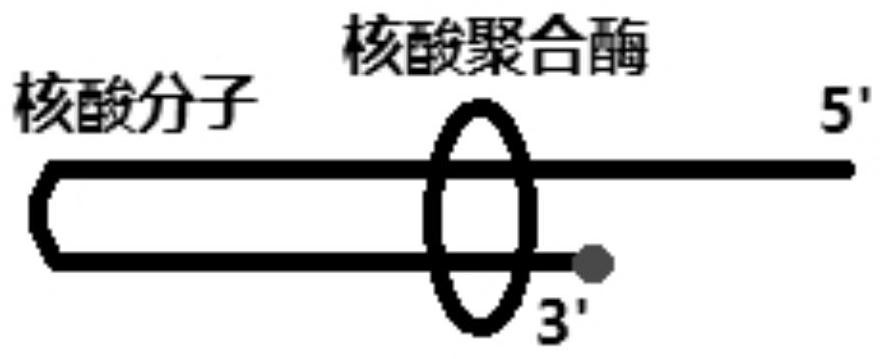
Nucleic acid ligand and application thereof
A nucleic acid ligand and nucleic acid technology, applied in chemical treatment to inactivate enzymes, organic chemistry, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve problems such as long cycle, slow process, and complexity, and achieve the purpose of inhibiting non-specific amplification, Reduce the effect of non-specific amplification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Embodiment 1: the assay method of nucleic acid ligand inhibition polymerase enzymatic activity
[0064] Using the single-strand extension method to detect, use the purchased NEB M13 single-stranded DNA and related primers to measure the activity, and use the fluorescence quantitative method to detect in real time. The instrument used in the present invention is Roche LC480II.
[0065] Primer M13R sequence and amplification system are as follows:
[0066] M13R Primer 1ACGCTCGTCATCAAAAATCACTCGCATCAACCAAACCGTTAT
[0067] Table 1
[0068] components concentration Add volume ul per serving 10x Buffer A 10x 2.5 MgCl 2
250mM 0.5 SG 100x 0.4 M13ssDNA 0.73mg / ml 0.45 dNTP 100mM 0.2 M13R 100uM 0.1 taq enzyme / 1 ddH2O / 19.85
[0069] Among them, 10X bufferA is 30mM, Tris 8.0; 50mM KCl; TWEEN20 0.05%; Buffer prepared by 10mM mercaptoethanol. This reaction system has high repeatability and accuracy...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2: Blocking experiment of polymerase (select optimal isothermal extension conditions to screen nucleic acid ligands)
[0076] Extend according to the method of Example 1 at 70°C, 60°C, 50°C, and 40°C to screen which nucleic acid ligands achieve the expected effect, such as the following nucleic acid ligands:
[0077] Nucleic acid ligand 1 (nucleic acid polymerase substrate analogue): TCGAACGGTATATATATTAATATATATAC (shown in SEQ ID NO: 1), 3' end dideoxy modification.
[0078] First mix 6U DNase with the above nucleic acid ligand 1, then add about 6U DNase and mix according to the 100uM 0.05ul system, and test at -20 overnight. At the same time, the system without nucleic acid ligand was used as the control system. According to the method for measuring activity in Example 1, the enzyme activities of the two systems were tested respectively.
[0079] Depend on Figure 4-7It can be seen that in the system without adding nucleic acid ligands, the signal of the pol...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3: the blocking experiment of polymerase
[0082] The 3' end modification of nucleic acid molecules or nucleic acid molecule analogs can be in common ways to prevent amplification (dideoxy modification, phosphorylation modification, amino modification, etc.). In this embodiment, the dideoxy method is selected to terminate terminal extension. At the same time, the nucleic acid molecule without modification at the 3' end was used as a control to test whether the unmodified nucleic acid molecule can also inhibit the enzyme activity. The experimental method refers to Example 1. The sequences of the two nucleic acid ligands are as follows:
[0083] Nucleic acid ligand 1 (nucleic acid polymerase substrate analogue): TCGAACGGTATATATATTAATATATATAC (shown in SEQ ID NO: 1), 3' end dideoxy modification;
[0084] Control nucleic acid ligand (nucleic acid polymerase substrate analog): TCGAACGGTATATATATTAATATATATAC, 3' end unmodified;
[0085] 6U DNA polymerase was mixed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com