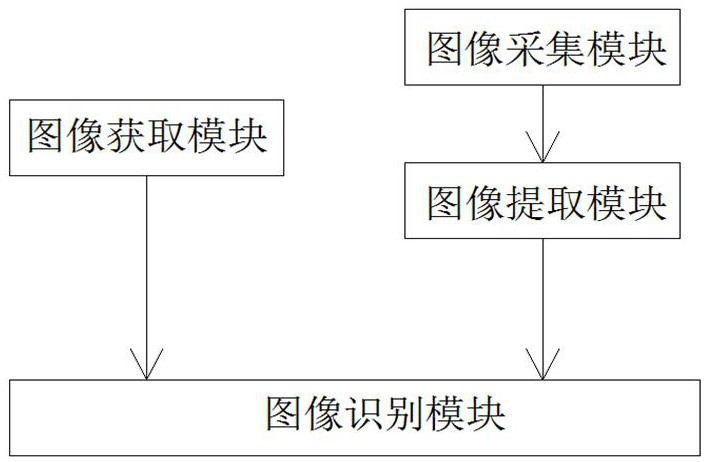
Method and device for identifying brain region position of fresh and live in-vitro tissue
An in vitro, fresh technology, applied in the field of neuroscience research experiments, can solve problems such as large errors, time-consuming and laborious, and researchers' troubles, so as to avoid differences between individuals, improve accurate identification, and improve accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] In order to make the technical problems, technical solutions and advantages to be solved by the present invention clearer, the following will describe in detail with reference to the drawings and specific embodiments.
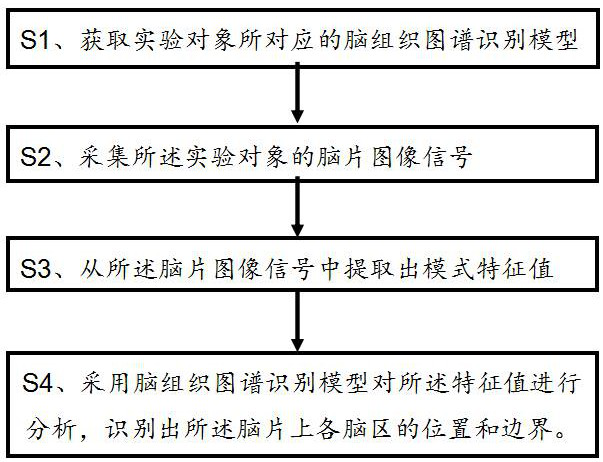
[0032] like figure 1 As shown, a method for identifying the brain region of a fresh isolated brain tissue comprises the following steps:
[0033] S1. According to the experimental subject from which the fresh isolated brain tissue comes from, obtain the brain tissue atlas recognition model corresponding to the experimental subject from the brain atlas model library.
[0034] S1-1. Pre-establishment of the brain atlas model library; the brain atlas model library includes brain tissue atlas recognition models corresponding to animals of different ages and genders;
[0035] S1-2. Acquiring the brain tissue atlas recognition model corresponding to the age group of the subject to which the fresh isolated brain tissue belongs.
[0036] Wherein, the pre-estab...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com