Application of staphylococcus nepalensis to degradation of residual sugar in fermentation industrial organic wastewater
A staphylococcus, fermentation wastewater technology, applied in water pollutants, biological water/sewage treatment, heating water/sewage treatment, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
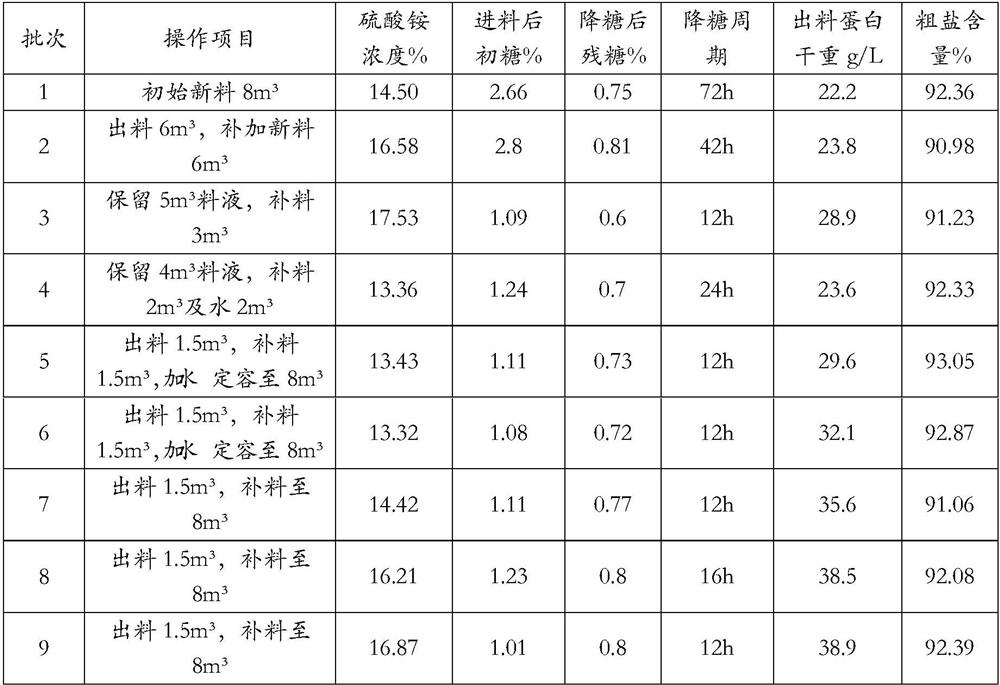
[0024] By adding high-salt-tolerant Staphylococcus nepalis to the high-salt fermentation wastewater treatment system, the purpose of rapidly degrading the residual sugar in the fermentation wastewater is achieved, and after the bacteria are removed by solid-liquid separation, the coarse salt contained in the fermentation wastewater is concentrated and recovered.
[0025] Get the glutamic acid wastewater containing 19.89% of salt (mass volume percentage, the same below), and the sugar content of 3.16% (mass volume percentage, the same below) into the fermenter, the initial pH is adjusted to 6.5 with ammonia water, and the fermentation temperature is 35°C , according to the amount of 1% (volume percentage, hereinafter the same) into Staphylococcus nepalese seed solution, after ventilating and culturing for 48 hours, its sugar content was reduced to 0.68% (mass volume percentage, hereinafter the same).
[0026] Adjust the pH of the fermentation broth to 3.5, heat it to 70°C, add 0...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The application of Staphylococcus nepalis in the rapid degradation of organic acid and / or amino acid fermentation to produce residual sugar in waste water under high-salt environment is as follows:
[0029] Take glutamic acid wastewater with a salt content of 14.91% and a sugar content of 2.75% and put it into a fermenter, adjust the initial pH to 5.0 with ammonia water, and ferment at a temperature of 33.5°C, insert Staphylococcus nepalese seed liquid at a ratio of 1%, and ventilate and cultivate After 33 hours, its sugar content dropped to 0.71%.
[0030] Adjust the pH of the fermentation broth to 3.8, heat it to 85°C, add 0.18‰ sodium polyacrylate, let it stand for 6 minutes, and separate the solid and liquid by plate and frame filter press, the dry weight of bacterial protein reaches 21.5g / L; Evaporation followed by fluidized bed drying at a drying temperature of 80°C to produce crude salt with an ammonium sulfate content of 9.53%.
Embodiment 3
[0032] The application of Staphylococcus nepalis in the rapid degradation of organic acid and / or amino acid fermentation to produce residual sugar in waste water under high-salt environment is as follows:
[0033] Take glutamic acid waste water with a salt content of 13.32% and a sugar content of 2.05% and put it into a fermenter, adjust the initial pH to 5.8 with ammonia water, and ferment at a temperature of 30°C, insert Staphylococcus nepalese seed liquid at a ratio of 1%, and ventilate and cultivate After 40 hours, its sugar content was reduced to 0.56%.
[0034] Through the solid-liquid separation of the disc centrifuge, after drying the bacteria, the dry weight reaches 28.7g / L, and the filtrate is firstly multi-effect evaporated, then dried in a fluidized bed at a drying temperature of 100°C, and the ammonium sulfate content is 92.06%. kosher salt.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com