Building material surface radiation absorption coefficient calculation method considering long and short wave difference
A technology for calculation of building materials and coefficients, applied in the field of engineering building materials, can solve the problems of not considering the influence of radiation absorption coefficient, no unified standard for relevant values of building structure materials, insufficient consideration of environmental load design, etc., and achieve the test cost Low, highly operable effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
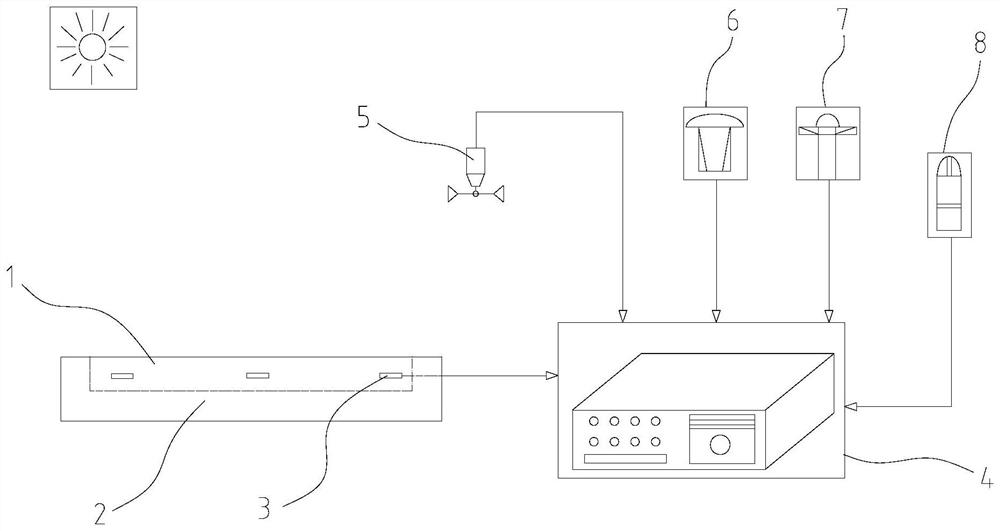
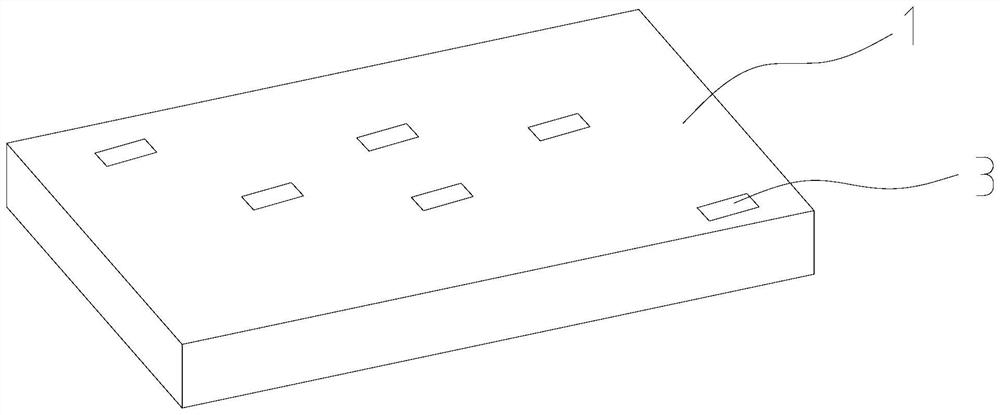
[0053] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for calculating the surface radiation absorption coefficient of building materials considering the difference between long and short waves, including building material specimen 1, thermal insulation box 2, thermocouple temperature sensor 3, simple weather station 4, wind speed Instrument 5, total solar radiation sensor 6, environmental long-wave radiation sensor 7 and atmospheric temperature sensor 8.
[0054] Such as figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the thermal insulation box is made of polyethylene, and the thermal insulation box wraps the building material specimen, so that only the outer surface of the building material specimen is in contact with the surrounding environment, and the outer surface and interior of the building material specimen are equipped with thermocouple temperature sensors , the anemometer, the environmental long-wave radiation sensor and the total solar radiation sens...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com