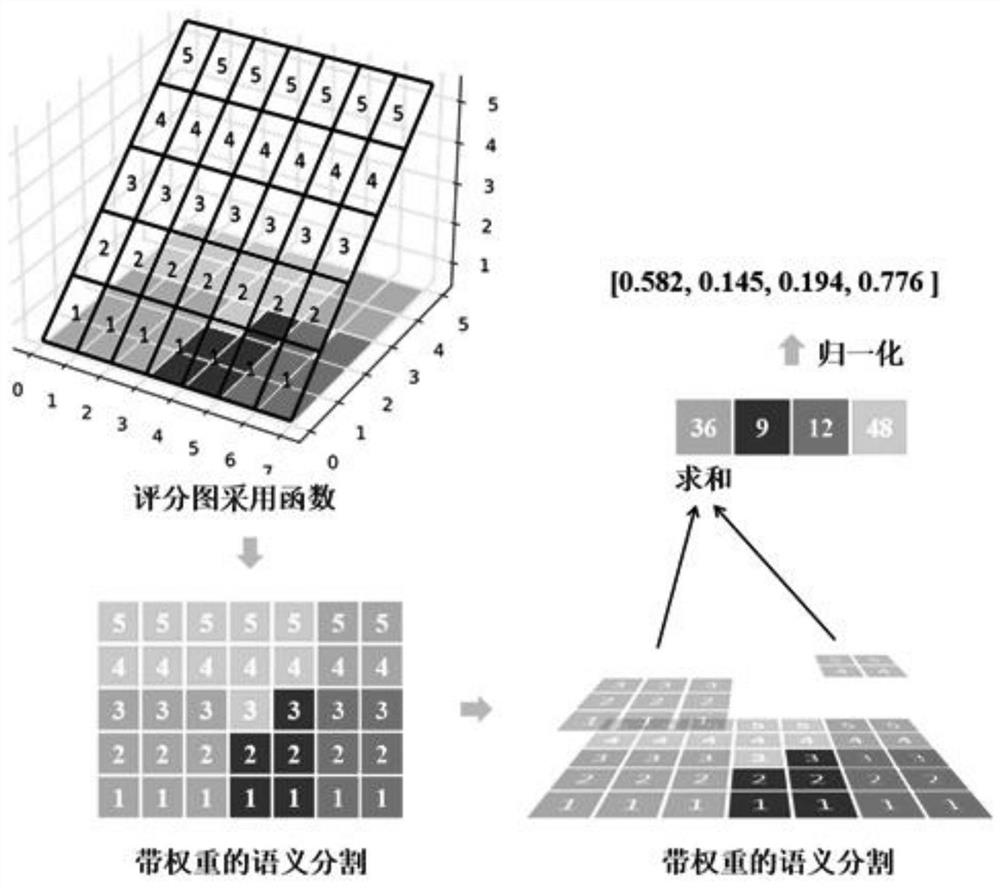
[0023] Step S1: Pre-acquire the RGB image sequence through the camera, which is used to restore the three-dimensional structure of the scene and construct an image database containing three-dimensional information; input the RGB image sequence into the semantic segmentation network to obtain a sequence of semantic segmentation results, and use the semantic map inpainting method to reconstruct the semantic segmentation results. The sequence is restored to obtain a static semantic map sequence, and the spatial distribution embedding algorithm is used to extract the semantic feature vector of the static semantic map sequence to construct a semantic feature database; extract the global feature vector of the RGB image sequence to construct a global feature database;
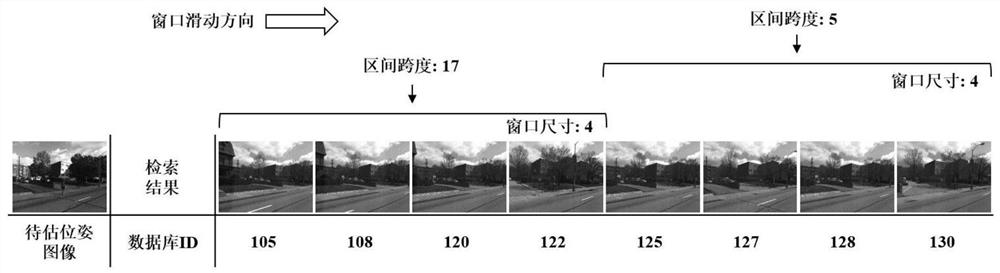
[0024] Step S2: Obtain an RGB image of the pose to be es...
Embodiment 2
[0064] like Figure 4 As shown, an embodiment of the present invention provides a semantic-based camera pose estimation system, including the following modules:
[0065]Data preprocessing module 61: used to obtain the RGB image sequence in advance through the camera, used to restore the three-dimensional structure of the scene and build an image database containing three-dimensional information; input the RGB image sequence into the semantic segmentation network to obtain a sequence of semantic segmentation results, and use the semantic map to repair The method restores the sequence of semantic segmentation results to obtain a static semantic map sequence, uses the spatial distribution embedding algorithm to extract the semantic feature vector of the static semantic map sequence, and constructs a semantic feature database; extracts the global feature vector of the RGB image sequence to construct a global feature database;
[0066] Obtaining the RGB retrieval result module 62 i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com