Preparation method of pickled vegetables with low biogenic amine and weak post-acidification
A technology of biogenic amines and post-acidification, applied in chemical instruments and methods, bacteria used in food preparation, food science, etc., can solve the problems of post-acidification, softening, unstable quality, easy accumulation of biogenic amines, etc., and shorten the maturity period, accelerating the ripening of kimchi, and the effect of rapidly acidifying the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] A preparation method of low biogenic amine and weak post-acidification kimchi, comprising the steps of:
[0049] (1) Vegetable pretreatment:
[0050] removing yellow leaves and rotten leaves in the vegetables, selecting fresh, moderately mature vegetables without impurities and sundries, cleaning them, drying them in the sun, removing moisture from the vegetables until the moisture content is 45%, and obtaining semi-dried vegetables;
[0051] (2) Salted fermentation
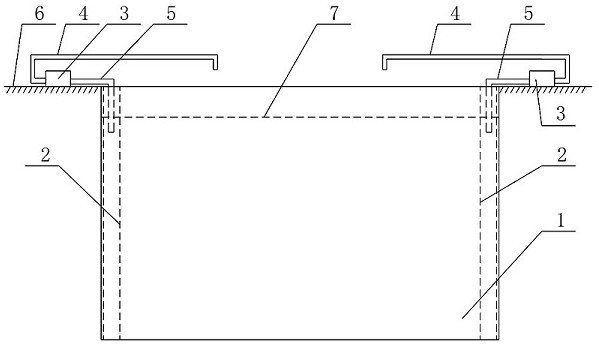
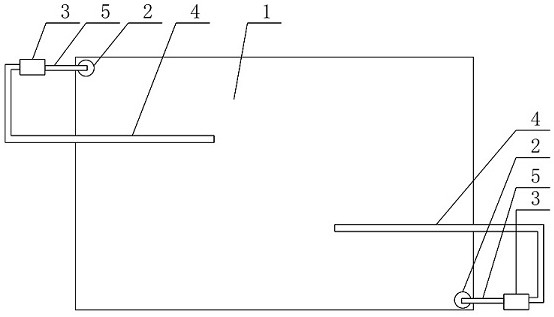
[0052] Adopt 90 tons of large-scale salting ponds 1 to carry out salting fermentation; The semi-dried vegetables that step (1) obtains is laid in the salting pond 1 by one layer of vegetables and one layer of salt at intervals, and the consumption of salt is 4% of the total weight of semi-dried vegetables %; After 2.5 days of salting, the vegetables were extracted from the salt water by the osmotic pressure of the salt with the circulation pump 3 and poured on the vegetable surface by the salt water pouri...
Embodiment 2
[0061] A preparation method of low biogenic amine and weak post-acidification kimchi, comprising the steps of:
[0062] (1) Vegetable pretreatment:
[0063] removing yellow leaves and rotten leaves in the vegetables, selecting fresh, moderately mature vegetables without impurities and sundries, cleaning them, drying them in the sun, removing moisture from the vegetables until the moisture content is 60%, and obtaining semi-dried vegetables;
[0064] (2) Salted fermentation
[0065] Adopt 120 tons of large-scale salting ponds 1 to carry out salting fermentation; The semi-dry vegetables that step (1) obtains is laid in the salting pond 1 by the interval of one layer of vegetables and one layer of salt, and the consumption of salt is 5% of the total weight of semi-dry vegetables %; After 2 days of salting, the vegetables are extracted from the brine due to the osmotic pressure of the salt with the circulation pump 3 and poured on the surface of the vegetables by the brine pourin...
Embodiment 3
[0074] A preparation method of low biogenic amine and weak post-acidification kimchi, comprising the steps of:
[0075] (1) Vegetable pretreatment:
[0076] removing yellow leaves and rotten leaves in the vegetables, selecting fresh, moderately mature vegetables without impurities and sundries, cleaning them, drying them in the sun, removing moisture from the vegetables until the moisture content is 55%, and obtaining semi-dried vegetables;
[0077] (2) Salted fermentation
[0078] Adopt 60 tons of large-scale salting pool 1 to carry out salting fermentation; The half-dried vegetables that step (1) obtains is laid in the salting pool 1 by one layer of vegetables and one layer of salt interval, and the consumption of salt is 7% of the total weight of semi-dry vegetables %; after 3 days of salting, the vegetables are extracted from the brine due to the osmotic pressure of the salt with the circulation pump 3 and poured on the surface of the vegetables through the brine pouring ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com