Density gradient microstructure, preparation method of density gradient microstructure and magnetically controlled switch
A microstructure and gradient technology, applied in the field of microfluidics, can solve the problems of weak real-time control capability and complex device structure, and achieve the effects of real-time control, increased liquid spreading speed, and obvious reverse cut-off effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown: the present embodiment provides a density-gradient microstructure 100, including a substrate 1, a plurality of array regions are arranged on the substrate 1, and each array region includes a number of evenly distributed micropillars 2, and micropillars 2 in different array regions The spacing of the micropillars increases from one end of the substrate 1 to the other end of the substrate 1, and the micropillars 2 are all magnetic.
[0045] In this embodiment, the shape of the micropillar 2 is cone, cylinder or prism.
[0046] In this embodiment, the width of the substrate 1 is 5-10 mm, the length of the substrate 1 is 30-50 mm, the distance between the micro-columns 2 in the same array area is the same, and the distance d of the micro-columns 2 is 150-550 μm. The gradient difference between the pitches of the micropillars 2 in adjacent array regions is the same, and the gradient difference Δ is 10 μm. For example, the pitch of micropillars 2 ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Such as Figure 2-Figure 4 Shown: This embodiment provides a method for preparing the density gradient microstructure 100 of Embodiment 1, including the following steps:
[0052] S1: The mold 4 with the same shape as the microcolumn 2 is used to make holes point by point on the substrate 3. The spacing of the holes is the same as that of the microcolumns 2 of the density gradient microstructure 100. Specifically, this embodiment adopts a tapered The mold 4 has a cone tip angle of 15°, the mold 4 is a steel needle, the substrate 3 is a paraffin plate, and the depth of the cone hole is between 100 and 500 μm;
[0053] S2: vacuumize the prepared hole, and pour the mixed solution 6 with magnetic particles 5 into the prepared hole;
[0054] S3: Vacuum again, scrape off the excess mixed solution 6 with magnetic particles 5, continue pouring the mixed solution 6 onto the substrate 3 to form the matrix 1, and ensure that the average thickness of the recasting is between 2 and ...
Embodiment 3
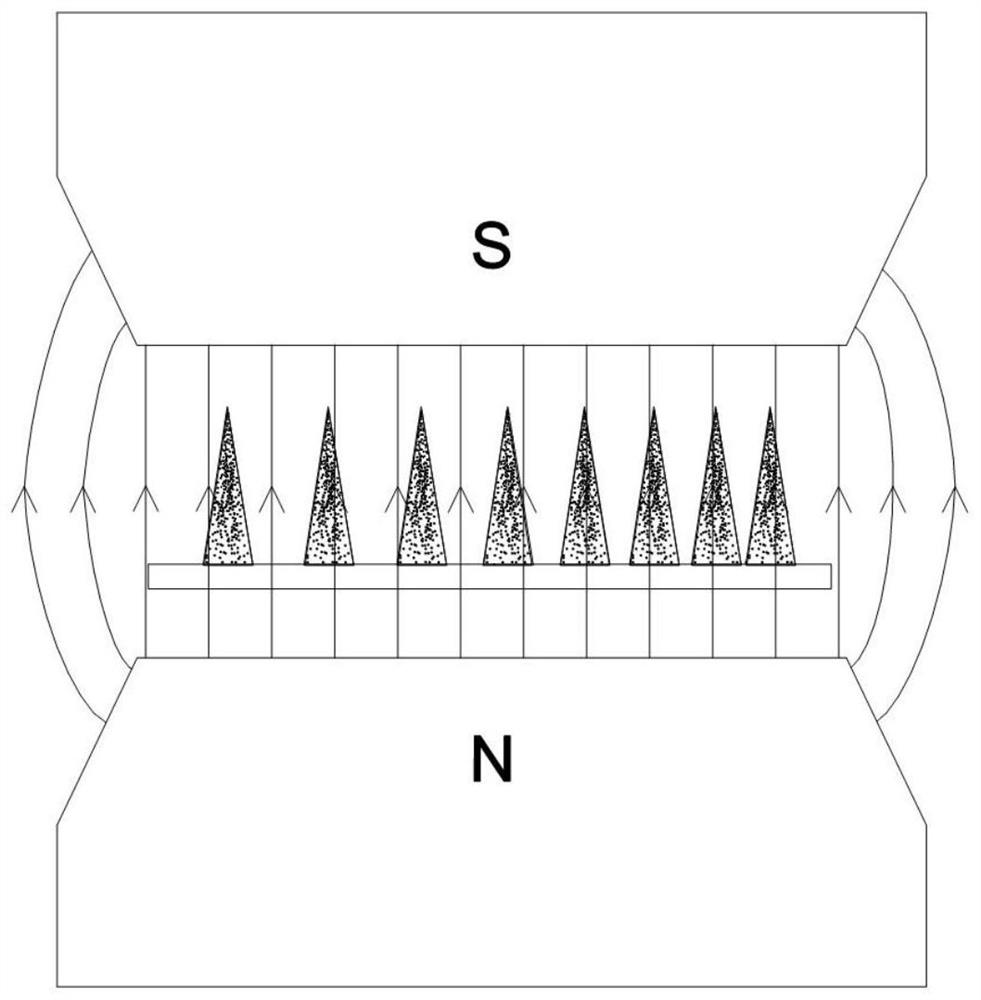
[0062] Such as Figure 5-Figure 10c As shown: this embodiment provides a magnetic control switch 200, including the density gradient microstructure 100 of the first embodiment, the density gradient microstructure 100 is located in the micro-channel 7, the micro-channel 7 is located in the magnetic field, and the micro-flow One end of the channel 7 is an N pole, and the other end of the microchannel 7 is an S pole. The microchannel 7 is made of PDMS. The width of the microchannel 7 is 5 mm and the length is 50 mm. The distance between the tops of 7 is 2 mm, the middle part of the micro-channel 7 is provided with an inlet 8, and the inlet 8 is connected to the capillary glass tube 11, one end of the micro-channel 7 is the first outlet 9, and the other end of the micro-channel 7 is the second outlet 10. One end (sparse end) of the matrix 1 of the density gradient microstructure 100 corresponds to the first outlet 9, the other end (dense end) of the matrix 1 corresponds to the sec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com