Method and device for splitting homologous chromosomes of polyploid genome and application thereof
A homologous chromosome, polyploid technology, applied in genomics, sequence analysis, proteomics and other directions, can solve the problem of difficult to split homologous chromosomes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
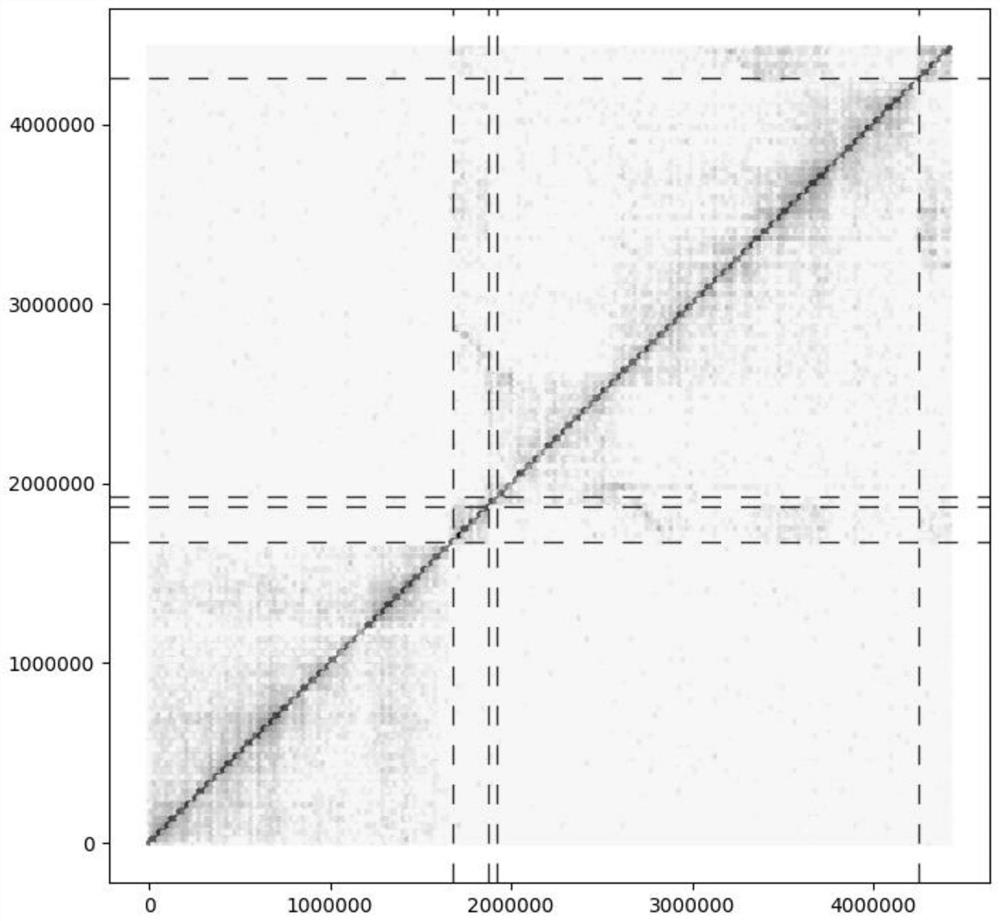
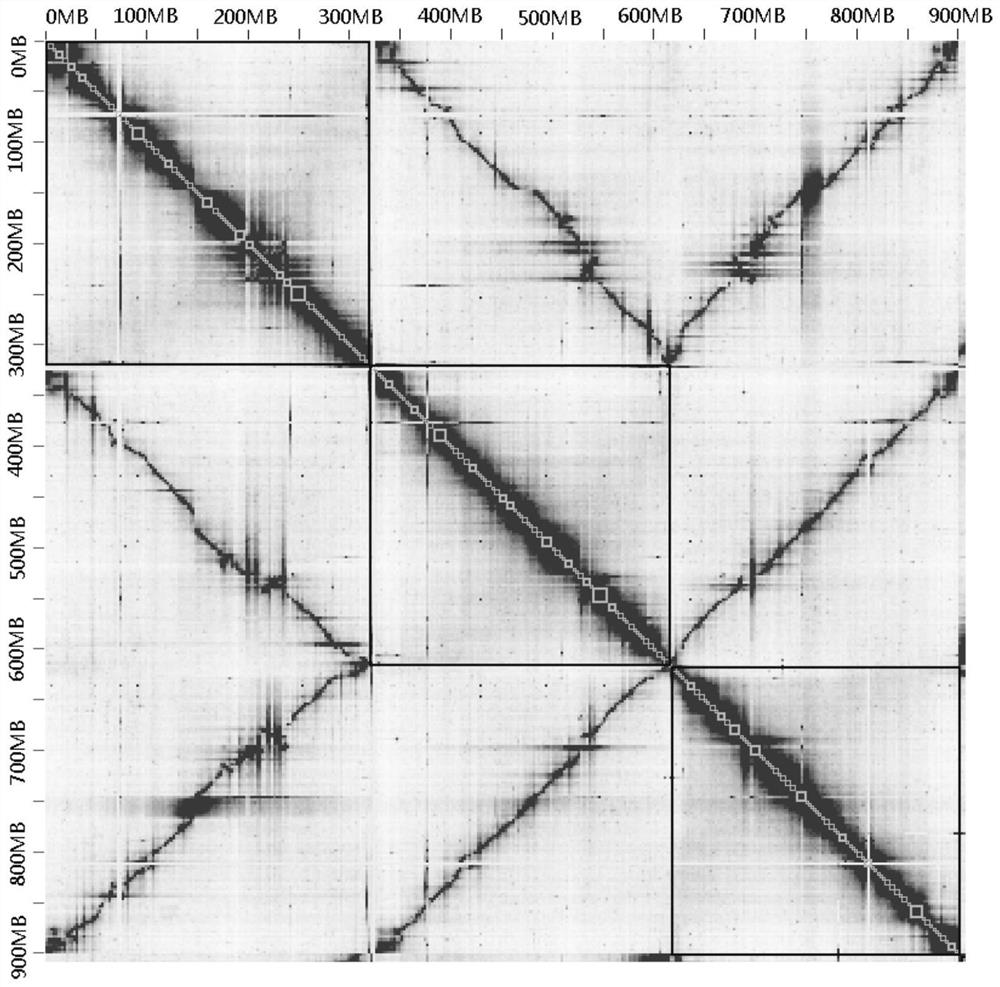
[0038] In a typical embodiment of the present application, a method for splitting homologous chromosomes in a polyploid genome is provided. The method comprises: according to the comparison file obtained by comparing the HiC data with the polyploid genome sequence, calculating the interaction strength between the genome contigs and within the contig; judging the accuracy of the corresponding contig connection according to the interaction strength within each contig, and Interrupt the wrongly connected contigs; compare all the contigs in the genome after the wrong connection is interrupted, and obtain the similarity between contigs; perform all contigs according to the interaction strength between contigs and the similarity between contigs Clustering, so as to realize the splitting of homologous chromosomes in polyploid genomes.
[0039] In this method, the wrongly connected contigs are identified through the interaction strength within the contigs, and interrupted at the wrong...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The above method provides a way to split the homologous chromosomes in the genome at the contig level, so that the genome assembly of polyploids can reach the chromosome level. Therefore, in the second typical embodiment of the present application, a method for assembling polyploid genome sequences is also provided. The method for assembling utilizes the above-mentioned method for splitting homologous chromosomes to separate homologous genomes at the contig level. The contigs of the chromosomes are clustered to split the contigs that belong to different classes (the different classes here refer to different homologous chromosomes); then sort the contigs in each class (that is, each homologous chromosome) and Orientation, so as to obtain the polyploid genome sequence at the chromosome level.
[0053] This method not only does not require the diploid close relatives of the target polyploid genome and its genome annotation files, but also recognizes the internal misassembl...
Embodiment 3
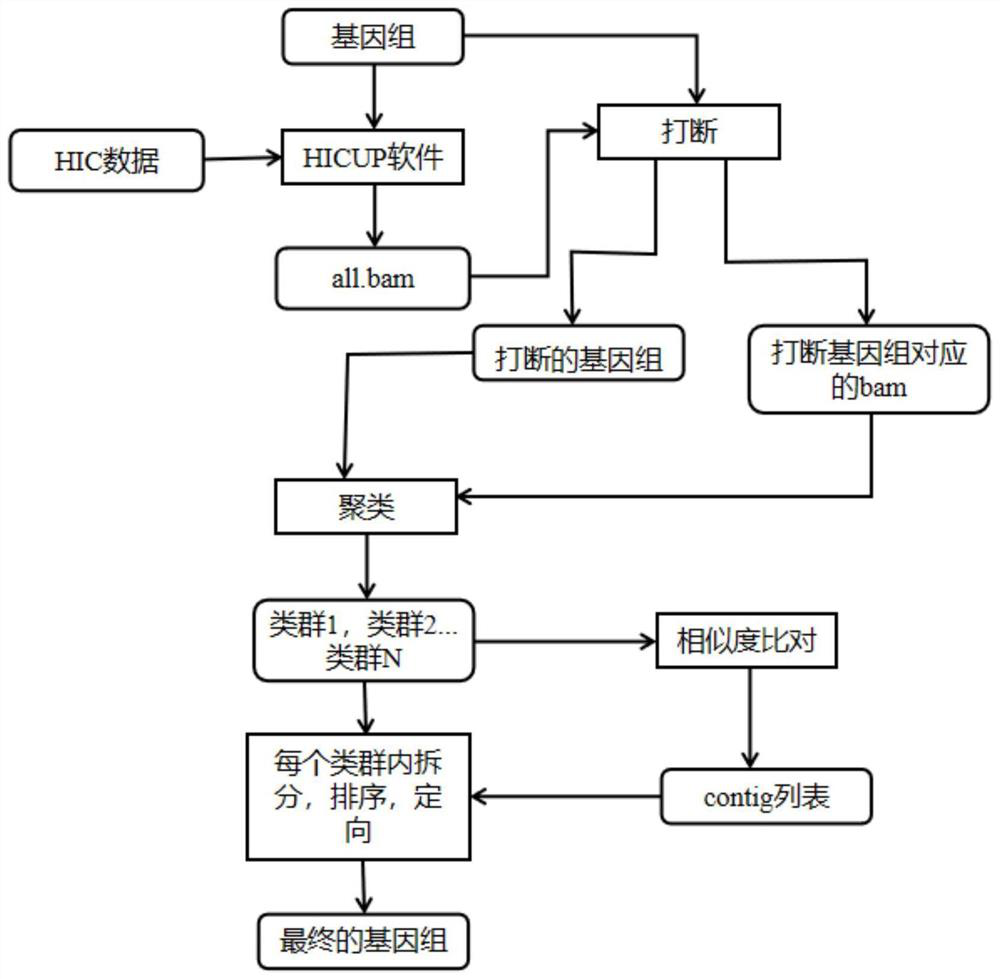
[0056] This embodiment provides a detailed method for assembling a polyploid genome sequence, the above specific process is as follows figure 1 (Rounded rectangles represent input / output, right-angled rectangles represent processing operations):
[0057] (1) Use the HICUP software to compare the HIC data with the polyploid genome, and obtain the comparison file all.bam (according to the comparison file, the interaction strength within the contig and the interaction strength between contigs can be calculated).
[0058] (2) According to the comparison file all.bam, calculate the HIC interaction strength in the contig, and interrupt the contig that is obviously connected incorrectly in the polyploid genome ratio file (interrupt the genome and correct the wrongly connected contig), Get the genome after contig interruption and the corresponding bam file.
[0059](3) Combining the files obtained in step (2), cluster the contig at the level of non-homologous chromosomes (the cluster...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com