Fine-grained image recognition algorithm for distributed labels based on inter-class similarity
An image recognition and similarity technology, which is applied in the field of fine-grained image recognition algorithms for distributed labels, can solve problems such as large visual differences in images and large image differences, and achieve the effect of avoiding over-fitting problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0046] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the embodiments.
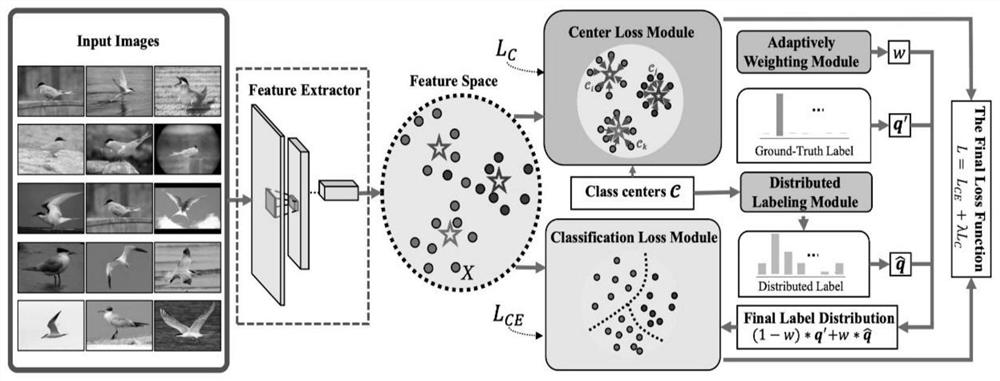
[0047] Such as figure 1 As shown, the fine-grained image recognition algorithm based on distributed labels between classes includes the following steps:
[0048](1) Use the backbone network to extract the feature representation X of the input image, and the extracted image feature representation is input to two parallel modules; the modules are a central loss module and a classification loss module;
[0049] Using the CUB200-2011 dataset, which is the most widely used image dataset in fine-grained recognition tasks, the full name is Caltech-UCSD Birds-200-2011, the dataset contains 200 categories of birds, a total of 11788 Image of bird. Usually the images of this data set are divided into 5994 training images (about 30 training images for each type of bird) and 5794 test images. In addition, in this data set, each picture contains a category label of a bird in an image, a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com