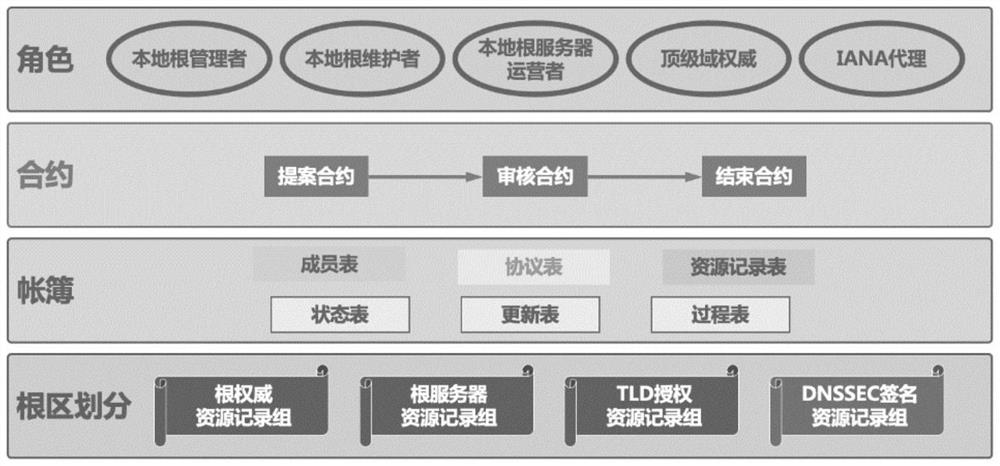
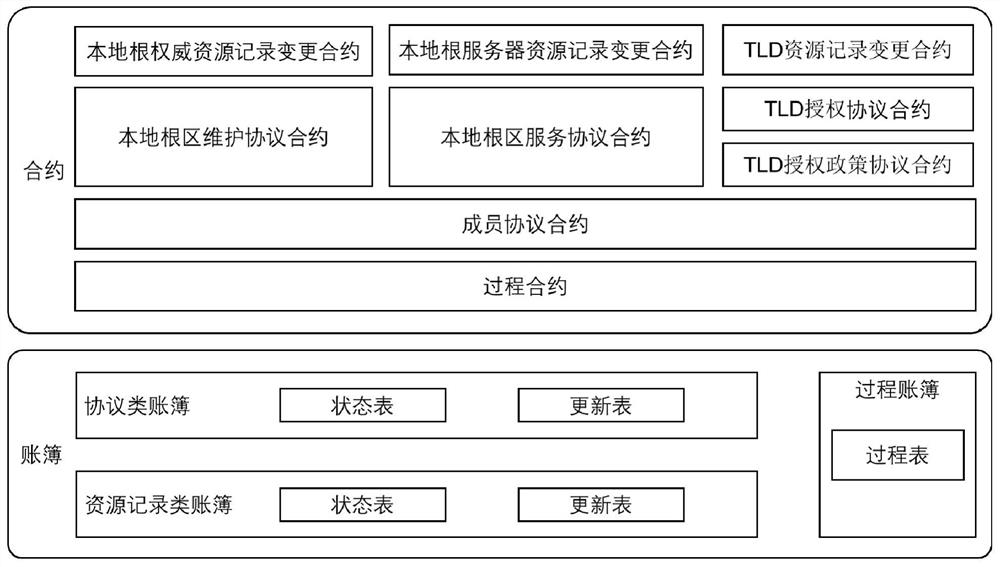
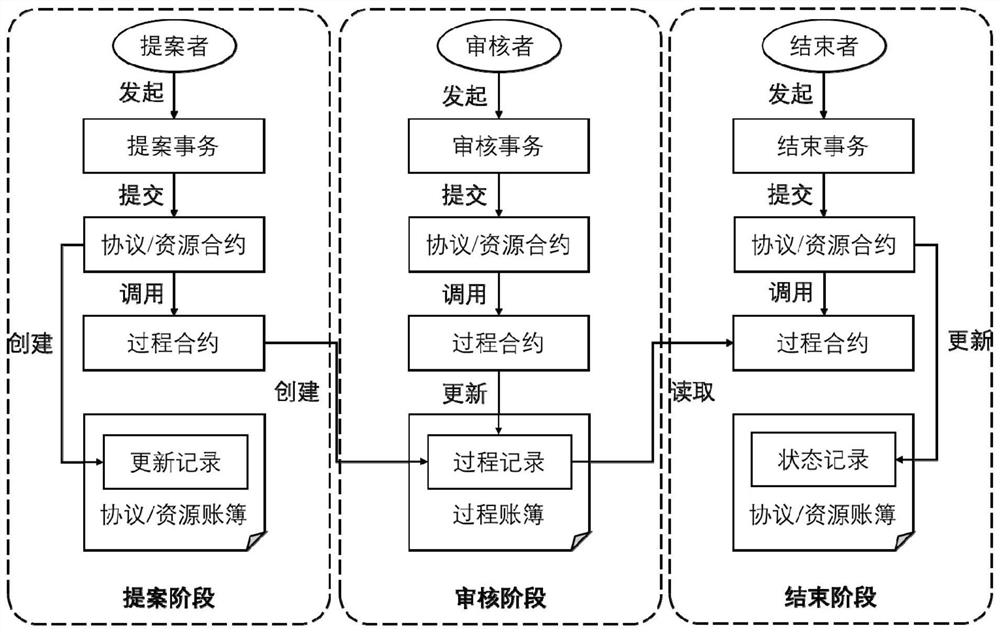
Intelligent contract system based on decentralized DNS root zone management
A smart contract, decentralized technology, applied in the Internet field, can solve problems such as malicious squatting, unclear governance subject, and namespace splitting.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0098] Example 1, join the local root member:
[0099] Background: The local root chain has been up and running, and currently only contains a local root member IANA proxy. In order to better promote the local root chain, more new local root members need to be added.
[0100] Scenario: The local root manager ORG_A applies to join the local root chain to participate in the establishment and governance of the local root chain; the authoritative organization ORG_B wants to join the local root chain to apply for top-level domain names; two companies mainly engaged in telecommunications business COM_A ((business scope: Local root operation)), COM_B (business scope: root server operation) also joined the local root chain to participate in the operation of the local root chain and root server system.
[0101] operate:
[0102] 1. The local root administrator ORG_A joins the local root chain: Proposal stage: ORG_A entrusts the IANA agent to submit a proposal for ORG_A to join the lo...
example 2
[0106] Example 2. Manage the local root zone:
[0107] Background: There are IANA proxy, local root manager ORG_A, authoritative organization ORG_B and two telecommunications companies COM_A and COM_B in the local root chain. Since the local root manager ORG_A lacks practical technical experience in the management of the local root zone, it seeks suitable partner institutions for cooperation.
[0108] Scenario: The local root manager ORG_A plans to reach a root server operation agreement with COM_A, a company mainly engaged in telecommunications business, and hand over the operation of the local root server to COM_A; ORG_A plans to reach a local root zone maintenance agreement with COM_B, another company mainly engaged in telecommunications business , the maintenance of the local root zone is handed over to COM_B.
[0109] operate:
[0110] 1. Formulation of the local root service agreement: Proposal stage: COM_A submits a proposal to participate in the operation of the loca...
example 3
[0114] Example 3. Register a top-level domain name:
[0115]Background: There are IANA proxy, local root manager ORG_A, authoritative organization ORG_B and two telecommunications companies COM_A and COM_B in the local root chain. There are currently no top-level domains registered on the local root chain.
[0116] Scenario: ORG_B applies to register the top-level domain CN. In line with the principle of ccTLD autonomy, ORG_A should decide whether to authorize CN to ORG_B. After ORG_B successfully registers the top-level domain, it plans to publish the first resource record (NS record) of CN on the local root chain.
[0117] operate:
[0118] 1. Formulation of TLD authorization policy agreement: Proposal stage: ORG_A submits a proposal to set the authorization policy of the top-level domain CN as "local root authorization". Review stage: The IANA agent submits the review transaction, and votes in favor of CN's authorization policy proposal within the transaction. Closing p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com