Radiation impact target and method for generating radiation impact waves with speed of more than 100km/s in xenon
A technology of shock wave and shock target, which is applied in the field of high energy density physics, can solve the problems that it is difficult to obtain radiation shock wave front images, etc., and achieve the effect of low cost, simple steps and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
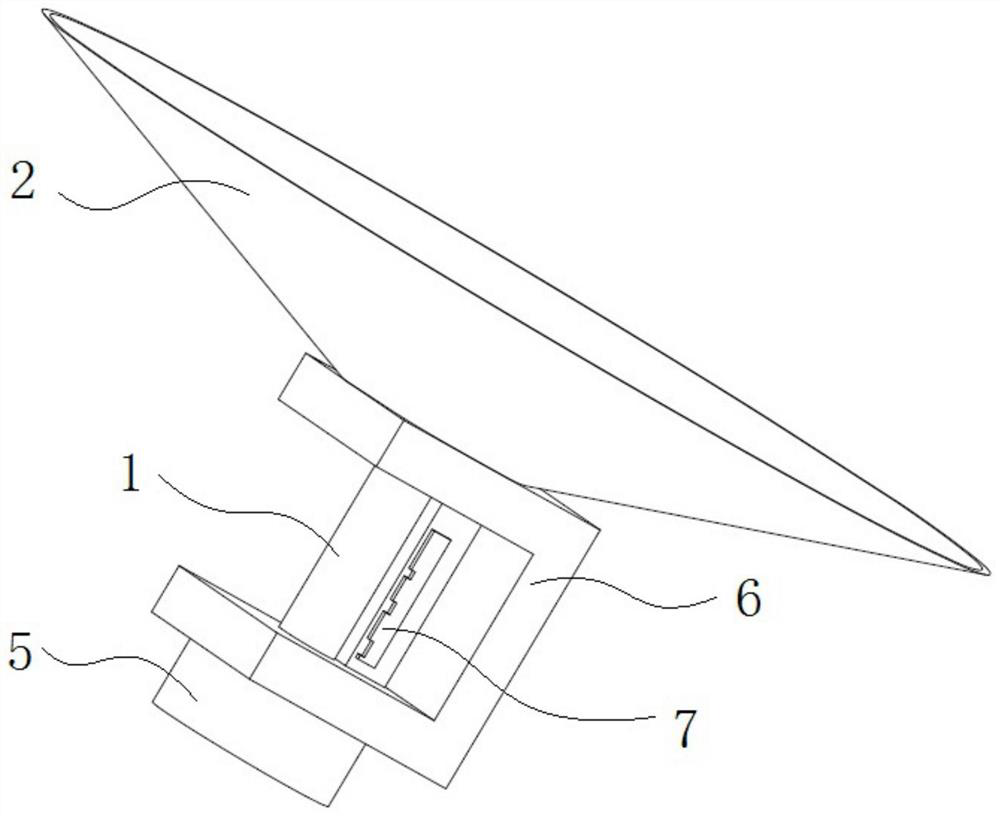
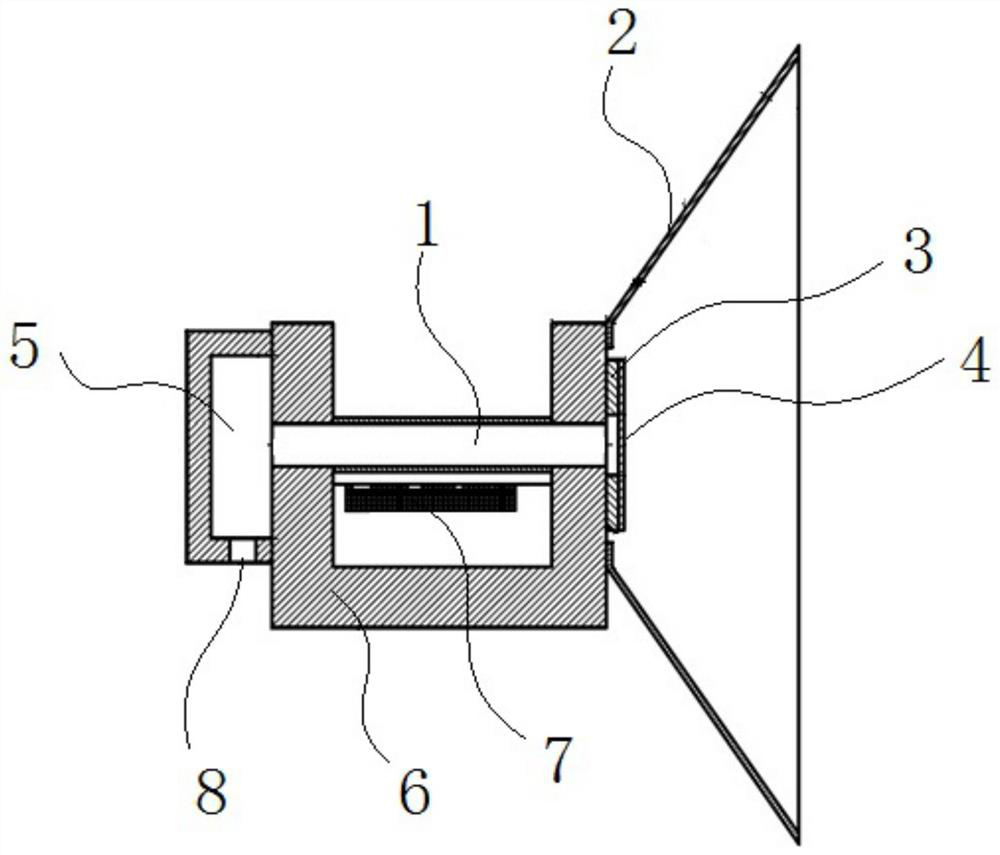
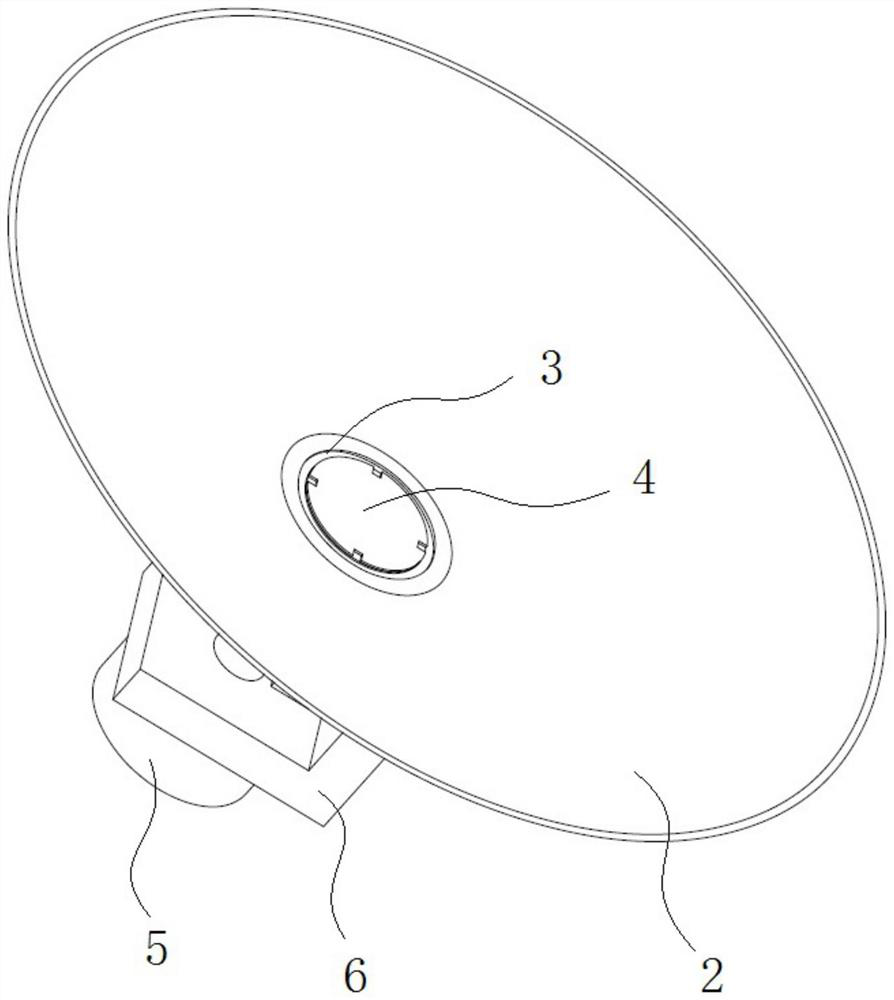
[0030] like Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, a radiation impact target includes a shock wave tube 1, a shielding cover 2, an annular metal sheet 3, an ablation layer 4, and a gas storage chamber 5; one end of the shock wave tube 1 is communicated with the gas storage chamber 5, and the other One end is communicated with one end of the shielding cover 2, and the other end of the shielding cover 2 is open; the annular metal sheet 3 is arranged on one end of the shock wave tube 1 connected with the shielding cover 2, and the ablation layer 4 is arranged on the annular metal sheet 3. on slice 3. The nanosecond laser is loaded on the ablation layer 4, and the heated material scatters backward, generating a forward driving force, and driving the remaining material to compress the xenon gas in the shock wave tube 1 inward, and its function is to generate a propagating into the shock wave tube 1. shock wave. The ring-shaped metal sheet 3 filters the X-rays on the target surface of th...
Embodiment 2
[0038] The other structures of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1. The difference is that it also includes a support member 6 for preventing the deformation of the shock wave tube 1 , and the support member 6 is sleeved on the shock wave tube 1 . Because the shock wave tube 1 has a thin and long wall and is composed of organic materials, it cannot be self-supporting, and an organic support structure is required to ensure that its structure remains unchanged; in this embodiment, a support member 6 is provided on the shock wave tube 1 to support the shock wave tube 1 . The protection function prevents the shock wave tube 1 from being deformed after receiving the action of the shock wave.
Embodiment 3
[0040] This embodiment provides a method for generating a radiation shock wave with a velocity of more than 100 km / s in xenon gas, using the shooting shock target described in Embodiment 1, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0041] Charge 1-2 atm of xenon gas into the gas storage chamber 5 communicated with the shock wave tube 1 through the gas charging tube;
[0042] Four nanosecond laser beams with an energy of 1.6kJ~3.2kJ, a spot diameter of 650μ~740μm, a pulse of 0.5ns~1.5ns, and a wavelength of 0.3μm~0.4μm are used to act on the ablation layer 4, nanosecond laser Loaded on the ablation layer 4, the heated material scatters backward, generating a forward driving force, driving the remaining material to compress the xenon gas in the shock wave tube 1 inward, and generating a shock wave propagating into the shock wave tube 1;
[0043] like Figure 4 As shown, the shock wave front image at a certain moment is obtained by using X-ray fluorophotography; the rad...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com