Method for efficiently producing levulinic acid from cellulose resources
A technology of levulinic acid and cellulose, applied in the field of biomass catalytic utilization, can solve the problems of difficult separation of levulinic acid and catalyst, uneconomical process route, and high production cost, and achieves low product separation cost, low price, and vaporization. low heat effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] (1) 1g cellulose microcrystal, 0.5g sulfuric acid and 5g acetic acid mass concentration are 90% acetic acid aqueous solution to mix;
[0026] (2) Heating to 100°C in a reactor equipped with a reflux device, and reacting for 30 hours;
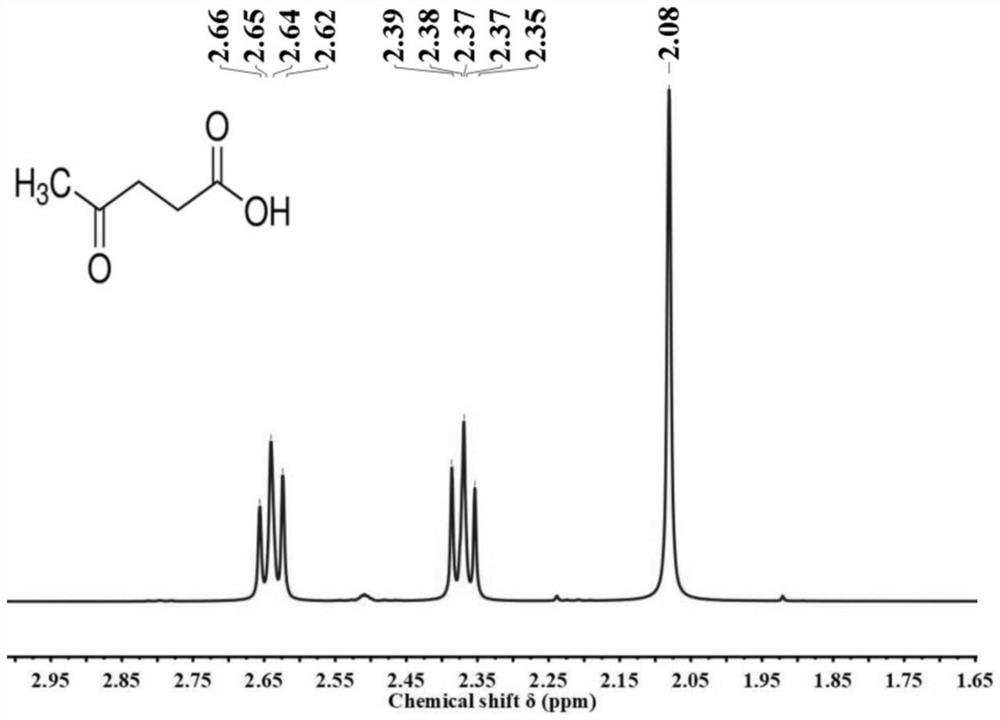
[0027] (3) after the reaction finishes, cool, filter, and filter to remove unreacted substances; add calcium hydroxide equal to sulfuric acid to neutralize the catalyzer in the filtrate, filter, and the filtrate is distilled under reduced pressure, and the solvent that distills out is recycled; Thick paste substance 0.8g, levulinic acid content is 83wt%, and levulinic acid structure is as follows figure 1 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0029] (1) Mix 1g of cellulose dry powder, 0.1g of silicotungstic acid and 2g of acetic acid;
[0030] (2) Heating to 120°C in a sealed reactor and reacting for 10 hours;
[0031] (3) After the reaction is finished, cool, filter, and filter to remove unreacted substances; add potassium hydroxide equivalent to silicotungstic acid to neutralize the catalyst in the filtrate, filter, and distill the filtrate at atmospheric pressure, and recycle the distilled solvent; distill to obtain The viscous pasty substance 0.8g, levulinic acid content is 80wt%.
Embodiment 3
[0033] (1) 1g cotton, 0.2g sulfuric acid and 6g acetic acid mass concentration are mixed with 80% acetic acid aqueous solution;
[0034] (2) Heating to 110°C in a reactor equipped with a reflux device, and reacting for 25 hours;
[0035] (3) after the reaction finishes, cool, filter, and filter to remove unreacted substances; add calcium hydroxide equal to sulfuric acid to neutralize the catalyzer in the filtrate, filter, and the filtrate is distilled under reduced pressure, and the solvent that distills out is recycled; Thick paste substance 0.8g, levulinic acid content 79wt%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com