Determining the rising levels of circulating ketone bodies in a physiological fluid
A physiological fluid and level technology, applied in biological testing, blood characterization devices, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to provide users with sufficient and timely measurement results, and being impractical
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
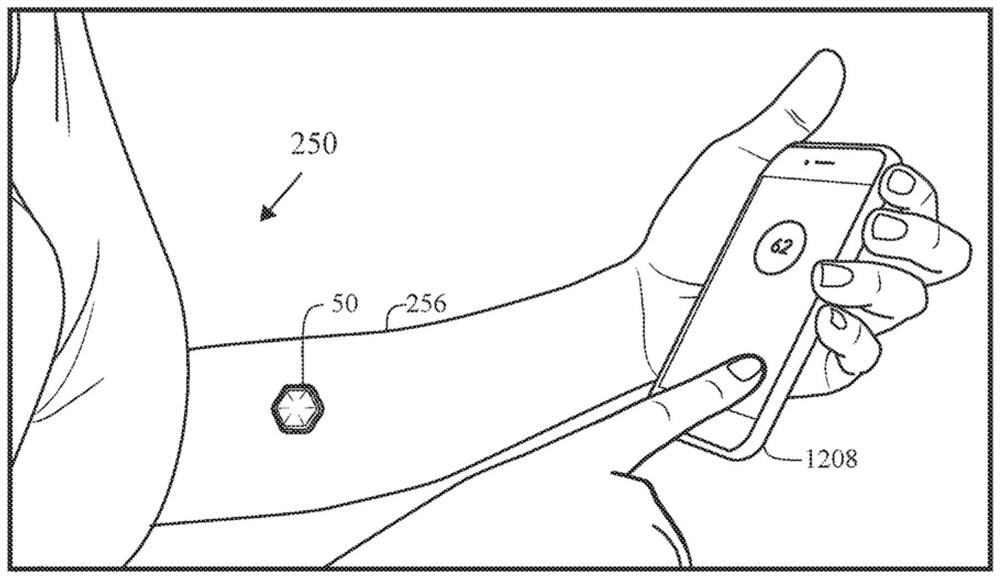
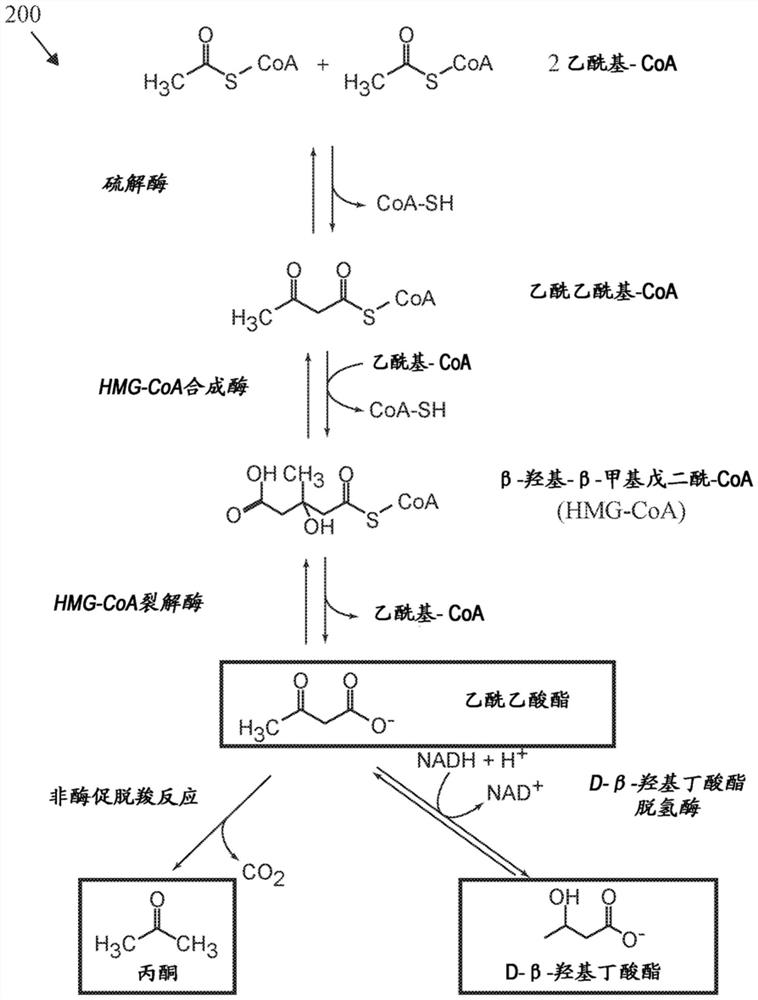
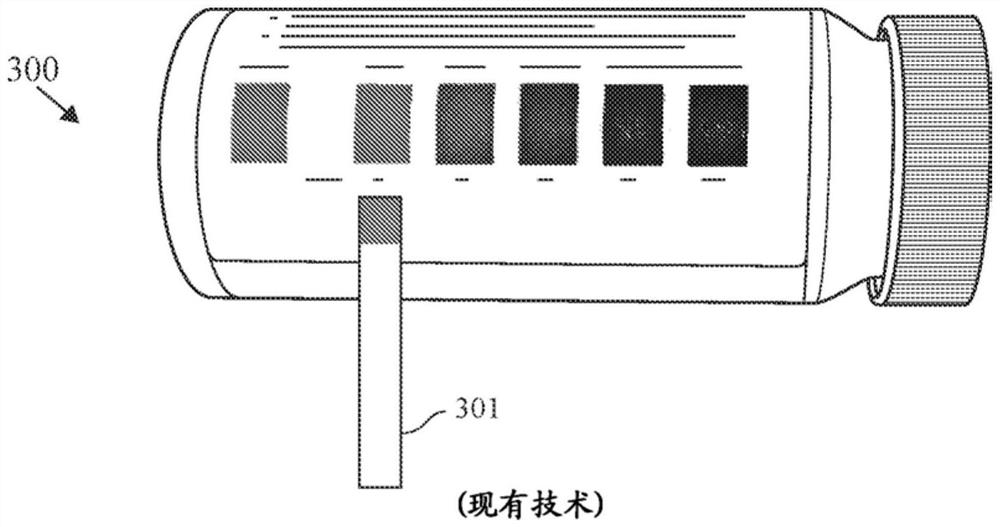
[0047] In healthy individuals, circulating ketone levels are typically well below 0.5 millimolar ("mM"). Slightly elevated ketone levels (i.e., between 0.5 and 1 mM) are usually a sign of ketosis, which often results from fasting or a low-carb diet as the liver clears its fat stores for energy. Healthy individuals are rarely at risk for ketoacidosis (>1 mM, resulting in acidification of the blood due to highly elevated levels of ketone bodies). A lack of insulin, which would otherwise allow glucose to enter cells to fuel them, causes the body to scavenge energy from free fatty acids in the liver, which causes an overproduction of ketone bodies and subsequent acidification of the blood, disrupting acid / base homeostasis. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening metabolic complication of diabetes with a mortality rate of 2-10%. DKA is typically manifested by prolonged hyperglycemia and overall poor blood glucose management, including inadequate insulin administration, i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com