Light path calibration module
A technology for calibrating optical paths and calibrating light beams, which is applied in the field of optical sensing, can solve problems such as distortion, photoelectric sensor failure, and accuracy degradation, and achieve the effects of facilitating production assembly or production line application testing, improving production efficiency, and ensuring output power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
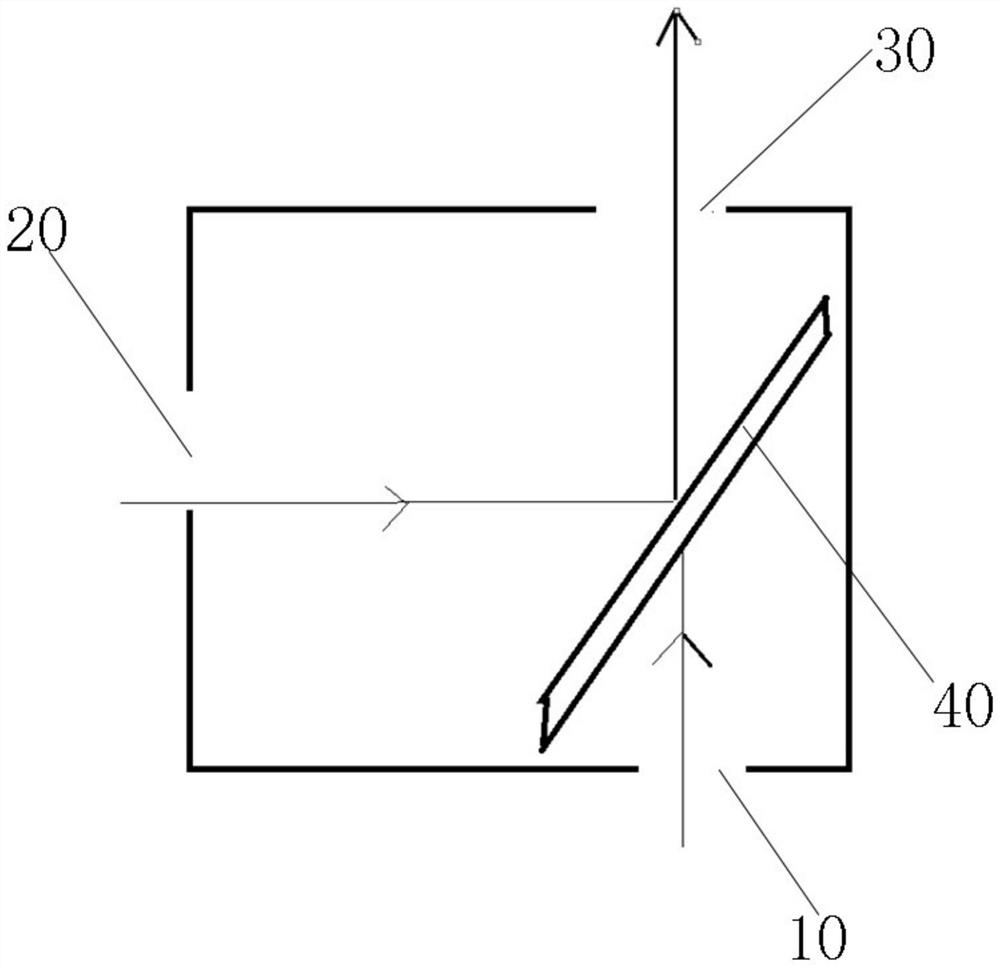
[0048] Example 2: as figure 1 , Figure 3-10 As shown, an optical path calibration module 1 is provided with a first light entrance port 10, a second light entrance port 20 and a first light exit port 30, and a first light splitting device 40 is provided inside it.
[0049] The first light entrance 10 first receives the calibration beam of the calibration light source, when the calibration is completed, the calibration light source is removed, and the first light entrance 10 is closed to prevent external stray light from entering the photoelectric sensor through the calibration module 1;
[0050] The second light entrance 20 receives the light beam of the target light source;
[0051] The first light outlet 30 emits a detection beam to the photoelectric sensor;
[0052] The first light splitting device 40 forms an included angle of 45° with both the first light entrance port 10 and the second light entrance port 20 .
[0053] In this embodiment, the first beam splitting dev...
Embodiment 3
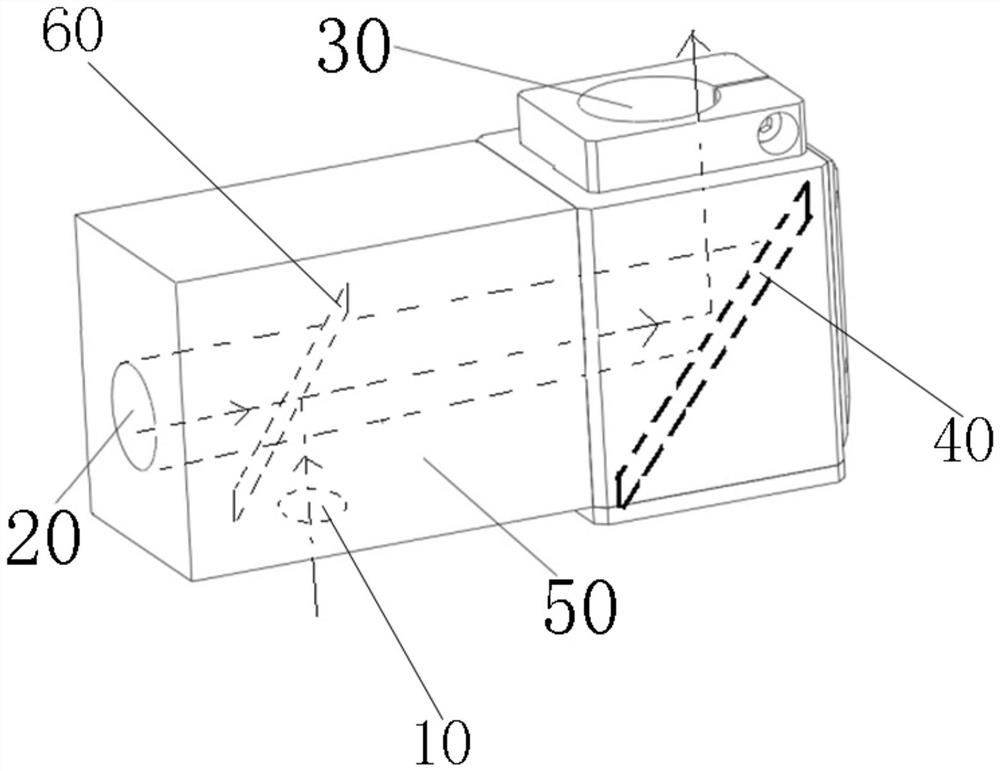
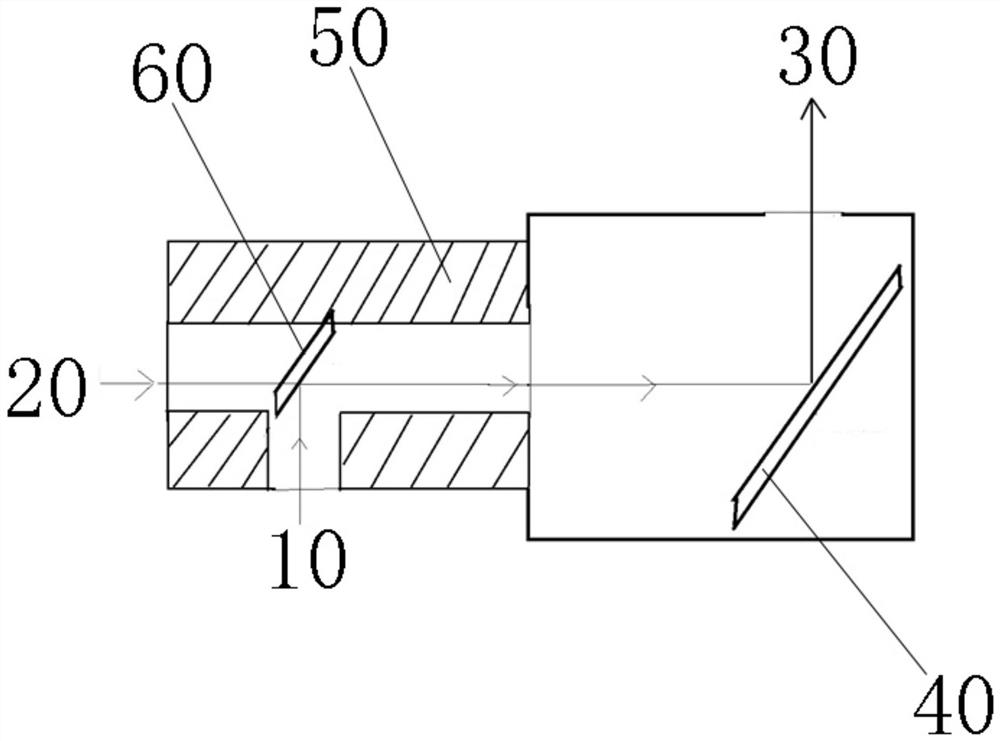
[0058] Example 3: as Figure 2-10 As shown, an optical path calibration module 1 is provided with a first light entrance port 10, a second light entrance port 20, a first light exit port 30, a T-shaped cavity structure 50, and a first light splitting device 40 is arranged inside it, and The second light splitting device 60, in this case, the T-shaped cavity structure 50 is installed on the left side of the calibration module described in Embodiment 1, and the cavity on the right side of the T-shaped cavity structure 50 passes through the second light entrance port of Embodiment 1 20 is connected to the first light splitting device 40 , the left cavity of the T-shaped cavity structure 50 is the second light entrance 20 , the lower cavity is the first light entrance 10 , and the right cavity is connected to the first light splitting device 40 , so that the light beam of the cavity on the right side is reflected to the first light outlet 30 after passing through the first beam sp...
Embodiment 4
[0066] Embodiment 4: In this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 3 is that the second spectroscopic device is replaced with a total reflection mirror 60, and the total reflection mirror 60 is inserted and installed in the T-shaped cavity structure 50 through the first light entrance 10. At the inner corner, an included angle of 45° is formed with the first light entrance port 50 and the second light entrance port 20 . On the one hand, the calibration beam from the first light entrance 10 is completely reflected, and is reflected by the first beam splitting device 40. The reflected calibration beam is emitted from the first light outlet 30 and received by the photoelectric sensor, which maximizes the calibration beam On the other hand, when the target light source beam enters the T-shaped cavity structure 50 from the second light entrance 20, the all-reflection mirror 60 reflects all the target light source beam upward, eliminating the interference of the target light sou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com