Stator and motor comprising same
A stator and stator tooth technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of uneven distribution of stator coil losses, low full rate of stator winding slots, and motor heating, etc., to achieve uniform distribution of conductor losses and improve Motor efficiency and the effect of improving the slot full rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
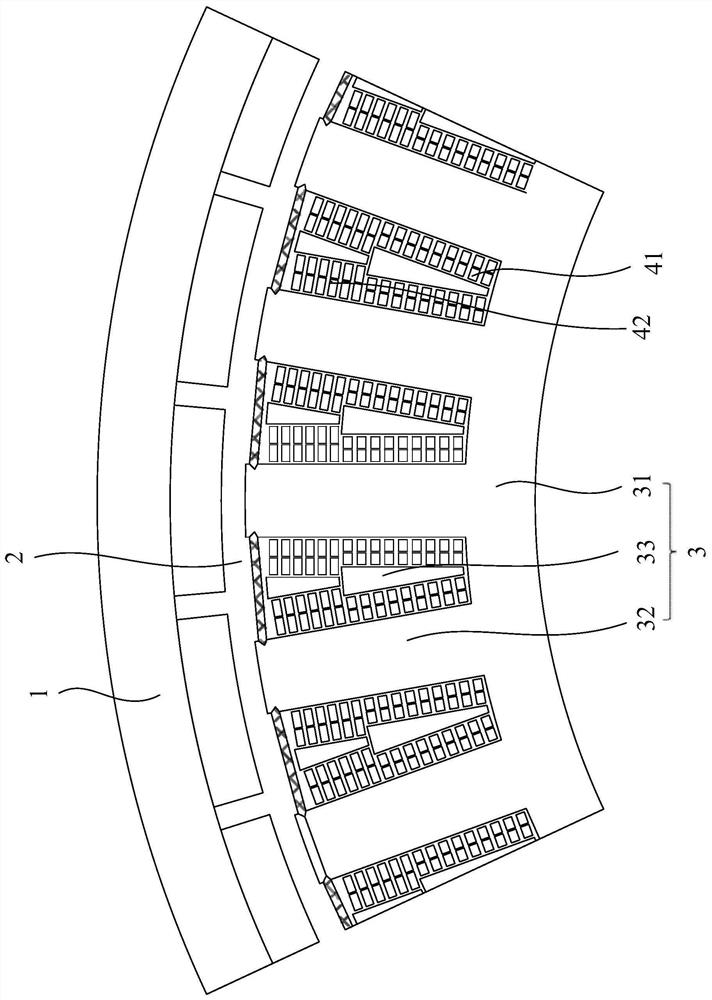
[0072] This embodiment provides a motor, including a stator and a rotor, and an air gap is formed between the stator and the rotor. Such as figure 1 As shown, in this embodiment, a motor with an inner stator and an outer rotor structure is taken as an example, and the rotor 1 is arranged radially outside the stator. In other alternative embodiments, the following stator structure is also applicable to a motor with an outer stator and an inner rotor. In this case, the rotor 1 is arranged on the radial inner side of the stator.
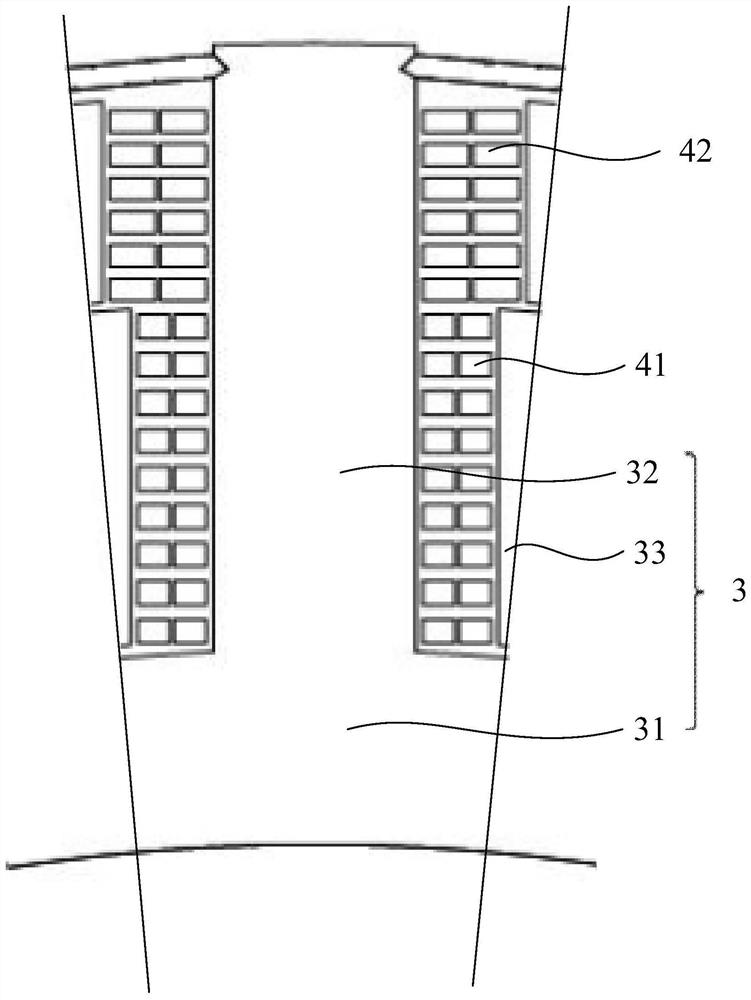
[0073] Such as Figure 1-2 As shown, the stator includes a stator core 3 and a stator winding. The stator core 3 is formed by stacking a plurality of tooth-shaped silicon steel sheets along the axial direction of the stator. The stator core 3 includes a stator yoke 31 and a plurality of stator teeth 32 arranged around the stator yoke 31. One end of the plurality of stator teeth 32 is connected to The stator yoke 31 is connected, and the other end of ...
Embodiment 2
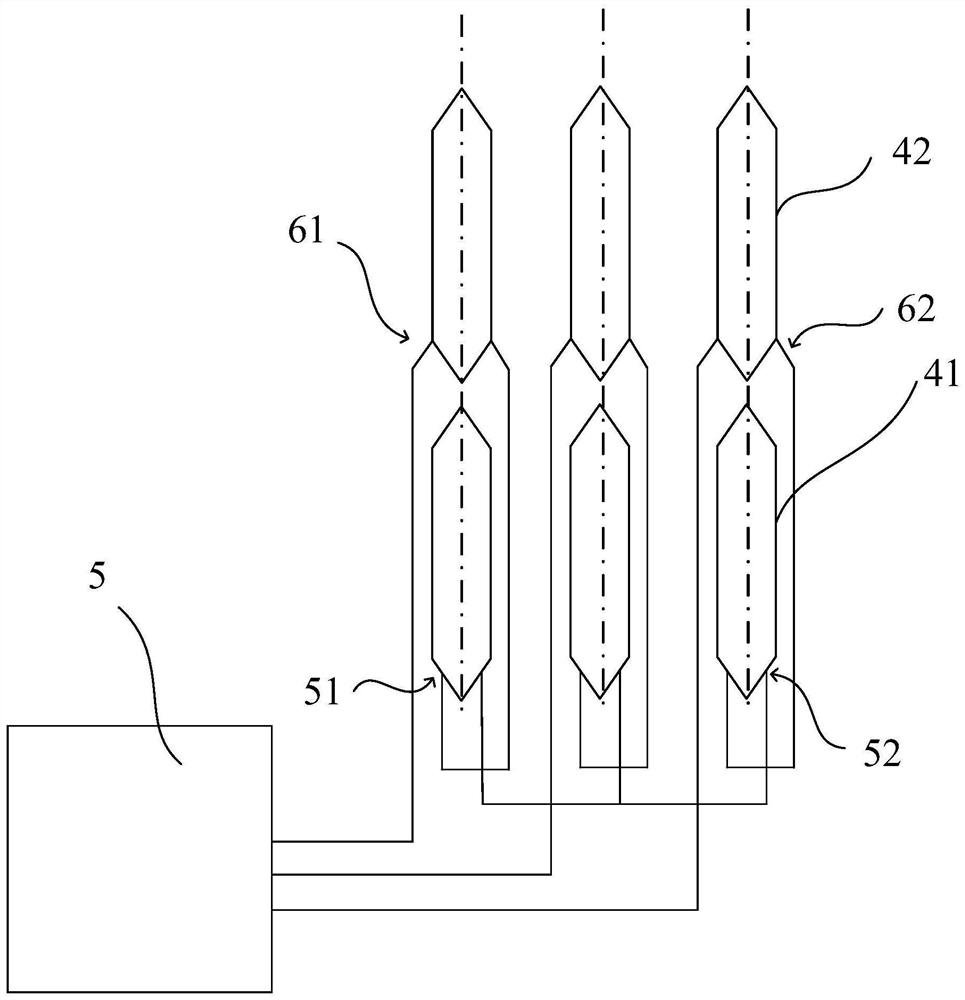
[0085] The structure of the motor in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, except that the difference between the first winding coil 41 and the second winding coil 42 is different.
[0086] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the coil diameters of the first winding coil 41 and the second winding coil 42 in this embodiment are the same, but the number of windings of the first winding coil 41 is smaller than the number of windings of the second winding coil 42, wherein , The number of parallel coils refers to the number of conductors that are simultaneously wound during the winding process of the winding coil, that is, the number of conductors of the winding coil in the circumferential direction of the stator. Specifically, in this embodiment, the number of parallel windings of the first winding coil 41 is 2, and the number of parallel windings of the second winding coil 42 is 3. In other alternative embodiments, the number of parallel windings of the first win...
Embodiment 3
[0091] The structure of the motor in this embodiment is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, except that the difference between the first winding coil 41 and the second winding coil 42 is different.
[0092] Such as Figure 5 As shown, the coil diameters of the first winding coil 41 and the second winding coil 42 in this embodiment are the same, but the resistivity of the first winding coil 41 is greater than that of the second winding coil 42 .
[0093] Since the leakage magnetic field formed by the harmonics in the air gap 2 will form a loop with the stator and the rotor 1, the second winding coil 42 closer to the air gap 2 is likely to be induced with more harmonic current, thus causing the second winding coil 42 has more conductor loss, which in turn causes uneven conductor loss of the first winding coil 41 and the second winding coil 42 . This embodiment reduces the conductor loss by reducing the resistivity of the second winding coil 42, the lower the resistivity...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com