Coking wastewater treatment method
A coking wastewater and treatment method technology, which is applied in special compound water treatment, multi-stage water treatment, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of human health hazards, degradation of biochemical properties, and wastewater that cannot meet national discharge standards, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
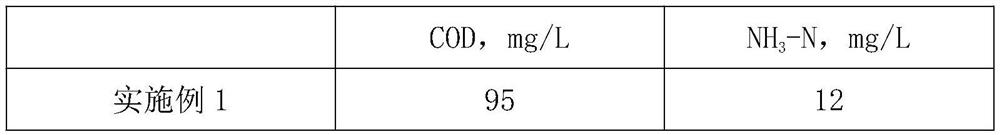
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Add a flocculant (magnesium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate with a molar ratio of 1:1) to the coking wastewater, the concentration of the flocculant is 30 mg / L, stir and mix well and let it stand for 8 hours to remove the flocs to obtain pretreated coking wastewater;
[0033] (2) After pretreatment, coking wastewater is inoculated with activated sludge (the volume ratio of coking wastewater and activated sludge is 5:1), and glucose, ammonium chloride, and dihydrogen phosphate are added according to the ratio of COD:N:P=100:5:1 Potassium is carried out stuffy exposure 12h, and the dissolved oxygen in the environment is controlled at 5mg / L during the process, and the supernatant is taken;
[0034] (3) The supernatant of step (2) is connected to direct current, with Ti-RuO 2 / IrO 2 As the anode material, the titanium plate is used as the cathode material, and iron plates are embedded at equal distances between the cathode and the anode to construct an elec...
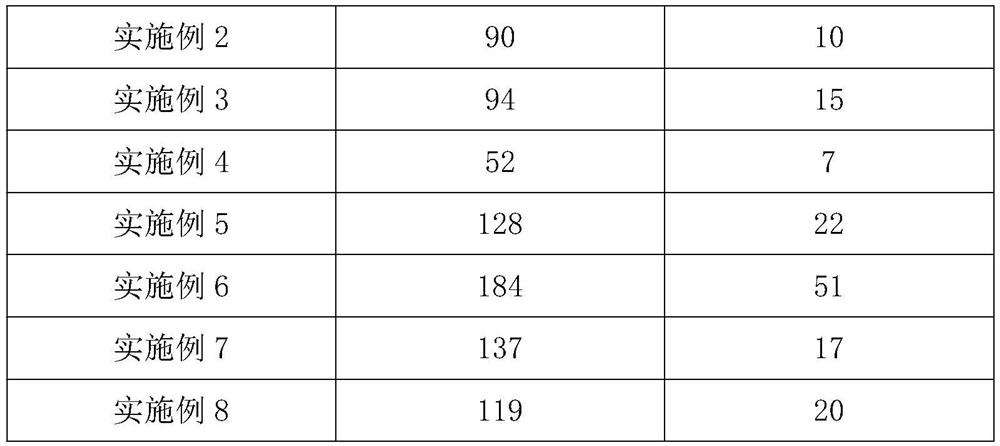
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Add a flocculant (magnesium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate with a molar ratio of 1:1) to the coking wastewater, the concentration of the flocculant is 20 mg / L, stir and mix well and let it stand for 12 hours to remove the flocs to get pretreated coking wastewater;
[0038] (2) After pretreatment, coking wastewater is inoculated with activated sludge (the volume ratio of coking wastewater and activated sludge is 5:1), and glucose, ammonium chloride, and dihydrogen phosphate are added according to the ratio of COD:N:P=100:5:1 Potassium was subjected to stuffy exposure for 12 hours, and the dissolved oxygen in the environment was controlled at 10mg / L during the process, and the supernatant was taken;
[0039] (3) The supernatant of step (2) is connected to direct current, with Ti-RuO 2 / IrO 2 As the anode material, the titanium plate is used as the cathode material, and iron plates are embedded at equal distances between the cathode and the anode to const...
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Add a flocculant (magnesium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate with a molar ratio of 1:1) to the coking wastewater, the concentration of the flocculant is 40 mg / L, stir and mix well and let it stand for 8 hours to remove the flocs to get pretreated coking wastewater;
[0043] (2) After pretreatment, coking wastewater is inoculated with activated sludge (the volume ratio of coking wastewater and activated sludge is 5:1), and glucose, ammonium chloride, and dihydrogen phosphate are added according to the ratio of COD:N:P=100:5:1 Potassium was exposed for 12 hours, and the dissolved oxygen in the environment was controlled at 8 mg / L during the process, and the supernatant was taken;
[0044] (3) The supernatant of step (2) is connected to direct current, with Ti-RuO 2 / IrO 2 As the anode material, the titanium plate is used as the cathode material, and iron plates are embedded at equal distances between the cathode and the anode to construct an electrochemica...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com