Distributed direct two-way coupling method for earth surface and pipe network
A two-way coupling and distributed technology, applied in the sewer system, waterway system, special data processing applications, etc., can solve the problems that the surface and the pipe network are not suitable for areas with insufficient pipe network data, and there is no distinction between different functions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
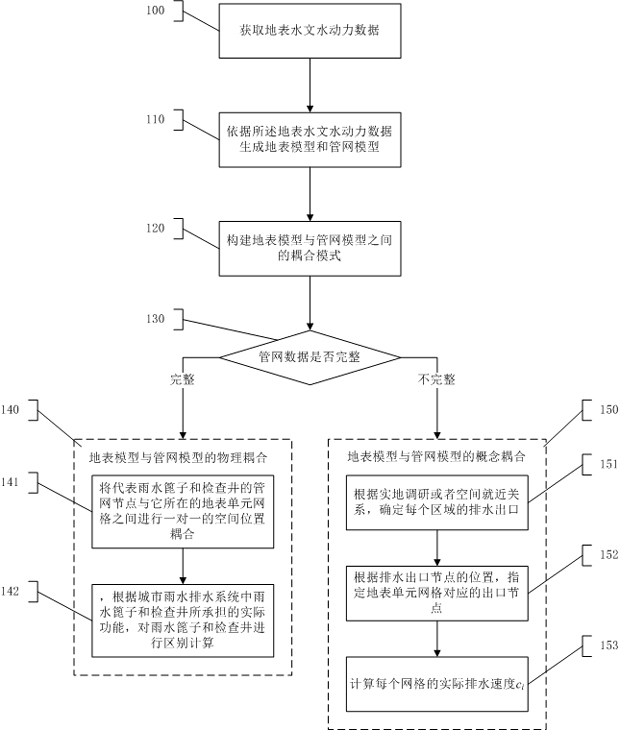
[0052] Such as figure 1 As shown, step 100 is executed to acquire surface hydrological and hydrodynamic data. The surface hydrological and hydrodynamic data include surface water depth, surface velocity, rainfall intensity, infiltration intensity, drainage intensity, frictional resistance, pipeline flow area, pipeline internal flow, pipeline internal velocity, water head and hydraulic radius.
[0053] Step 110 is executed to generate a surface model and a pipe network model according to the surface hydrological and hydrodynamic data. The surface model is a surface distributed hydrological and hydrodynamic model. Based on the distributed hydrological and hydrodynamic model of the surface, the rainfall production and confluence and surface water accumulation are all calculated based on the same surface grid, and the calculation formula is:
[0054]
[0055]
[0056]
[0057] in, is the partial differential sign, t it's time h is the water depth, u and v yes x ...
Embodiment 2
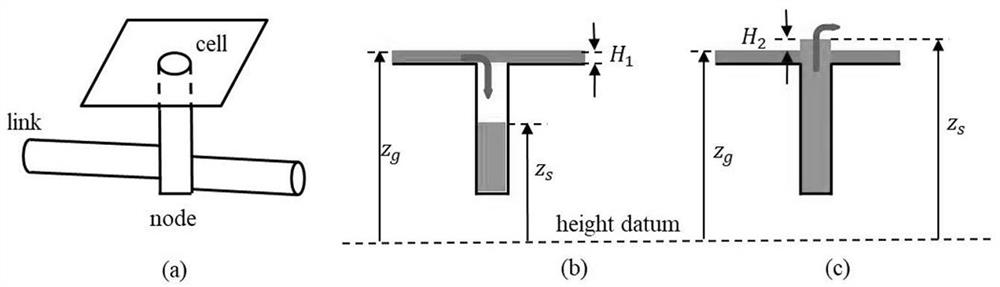
[0076] The present invention proposes a new direct two-way coupling mode, that is, the coupling mode of Rainfall-Overland-Sewer, hereinafter referred to as ROS mode. In this mode, the surface adopts a distributed hydrological and hydrodynamic model, and the rainfall directly acts on the surface grid, and the calculation of rainfall generation, confluence and water inundation is based on the unified surface grid, and the surface model and the pipe network model perform two-way coupling. This model conforms to the actual physical process of water accumulation caused by urban rainfall, so it can more reasonably simulate the surface flooding process caused by urban rainstorms.
[0077] In the ROS model, firstly, the surface model adopts a distributed hydrological and hydrodynamic model, as shown in formulas (1), (2) and (3). This is the basis for the direct two-way coupling between the surface model and the pipe network model. Based on the distributed hydrological and hydrodynam...
Embodiment 3
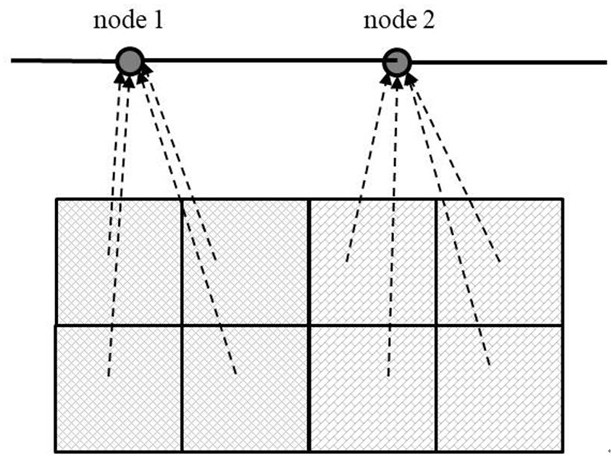
[0096] The distribution of the surface model and pipe network model of a certain urban area is shown as Figure 4 As shown, the pipe network data on the main road is detailed, the rainwater grates and inspection wells are classified and the connection relationship is clear and reliable. However, the internal pipe network data of the community other than the main road are missing. According to the existing pipe network data, the surface grid units on the main roads, and the rainwater grates and inspection wells of the drainage pipe network are constructed according to the positional relationship to establish a one-to-one physical coupling relationship. For the surface grid units of residential areas and buildings, the drainage outlets of the grid units are allocated according to the spatial proximity relationship, such as Figure 5 As shown, the number marked on each surface grid unit represents the drainage outlet of the unit grid, that is, the number of the inspection well. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com