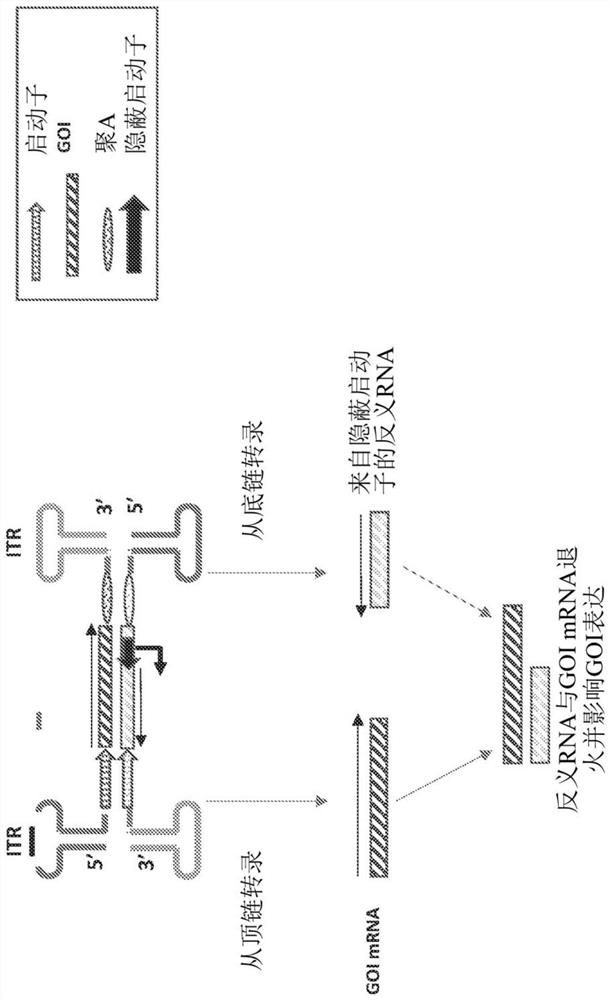
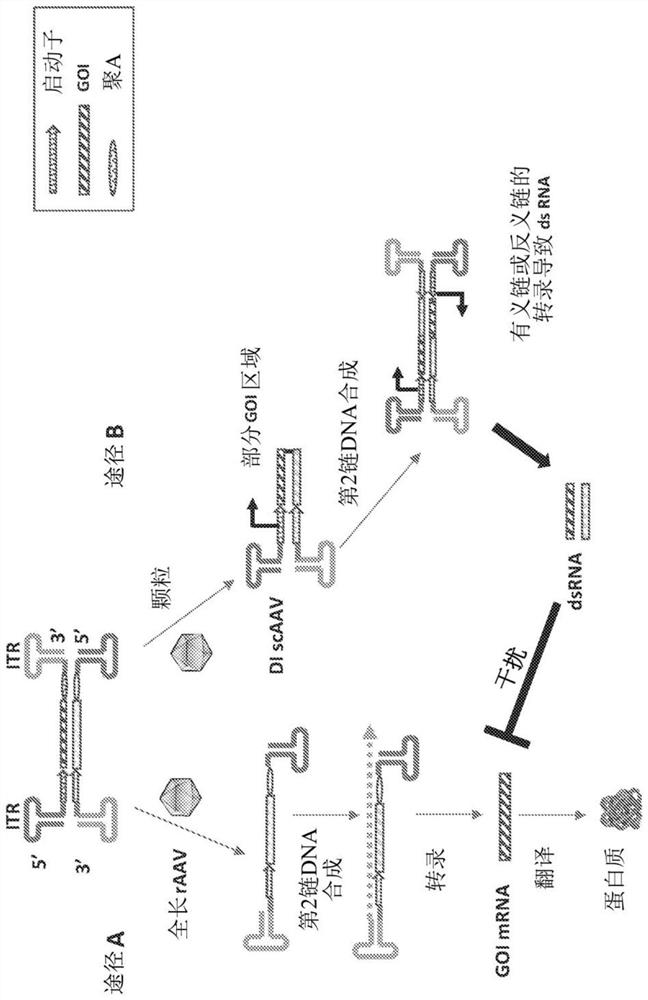
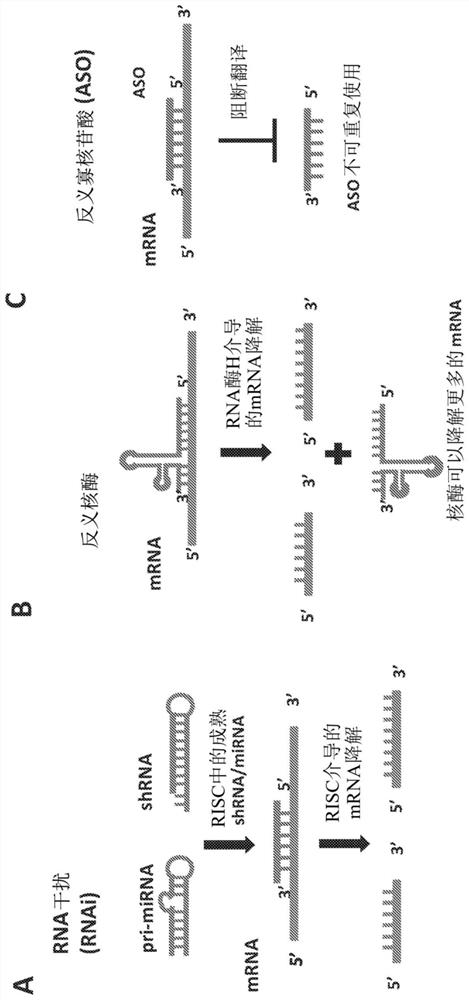
Parvoviral vectors and methods of making and use thereof
A technology of parvoviruses and vectors, applied in the direction of viruses/bacteriophages, biochemical equipment and methods, viruses, etc., which can solve the problems of reduced virus production yields and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0112] Example 1: ubiquitously expressed miR-16-TS for antisense RNA and dsRNA elimination remove
[0113]The hsa-miR-16 sequence was obtained from the miRNA registry (Griffiths-Jones, 2004). RDDD with the miR-16 target sequence was synthesized and cloned into the factor VIII (FVIII) expression construct pAAV-F8, which has the B domain deleted under the control of the liver-specific promoter TTR Factor VIII. The RDDD sequence with the miR-16 sequence inserted between the promoter and the FVIII start codon includes the sequence TAGCAGCACGTAAATATTGGCG (SEQ ID NO: 1). The underlined sequences in the GOI strands are designed to be exact matches to specific miRNAs. In the bottom strand, the sequence is perfectly complementary to a specific miRNA (miR-16 in this case). The resulting construct was pAAV-F8-miR-16-PG. Only one copy of the miRNA was used to avoid long gaps between the promoter and the GOI. The pAAV-F8-miR-16-PG-based vector was generated by a triple plasmid t...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Example 2: Multiple copies of miR-16-TS for antisense RNA and dsRNA depletion
[0115] RDDDs with four copies of the miR-16 target sequence were synthesized and cloned into the factor VIII (FVIII) expression construct pAAV-F8 with the liver-specific promoter TTR deleted for the B domain Factor VIII under control. Since there is no poly-A signal in the antisense strand of the promoter of the GOI, transcripts of antisense RNA and dsRNA will extend beyond the promoter and terminate at the ITR (which appears to function as a poly-A site). An RDDD with 4 copies of miR-16 was inserted between the promoter and the 5'ITR, including the following sequence: gtac TAGCAGCACGTAAATATTGGCG gctagc TAGCAGCACGTAA ATATTGGCG gtcagc TAGCAGCACGTAAATATTGGCG agctgc TAGCAGCACGTAAATATTGGCG cgta (SEQ ID NO: 2). The underlined sequences in the GOI strands were designed to exactly match specific miRNAs. In the bottom strand, these sequences are perfectly complementary to a specific mi...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Example 3: miR-16-TS and miR-122 for antisense RNA and dsRNA depletion in liver.
[0117] Since there is no poly-A signal in the antisense strand of the promoter of the GOI, transcripts of antisense RNA and dsRNA will extend beyond the promoter and terminate at the ITR (which appears to function as a poly-A sequence). In this study, with two copies of miR-16 and two copies of miR-122 ( CAAACACCATTGTCACACTCCA (SEQ ID NO:3) ) is inserted between the promoter and the enhancer and includes the following sequence: gtac CAAACACCATTGTCACACTCCA gctagc TAGCAGCAC GTAAATATTGGCG gtcagc CAAACACCATTGTCACACTCC Aagctgc TAGCAGCACGTAAATATTGGCG cgta (SEQ ID NO: 4)
[0118] The underlined sequences in the GOI strands were designed to exactly match specific miRNAs. In the bottom strand, these sequences are perfectly complementary to specific miRNAs (in this case miR-16 and miR-122). The resulting construct was pAAV-F8-miR-16-122-EP. The pAAV-F8-miR-16-122-EP based vector...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com