Rapid sensitive detection method of GGC repetitive sequence of NOTCH2NLC gene and application of rapid sensitive detection method
A repetitive sequence and gene technology, applied in the medical field, can solve the problems of misjudgment of test results and high proportion of CG in amplified fragments, and achieve the effects of rapid detection, reduced detection cost and sensitive detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] This embodiment discloses a method for rapidly detecting the GGC repeat sequence of the NOTCH2NLC gene, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0031] 1. Obtain the genomic DNA of the sample to be tested;
[0032] 2. Using the amplification reaction system to amplify the NOTCH2NLC gene;
[0033] 3. Detect the repetitive sequence GGC of the NOTCH2NLC gene in the obtained amplification product.
[0034] Wherein the amplification reaction system includes a primer composition, which is composed of an upstream primer, a downstream primer and a third primer of a non-human gene sequence, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific sequence is shown in Table 1.
[0035] Table 1
[0036]
[0037] The amplification reaction system is shown in Table 2 below.
[0038] Table 2
[0039]
[0040] Citing the document 2 program, that is, the amplification program is:
[0041] React at 98°C for 10min; then react at 98°C for 30sec, 66°C for 1min (each cycle reduces 0.5°...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The only difference between the method of this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the amplification procedure is:
[0045] React at 98°C for 10min; then react at 98°C for 30sec, 66°C for 1min (each cycle reduces 0.5°C), and 68°C for 1min, a total of 20 cycles; then react at 98°C for 30sec, 56°C for 30sec, and 68°C React for 1 min, a total of 15 cycles; last 10 minutes at 68°C. The adjustment of all cycle steps is 0.5°C / sec, which is the new program.
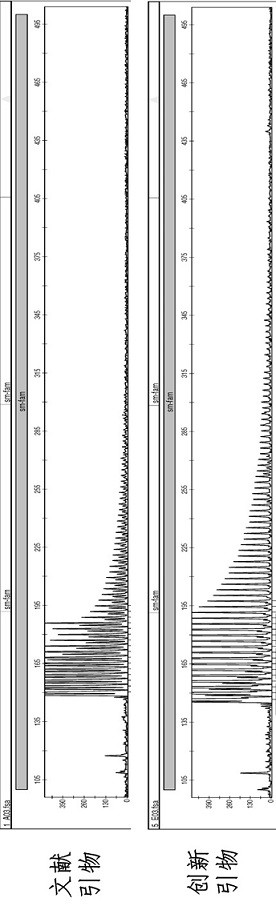
[0046] It was found that the new procedure of the innovative primers of the present invention (as shown in Table 1 above) well solved the PCR amplification of the abnormal repeat of 5'UTR GGC in the NOTCH2NLC gene, as follows Figure 4 As shown, it was found that the procedure of 1 hour and 40 minutes can complete the PCR amplification of the 5'UTR GGC abnormal repeat in the NOTCH2NLC gene.
Embodiment 3
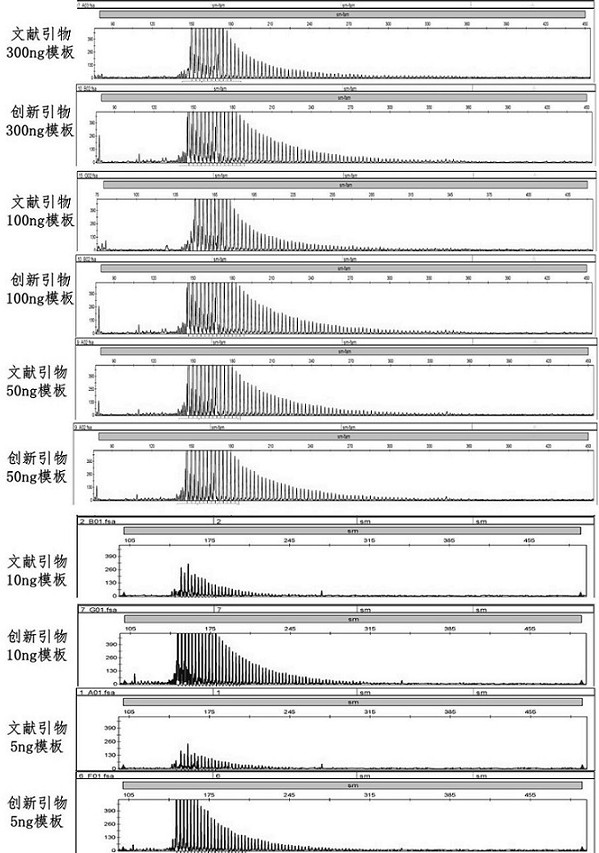
[0048] This example studies the sensitivity of the innovative primers to the 5'UTR GGC abnormal repeat amplification in the positive control NOTCH2NLC gene with different templates, and the results are as follows image 3 shown. Among them, the DNA samples (5ng-300ng) of the positive control patients were amplified by PCR with the literature primers and the innovative primers, and the capillary electrophoresis results were compared, and it was found that the innovative primers were more sensitive, and positive signals could be detected at 5ng.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com