Covalent organic framework-platinum composite nano antibacterial agent for killing drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria
A covalent organic framework and nano-antibacterial agent technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problems of sharp decline in catalytic antibacterial activity, restrictions on the practical application of PtNPs, and easy agglomeration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] 1. Experimental method
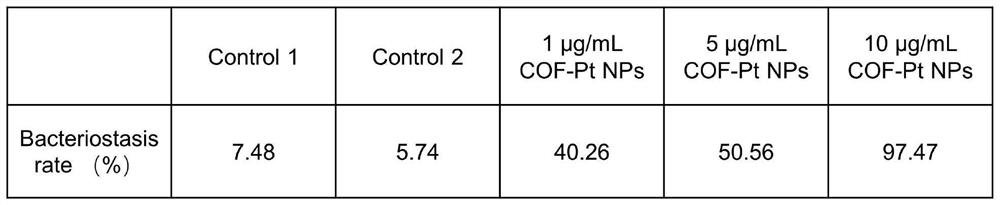
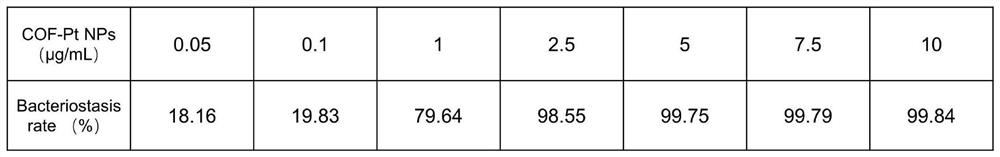
[0016] Using MRSA as a representative, the antibacterial properties of COF-PtNPs were studied. The bacteria were inoculated in about 4 mL of broth medium, placed in a shaking incubator at 37 ° C, and cultured at a speed of 220 rpm / min for about 3 h, by using a UV-visible spectrophotometer at 600 nm (OD 600nm ) to record the optical density, adjust the cell density of the cultured bacteria to 0.5OD 600nm . Then dilute the bacteria 20 times with normal saline, and add samples in the following groups: (1) Control 1: NaAc / HAc; (2) Control 2: H 2 o 2 ; (3) COF-PtNPs; (4) COF-Pt NPs+H 2 o 2 , the total volume of each tube is 400 μL, after mixing, incubate at 37°C for 1h, spread the bacterial suspension on the LB agar plate, and place it upside down in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C for about 18h. In addition, by measuring OD 600nm To detect the concentration of bacteria to quantify its antibacterial rate. OD of LB medium containing b...
Embodiment 2
[0021] 1. Experimental method
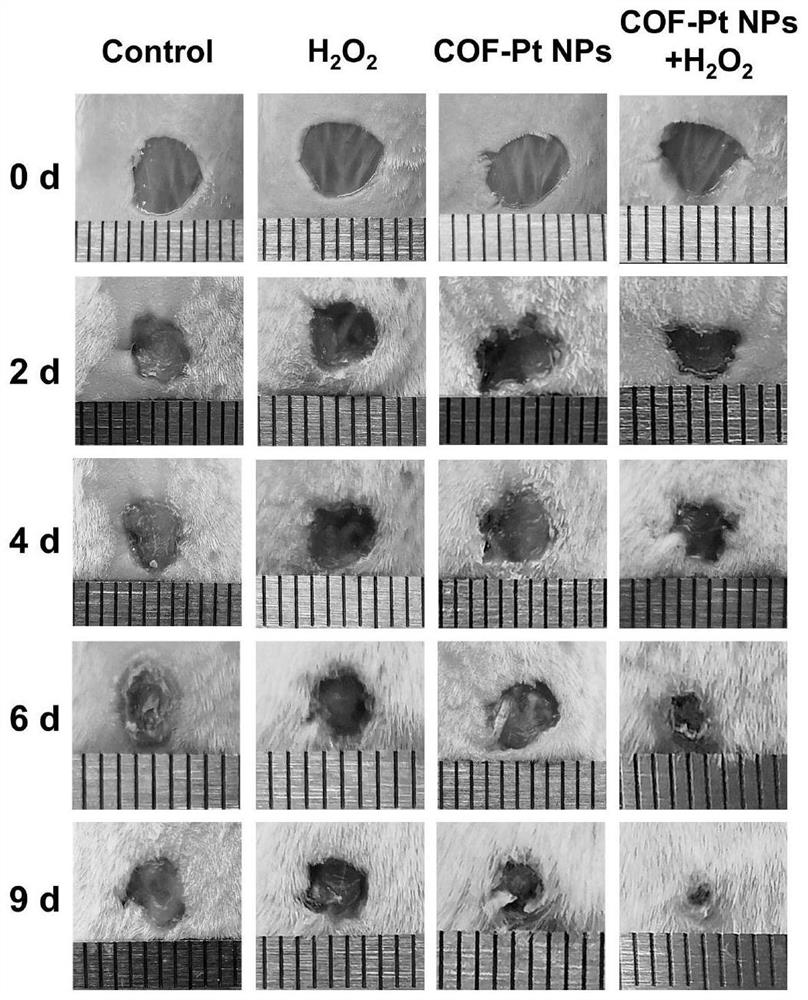
[0022] In order to evaluate the antibacterial effect of COF-PtNPs in vivo, male BALB / c mice (about 7 weeks old, about 20 g, 2 mice per group) were used to establish a mouse wound infection model. The mice were weighed and marked first, and then the mice were anesthetized with ether. After the hair on the back of the mice was shaved, a circular skin wound with a diameter of about 4.5 mm was produced on the back of each mouse, and 60 μL of MRSA (10 8 CFU / mL) suspension was placed on the wound. After infection, the mice were divided into 4 groups and treated with different treatments: (1) Control; (2) H 2 o 2 ; (3) COF-PtNPs; (4) COF-PtNPs+H 2 o 2 . H used in this study 2 o 2 The dose was 70 μL (250 μM) per site. The dose of nanozymes was 70 μL per site (5 μg / mL). Treatments were performed once a day, and wound photographs were taken for each group at each expected time point.
[0023] 2. Result analysis
[0024] With COF-PtNPs and COF-P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com