Thermosensitive semiconductor ceramic material and preparation method thereof
A heat-sensitive semiconductor and ceramic material technology, applied in the field of heat-sensitive semiconductor ceramic materials and their preparation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] see Figure 1-6 As shown, the present embodiment is a heat-sensitive semiconductor ceramic material, comprising the following components in parts by weight:
[0044] 30 parts of copper oxide, 15 parts of ferric oxide, 8 parts of cobalt oxide, 8 parts of nickel oxide, 7 parts of mullite, and 3 parts of quartz sand.
[0045] A method for preparing a heat-sensitive semiconductor ceramic material, comprising the following steps:
[0046] Step 1: Pre-fire copper oxide, ferric oxide, cobalt oxide, nickel oxide, mullite, and quartz sand in a high-temperature sintering furnace, control the pre-fire temperature at 600°C, and control the pre-fire time for 2 hours, and then sinter The final product is mixed to obtain a mixed raw material;
[0047] Step 2: adding the mixed raw materials into a ball mill for wet ball milling, controlling the ratio of the mixed raw materials to water to 1:0.8, and controlling the ball milling time to 40 hours to obtain a mixed slurry;
[0048] Ste...
Embodiment 2
[0054] see Figure 1-6 As shown, the present embodiment is a heat-sensitive semiconductor ceramic material, comprising the following components in parts by weight:
[0055] 50 parts of copper oxide, 25 parts of ferric oxide, 12 parts of cobalt oxide, 12 parts of nickel oxide, 9 parts of mullite, and 7 parts of quartz sand.
[0056] A method for preparing a heat-sensitive semiconductor ceramic material, comprising the following steps:
[0057] Step 1: Pre-fire copper oxide, ferric oxide, cobalt oxide, nickel oxide, mullite, and quartz sand in a high-temperature sintering furnace, control the pre-fire temperature to 1200°C, control the pre-fire time for 4 hours, and then sinter The final product is mixed to obtain a mixed raw material;
[0058] Step 2: adding the mixed raw materials into a ball mill for wet ball milling, controlling the ratio of the mixed raw materials to water to 1:1.2, and controlling the ball milling time to 60 hours to obtain a mixed slurry;
[0059] Step...
Embodiment 3
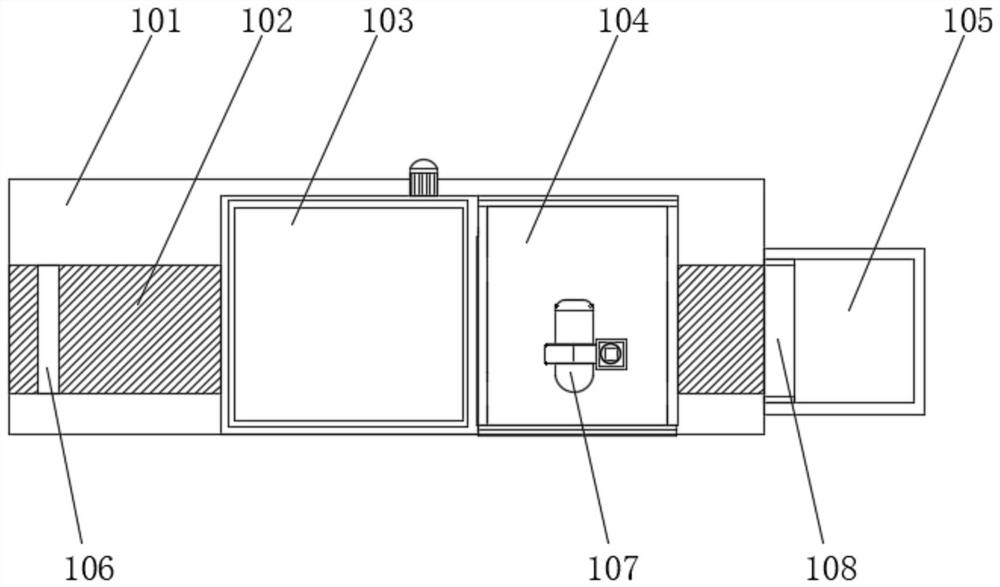
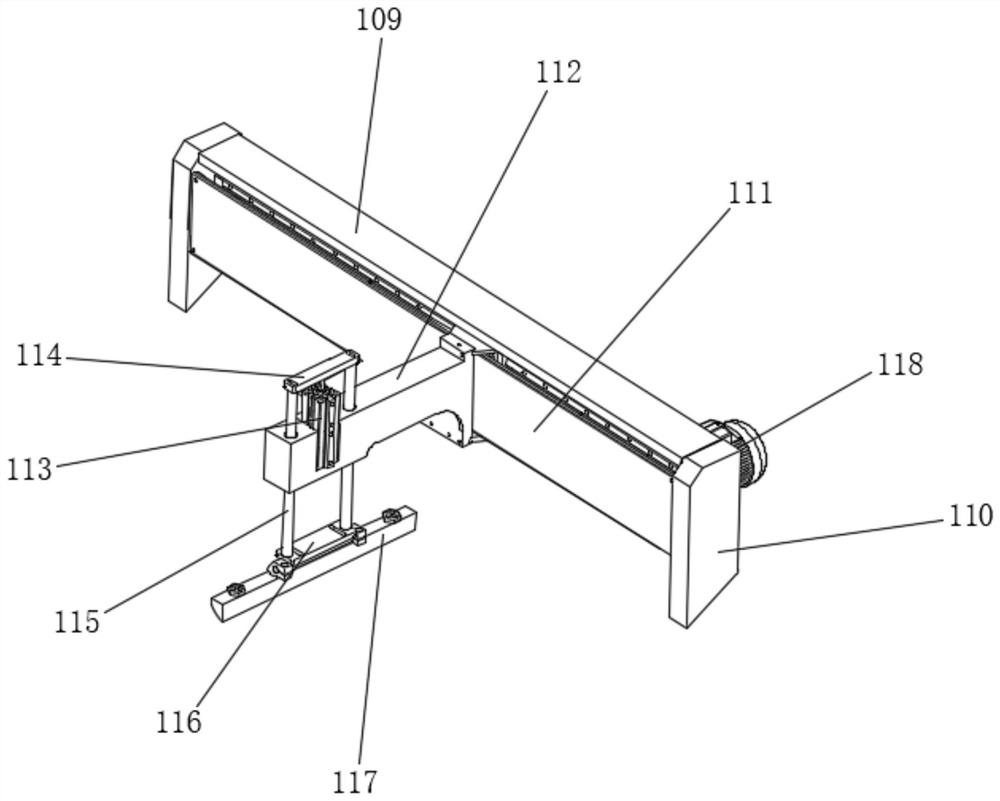
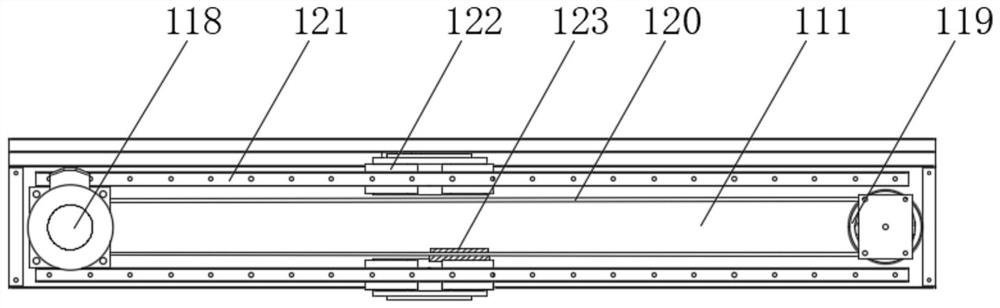
[0065] see Figure 1-6 As shown, the slurry drying equipment in this embodiment includes an installation base 101, a conveyor 102, a spreading box 103, a drying box 104, a storage box 105, a baffle plate 106, a blower 107, a scraping hopper 108, and an installation box 109, the top of the installation pedestal 101 is embedded with a conveyor 102, the top of the installation pedestal 101 is equipped with a material spreading box 103 and a drying box 104, and the material spreading box 103 and the drying box 104 are erected on the conveyor 102, the material spreading box 103 and the drying box 104 are connected;
[0066] Above one end of the conveyor 102 is provided with a material blocking plate 106, and the material blocking plate 106 is installed on the installation base 101, and a scraping hopper 108 is arranged below the other end of the conveyor 102, and the top of the scraping hopper 108 is On the conveyor belt of the abutting conveyor 102, the scraping hopper 108 is obl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com