Plant fiber-based controllable permeable material and preparation method thereof
A technology of plant fibers and water-permeable materials, applied in botany equipment and methods, fiber raw material processing, non-fibrous pulp addition, etc., can solve the problems of non-degradable water storage containers, uncontrollable irrigation rates, environmental pollution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
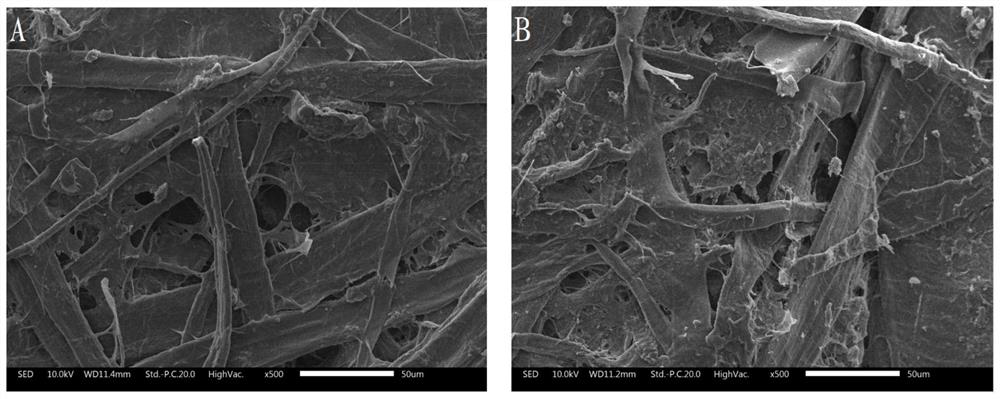
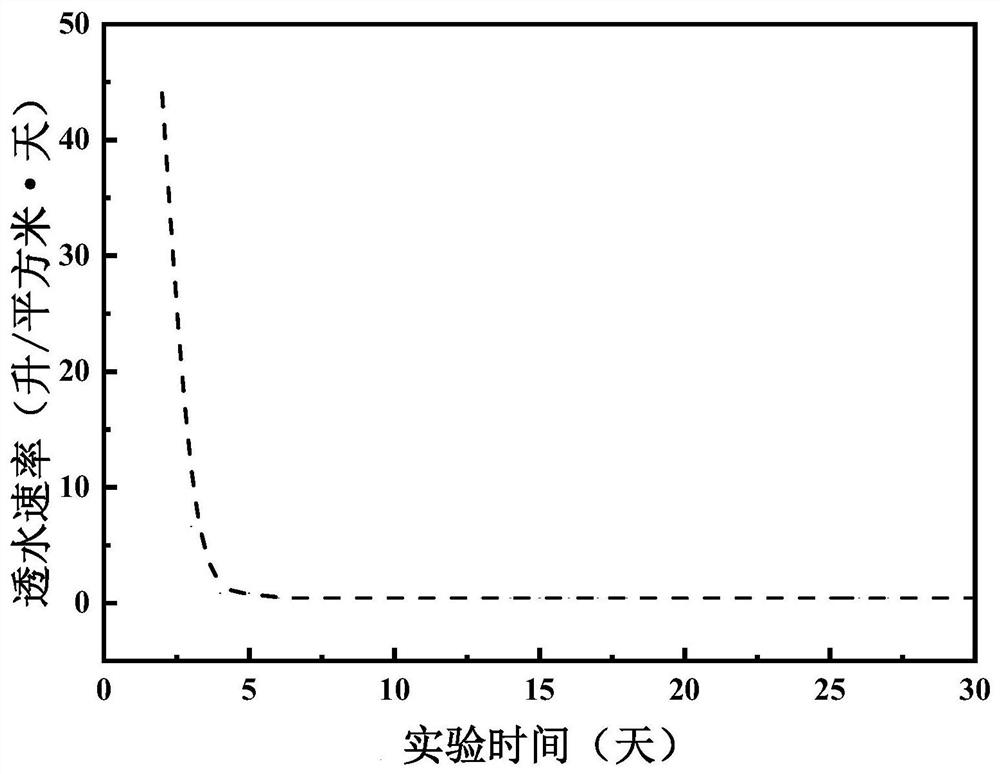
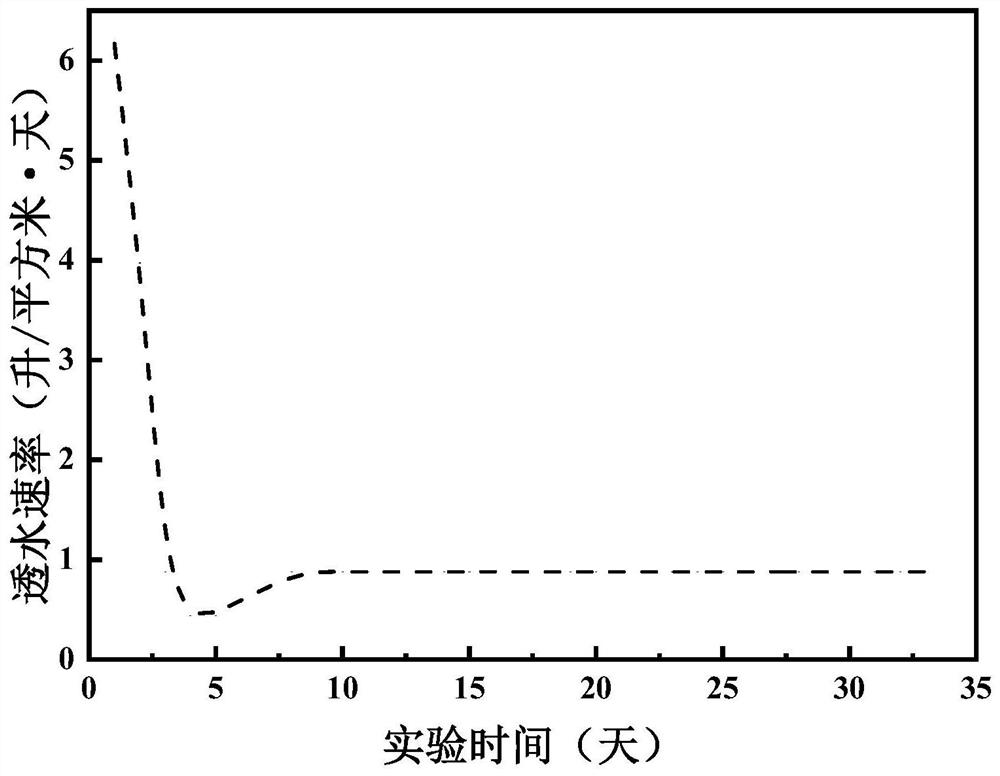
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] The embodiment of this application provides the first plant fiber-based controllable water-permeable material, and the specific preparation method is as follows:
[0074] Mix waste paper fiber slurry, polyamide polyamine-epichlorohydrin resin, carboxymethyl cellulose and styrene-acrylic acid ester, form it by wet method, and then dry it by hot pressing to obtain a controllable plant fiber base. Permeable material, labeled Sample 1.
[0075] Wherein, the addition of polyamide polyamine-epichlorohydrin resin is 1.5% of the dry pulp quality of waste paper fiber slurry; the addition of styrene-acrylate is 1.5% of the dry pulp quality of waste paper fiber slurry. 5%; the added amount of carboxymethyl cellulose is 0.5% of the weight of the dry pulp of waste paper fiber pulp. The beating degree of the waste paper fiber slurry is 30°SR, the drying method is hot-press drying, the drying temperature is 180°C, and the drying time is 20 minutes.
Embodiment 2
[0077] The embodiment of this application provides the second plant fiber-based controllable water-permeable material, and the specific preparation method is as follows:
[0078] Take agricultural straw fiber slurry, alkyl ketene dimer, styrene-acrylic ester and polyamide polyamine-epichlorohydrin resin, mix them, use wet papermaking to form paper, and then dry in an oven to obtain plant fiber base The controllable water-permeable material is marked as sample 2.
[0079] Wherein, the addition amount of polyamide polyamine-epichlorohydrin resin is 2% of the dry pulp mass of agricultural straw fiber slurry; the addition amount of alkyl ketene dimer is the dry pulp of agricultural straw fiber slurry 0.5% of the mass of the material; the addition of styrene-acrylate is 4% of the dry mass of the agricultural straw fiber slurry. The beating degree of the agricultural straw fiber slurry is 40°SR, the drying method is oven drying, the drying temperature is 160°C, and the drying time ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] The embodiment of this application provides the third plant fiber-based controllable water-permeable material, the specific preparation method is as follows:
[0082] The waste paper fiber slurry, urea-formaldehyde resin, cationic polyacrylamide and styrene-acrylate were mixed, formed by wet method, and then dried by hot pressing to obtain a plant fiber-based controllable water-permeable material, marked as sample 3.
[0083] Among them, the addition of urea-formaldehyde resin is 3% of the dry pulp mass of waste paper fiber pulp; the addition of styrene-acrylate is 15% of the dry pulp mass of waste paper fiber pulp; cationic polypropylene The amount of amide added is 1% of the dry pulp mass of the waste paper fiber pulp. The beating degree of the waste paper fiber slurry is 25°SR, the drying method is hot-press drying, the drying temperature is 140°C, and the drying time is 40 minutes.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com