An axis-shifting reversing dual-rotor aircraft
An aircraft and dual-rotor technology, applied in the field of aircraft, can solve the problems of increased aircraft height, complex control mechanism, and difficult maintenance, and achieve the effects of shortened rotor spacing, sensitive control, and reduced rotor diameter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
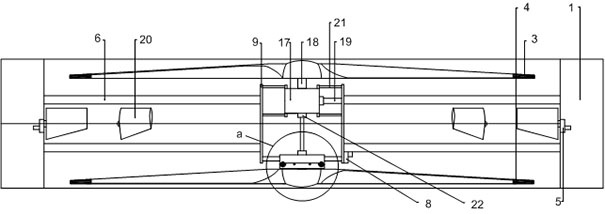
[0048] Example 1: as Figure 1 to Figure 11 As shown, an axis-shifting and reversing dual-rotor aircraft includes an aircraft power unit and a translation rotor assembly, and the translation rotor assembly includes a rotor, a universal joint transmission device and a translation device; the output end of the aircraft power device and The fixed point connection of the universal joint transmission device, the moving point of the universal joint transmission device is connected with the translation device, the translation device is connected with the rotor, and the moving point and translation device of the rotor and the universal joint transmission device can be along the Movement in the X-axis and / or Y-axis direction; the universal joint transmission device transmits the torsion force of the aircraft power device to the rotor, so as to drive the rotor to rotate.
[0049] In the prior art, the traditional cyclic pitch control system is used to increase the distance between the t...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2: This embodiment is further limited on the basis of Embodiment 1, such as Figure 12 to Figure 17 shown;
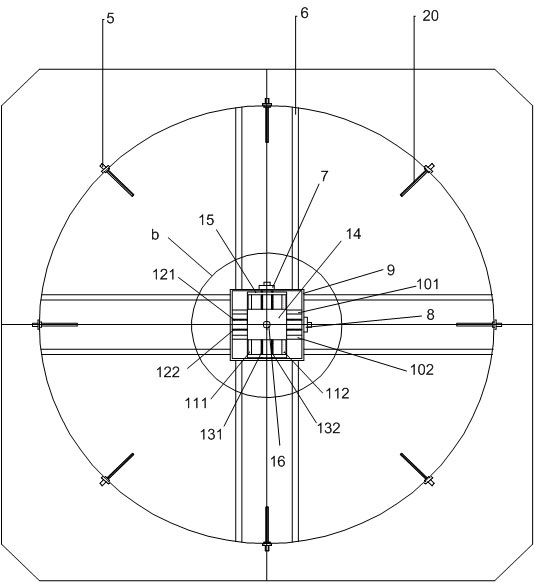
[0060] In this embodiment, it also includes an upper translation rotor assembly, a lower translation rotor assembly and a fixed rotor assembly. The fixed rotor assembly includes a rotor and a rotor drive shaft 18, and the output end of the aircraft power device is connected to the rotor through the rotor drive shaft 18. , used to control the rotor to rotate around itself; the upper output end of the aircraft power unit is used to connect the upper translation rotor assembly or the fixed rotor assembly, and the lower output end of the aircraft power unit is used to connect the lower translation rotor assembly or fixed rotor assembly , at least one upper translation rotor assembly or one lower translation rotor assembly is connected to the output end of the power device of the aircraft; in order to further improve its control accuracy, in this scheme, it...
Embodiment 3
[0061] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is further limited on the basis of Embodiment 1, such as Figure 18 to Figure 23 shown;
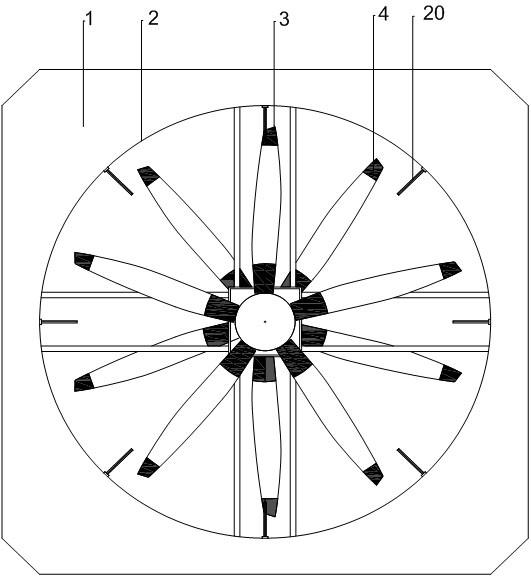
[0062] In the present embodiment, since the solution adopts fixed-pitch rotors and the rotational speed of the upper and lower rotors is the same, taking into account the needs of the aircraft heading control, it also includes a heading control wing 20 and a control wing servo 5, and the control wing servo 5 is provided in the overflow hole. 2. Outer side wall, the course control wing 20 is an airfoil with a biconvex symmetrical airfoil in section, the leading edge of the airfoil of the course control wing 20 faces the reverse direction of the rotor slip flow, and the airfoil of the course control wing 20 The direction of the trailing edge is the same as the direction of the rotor slipstream, the wing root of the heading control wing 20 is prefabricated with a rotating shaft that can change the angle of attack of the airfoil and fix the airfoil surface...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com