Secondary traveling salesman problem solving method and system based on deep reinforcement learning
A traveling salesman problem and reinforcement learning technology, applied in the field of solving the secondary traveling salesman problem, can solve the problem that the secondary traveling salesman problem cannot be solved, and achieve the effect of avoiding the dependence on professional knowledge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
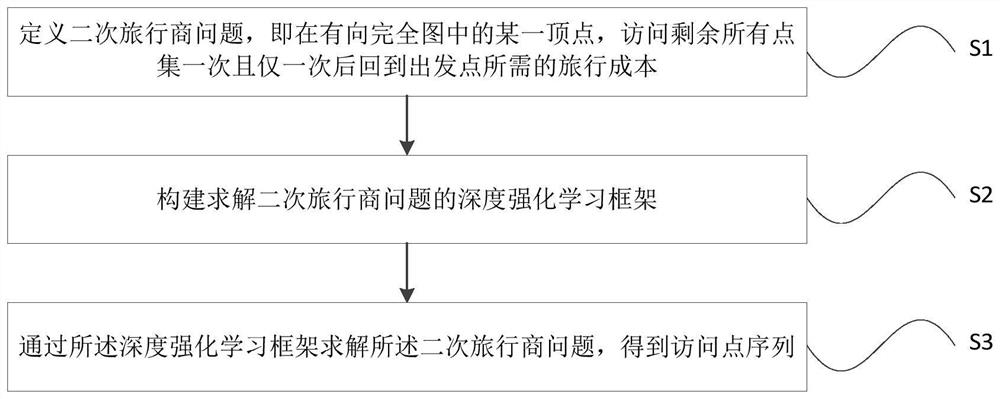
[0055] This embodiment provides a method for solving the quadratic traveling salesman problem based on deep reinforcement learning, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0056] S1: Define the quadratic traveling salesman problem, that is, in a vertex in a directed complete graph, the travel cost required to return to the starting point after visiting all the remaining point sets once and only once;
[0057] S2: Construct a deep reinforcement learning framework for solving the quadratic traveling salesman problem;
[0058] S3: Solving the quadratic traveling salesman problem through the deep reinforcement learning framework to obtain a sequence of access points.
[0059] The secondary traveling salesman problem in the step S1 is specifically:
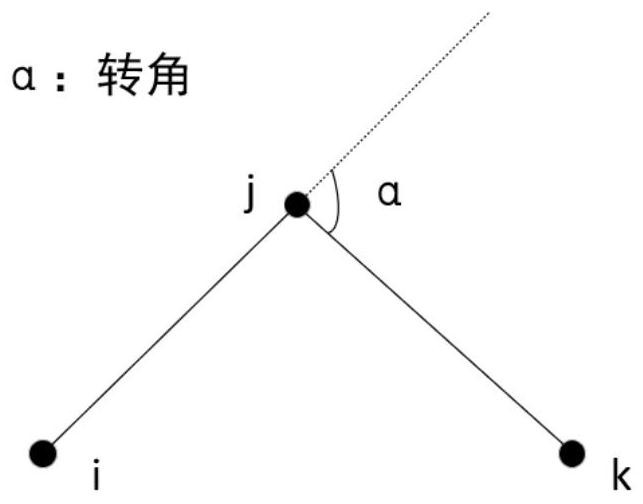
[0060] In the directed complete graph G=(V, E), where V represents a point set, which contains n vertices to be visited; E represents an edge set, and the lengths of the opposite sides in the edge set E are equal in ...
Embodiment 2
[0087] This embodiment provides a specific embodiment of embodiment 1, specifically:
[0088] The angle-distance traveling salesman problem is tested in ten sets of data with instance sizes 30 and 40, respectively. For the angle-distance traveling salesman problem, we test in five sets of data with instance sizes 30 and 40, respectively. Table 1 shows the test results of the angle traveling salesman problem, and table 2 shows the test results of the angle-distance traveling salesman problem.
[0089] Optimal corresponds to the exact solution opt of each group of instance data, ours corresponds to the solution under the method of the present invention, gap is the gap between the present invention and the exact solution, the calculation formula is (ours-opt) / opt, and the penultimate line The average gap is the average gap of the solution of the method of the present invention, and the optimal gap is the gap between the optimal solution and the exact solution in the heuristic alg...
Embodiment 3
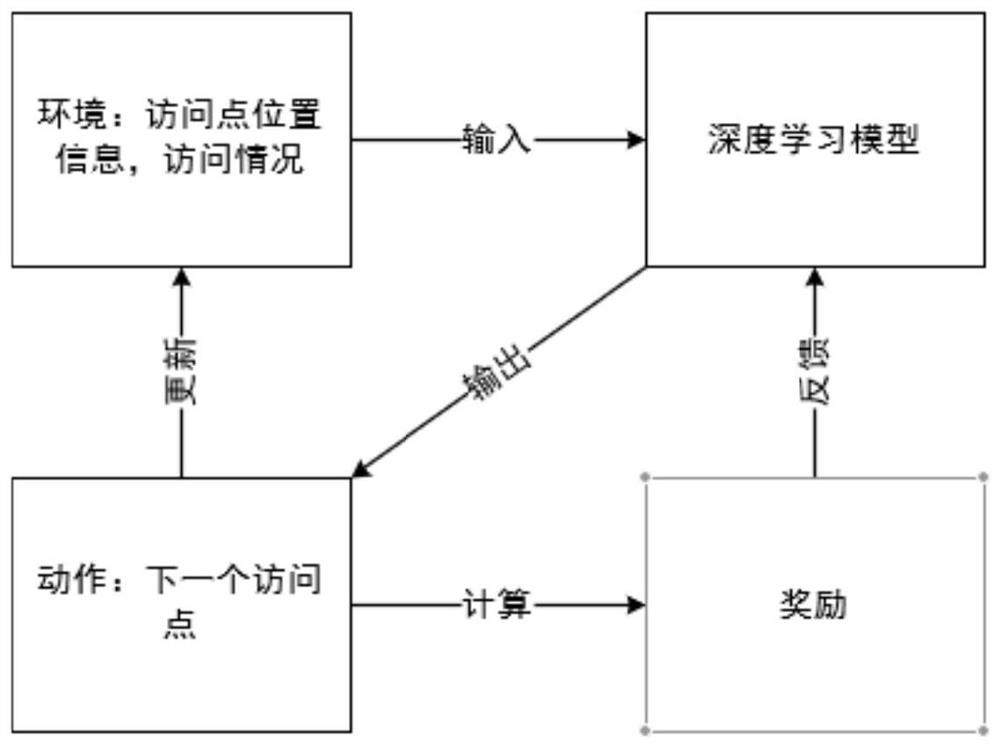
[0095] A quadratic traveling salesman problem solving system based on deep reinforcement learning, such as Figure 6 shown, including:
[0096] A problem module, the problem module defines a quadratic traveling salesman problem, that is, in a certain vertex in a directed complete graph, the travel cost required to return to the starting point after visiting all remaining point sets once and only once;
[0097]A deep reinforcement learning module, the depth reinforcement learning module constructs a deep reinforcement learning framework for solving the secondary traveling salesman problem;
[0098] A solving module, the solving module solves the quadratic traveling salesman problem through the deep reinforcement learning framework, and obtains a sequence of access points.
[0099] The same or similar reference numerals correspond to the same or similar components;
[0100] The terms describing the positional relationship in the drawings are only for illustrative purposes and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com