Method for reducing base number of pests in rice field by using entomopathogenic nematodes
A technology of entomopathogenic nematodes and application methods, applied in the field of using entomopathogenic nematodes to reduce the base number of rice field pests, can solve problems such as no control effect, reduce labor costs and material costs, and achieve simple and easy-to-operate application processes and realize the use of pesticides Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
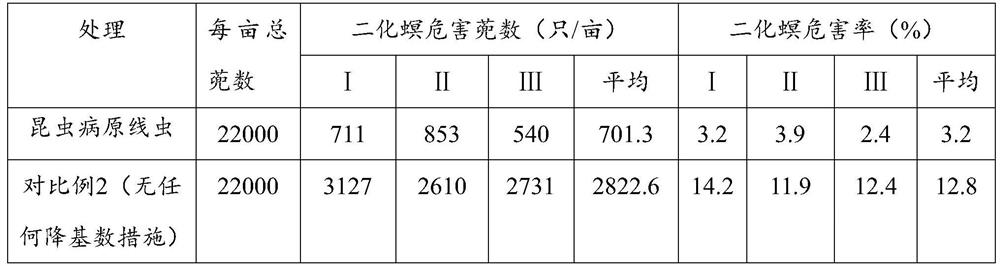
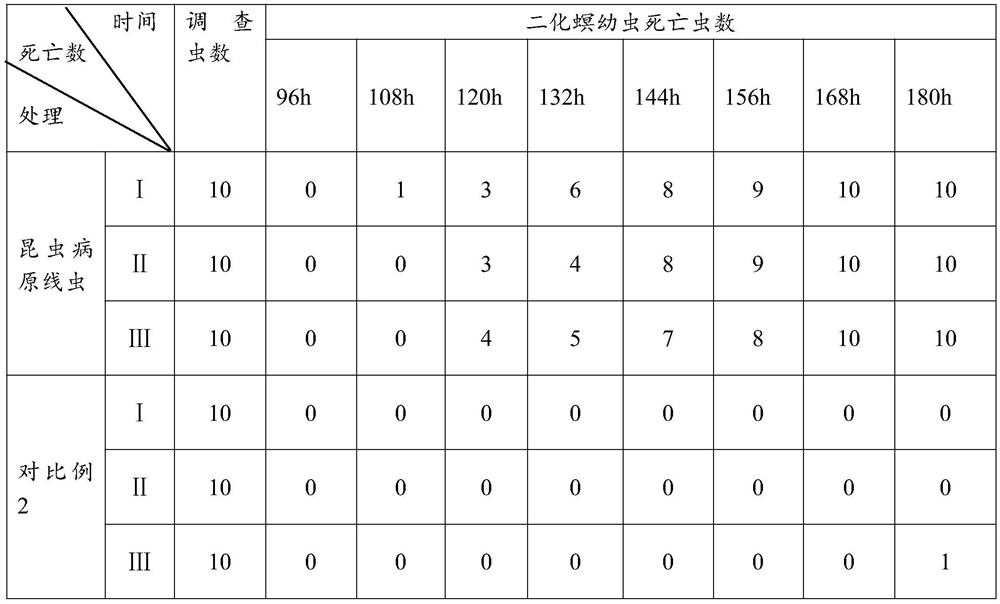
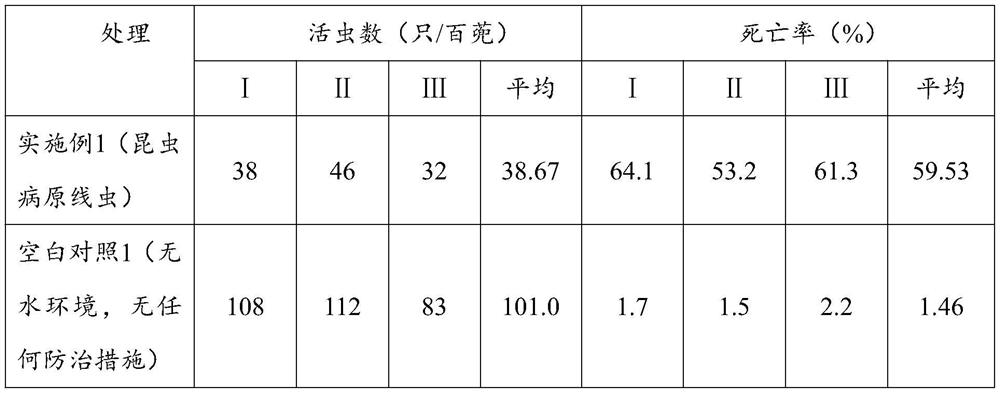
[0044] From October 2019 to July 2020, experiments were carried out in 80 mu of rice fields in Lingling District, Yongzhou City, Hunan Province.
[0045] 1. When the first season rice (late rice in 2019) is harvested, the rice is harvested with low piles, and the height of the rice piles is 10cm;
[0046] 2. Irrigate the harvested paddy fields so that the depth of the water layer in the paddy fields reaches 1cm, so that the soil in the paddy fields becomes moist; at the same time as the irrigation, add entomopathogenic nematodes to the water inlet for irrigation, and the application rate is 20 million / mu. The average air temperature within 3 days after application of entomopathogenic nematodes is not lower than 25°C;
[0047] 3. Before transplanting the current season rice (early rice in 2020), apply the entomopathogenic nematode for the second time after plowing the field. The application method and application amount are the same as step 2. The average temperature within 3 d...
Embodiment 2
[0051] From October 2019 to July 2020, experiments were carried out in 50 mu of rice fields in Oujiangcha Town, Heshan District, Yiyang City.
[0052] 1. When the first season rice (late rice in 2019) is harvested, the rice is harvested with low piles, and the height of the rice piles is 10cm;
[0053] 2. Spray entomopathogenic nematodes in the harvested paddy fields that have just had light rain, and the spraying rate is 30 million / mu. The average air temperature within 3 days after application of entomopathogenic nematodes is not lower than 25°C;
[0054] 3. Before transplanting the current season rice (early rice in 2020), apply the entomopathogenic nematode for the second time after plowing the field. The application method and application amount are the same as step 2. The average temperature within 3 days after applying the entomopathogenic nematode is not low at 25°C;
[0055] 4. After the rice is transplanted in the current season, if insect damage occurs at the seed...
Embodiment 3
[0058] From October 2019 to July 2020, experiments were carried out in 50 mu of rice fields in Longtan Town, Lukou District, Zhuzhou City.
[0059] 1. When the first season rice (late rice in 2019) is harvested, the rice is harvested with low piles, and the height of the rice piles is 10cm;
[0060] 2. Irrigate the harvested paddy field to make the water layer depth of the paddy field reach 1cm, so that the soil of the paddy field becomes moist; at the same time of irrigation, add entomopathogenic nematodes to the water inlet for irrigation, and the application rate is 25 million / mu. The average air temperature within 3 days after application of entomopathogenic nematodes is not lower than 25°C;
[0061] 3. Before transplanting the current season rice (early rice in 2020), apply the entomopathogenic nematode for the second time after plowing the field. The application method and application amount are the same as step 2. The average temperature within 3 days after applying t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com