Cosmetic composition comprising rose stem cell-derived exosome as effective ingredient
A cosmetic composition and stem cell technology, applied in the direction of cosmetics, cosmetic preparations, dressing preparations, etc., can solve problems such as foreign body sensation, side effects, and short duration of action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Preparation of rose stem cells
[0045] According to the preparation and culture methods of plant stem cells known in the art, callus tissue is induced from rose embryos and / or leaves, and cells of the induced callus tissue are cultured. In addition, the callus with good growth state was selected and cultured in large quantities, so as to prepare the conditioned medium of rose stem cells.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: Preparation of exosomes derived from rose stem cells
[0047] The conditioned medium of rose stem cells prepared as described in Example 1 was purchased from BIO-FD&C Co., Ltd. (located in Incheon, Korea, and supplying conditioned medium of rose Damascena stem cells). Filter the conditioned medium of rose stem cells through a 0.22 µm filter to remove impurities such as cell debris, waste, and large particles. Rose stem cell-derived exosomes were isolated from filtered conditioned medium by tangential flow filtration (TFF).
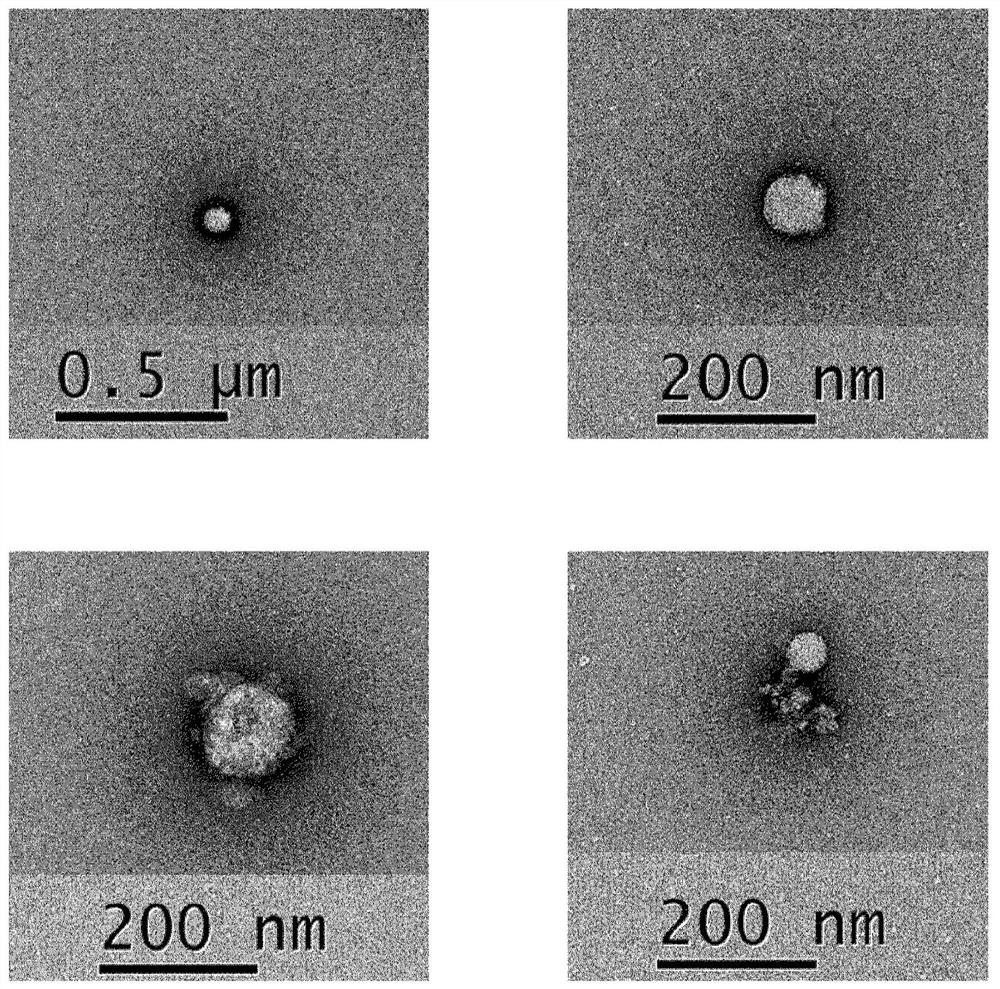
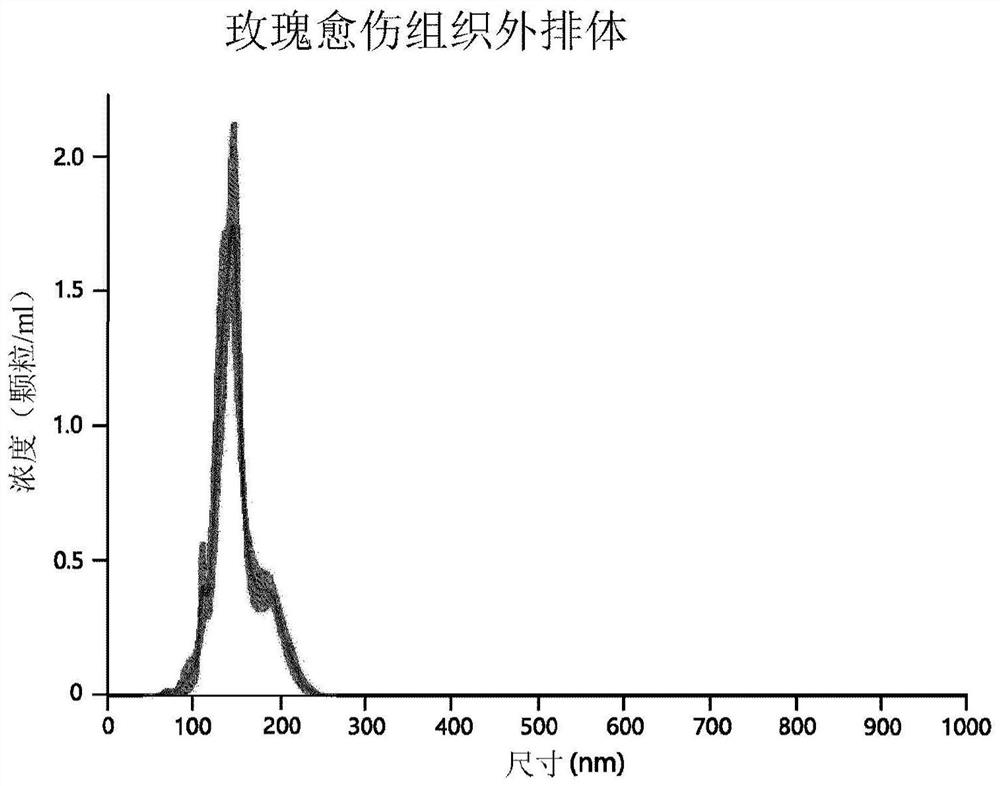
[0048] The size of isolated rose stem cell-derived exosomes was analyzed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). As shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B , isolated rose stem cell-derived exosomes were determined to be nano-sized vesicles. The size and concentration of rose stem cell-derived exosomes were analyzed by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) using NS300 (purchased from Malvern Panalytical) ( figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Evaluation of the delivery ability of rose stem cell-derived exosomes into dermal fibroblasts
[0050] In order to examine whether rose stem cell-derived exosomes would be delivered to human dermal fibroblasts (purchased from CEFO Co., Ltd.), the following analysis was performed. In order to fluorescently stain the membrane of rose stem cell-derived exosomes prepared in Example 2, the exosomes were reacted with PKH67 fluorescent dye (purchased from Sigma-Aldrich). After the reaction, the reaction solution was fractionated with a MW3000 column (purchased from ThermoFisher Scientific) to remove unstained free PHK67 in the exosome membrane. A negative control was prepared by reacting PKH67 fluorescent dye with buffer solution and fractionating the reaction product with a MW3000 column. Exosomes stained with PKH67 were incubated with pre-cultured human dermal fibroblasts, and fluorescence microscopy was then used to observe whether exosomes would be delivered in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com