Ligand use cost evaluation method based on unit protein adsorption cost
A protein and ligand technology, applied in the field of protein chromatography separation, can solve the problems of infeasibility, increase in the cost of adsorbent preparation, and decrease in adsorption capacity, etc., and achieve the effect of high industrialization potential, good guiding significance, and small workload
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
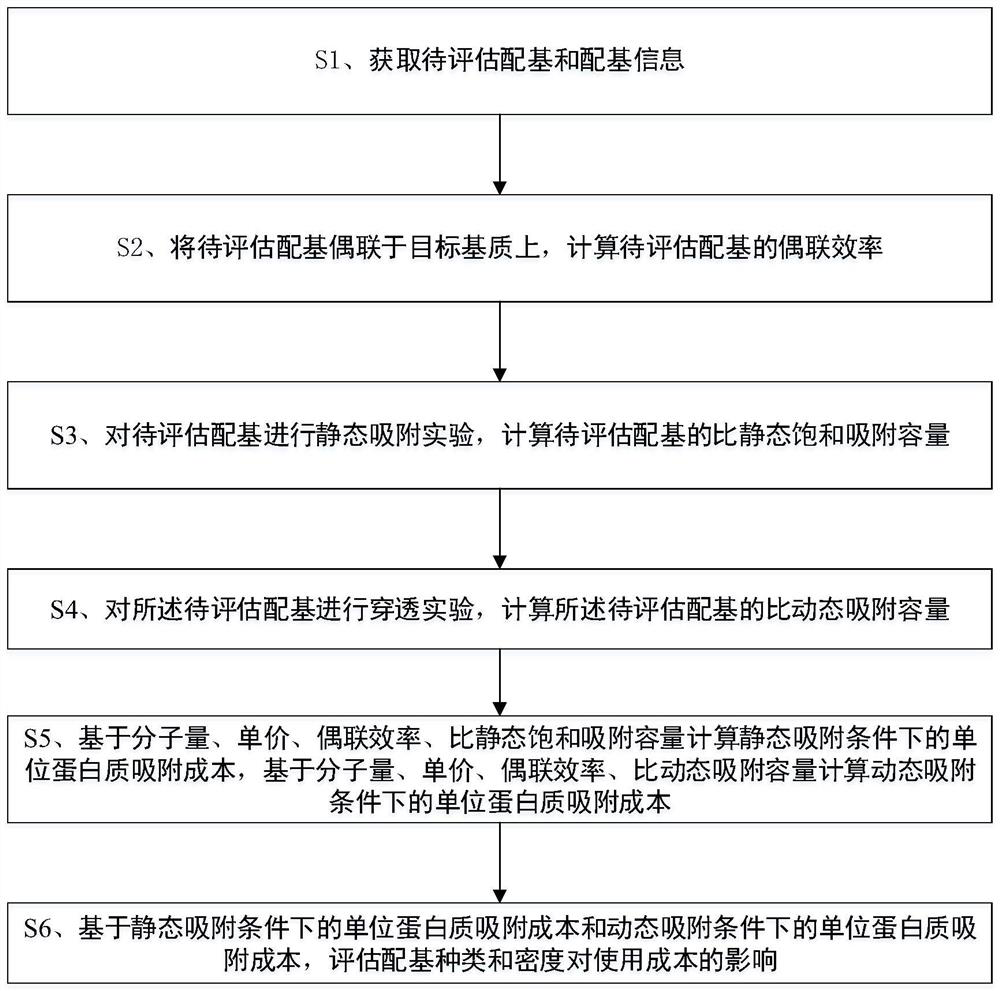
[0042] Such as Figure 1-6 As shown, the evaluation method includes the following steps:
[0043] S1. Obtain ligands to be evaluated and ligand information.
[0044] The ligand to be evaluated is a hydrophobic charge-inducing ligand, and tryptophan ligand is used in this example. Obtain basic information of tryptophan ligands from suppliers, including molecular weight, brand, unit price, etc.
[0045] S2. Coupling the ligand to be evaluated to the target substrate, and calculating the coupling efficiency of the ligand to be evaluated.
[0046] The target substrate is a hydrophilic medium with a porous structure and surface hydroxyl groups. In this embodiment, the target matrix is agarose gel microspheres. The basic information of matrix and tryptophan ligand in the present embodiment is as shown in table 1:
[0047] Table 1
[0048]
[0049] 4% agarose gel microspheres were taken for coupling reaction to prepare hydrophobic charge-induced adsorbents with different l...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Obtain basic information of tryptamine ligands from suppliers, including molecular weight, brand, unit price, etc. 4% agarose gel microspheres were taken for coupling reaction to prepare hydrophobic charge-induced adsorbents with different ligand densities. The specific preparation process is as follows: the drained cross-linked agarose matrix is first activated by allyl bromide, and then brominated by N-bromosuccinimide. By controlling the amount of ligand added in the coupling reaction, different ligand densities can be obtained. Finally, the prepared adsorbents were washed with 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M NaOH, and deionized water, respectively. Referring to Example 1, perform data processing and calculation to obtain molecular weight, unit price, coupling efficiency, specific static saturation adsorption capacity or specific dynamic adsorption capacity (10% breakthrough), and calculate the unit protein adsorption cost under static adsorption and dynamic adsorption condition...
Embodiment 3
[0071] Obtain the basic information of 2-(aminomethyl)pyridinium from the supplier, including molecular weight, brand, unit price, etc. 4% agarose gel microspheres were taken for coupling reaction to prepare hydrophobic charge-induced adsorbents with different ligand densities. The specific preparation process is as follows: the drained cross-linked agarose matrix is first activated by allyl bromide, and then brominated by N-bromosuccinimide. By controlling the amount of ligand added in the coupling reaction, different ligand densities can be obtained. Finally, the prepared adsorbents were washed with 0.1 M HCl, 0.1 M NaOH, and deionized water, respectively. Referring to Example 1, perform data processing and calculation to obtain molecular weight, unit price, coupling efficiency, specific static saturation adsorption capacity or specific dynamic adsorption capacity (10% breakthrough), and calculate the unit protein adsorption cost under static adsorption and dynamic adsorp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com