A low-power-consumption sun capture and directional attitude control method for magnetically controlled small satellites
A technology of attitude control and low power consumption, which is applied in the directions of space navigation equipment, space navigation aircraft, space navigation aircraft guidance devices, etc. problems such as small level, to achieve the effect of ensuring high-efficiency charging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
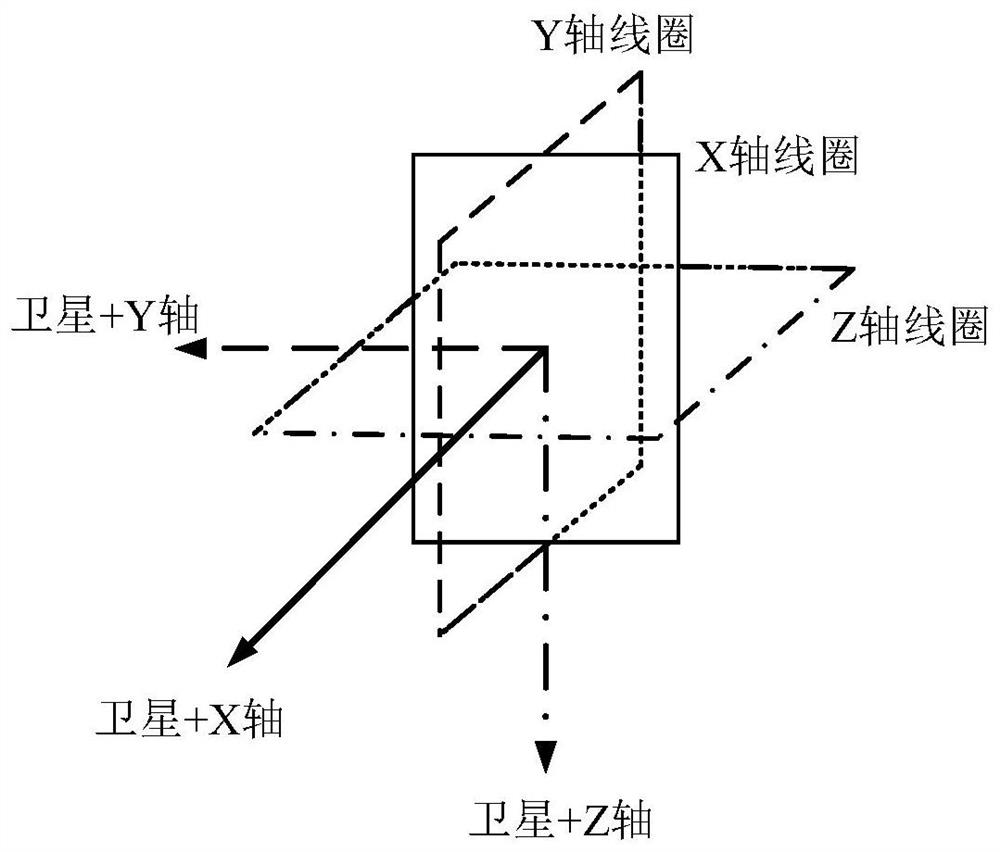
[0027] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figure 1 to Figure 5 To illustrate this embodiment, for a small satellite with a hexahedral configuration, it is equipped with a 0-1 solar sensor on each surface, and six 0-1 solar sensors cover the entire sky; a digital solar sensor is configured and installed On the largest sun-facing surface of the satellite; configure a magnetometer; configure a set of MEMS gyroscopes for measuring the satellite's three-axis attitude angular velocity information; configure a set of magnetic coils that can control the satellite's three axes.
[0028] A low-power-consumption sun capture and directional attitude control method for a magnetron satellite, the method is realized by the following steps:
[0029] Step 1: Obtain the magnetic field strength vector and attitude angular velocity vector under the star system according to the measurement information of the magnetometer and MEMS gyroscope;
[0030] Step 2: According to whether the sun ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0038] Specific embodiment two, combine Figure 1 to Figure 5 This embodiment is described. This embodiment is an embodiment of the method for capturing the sun with low power consumption and directional attitude control of a magnetron satellite described in Embodiment 1. The specific process is as follows:
[0039] Step 1: According to the measurement information of the magnetometer at the current moment, through the transformation of the magnetometer installation matrix, the magnetic field intensity vector at the current moment under the star system is obtained According to the measurement information of the MEMS gyroscope at the current moment, through the transformation of the MEMS gyroscope installation matrix, the attitude angular velocity vector of the star system relative to the inertial system at the current moment is obtained
[0040] Step 2: According to the current moment sun direction information obtained by the 0-1 sun sensor measurement, according to the pres...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0056] Specific implementation mode three, this implementation mode is the embodiment of specific implementation mode two:
[0057] In this implementation, a certain type of magnetically controlled small satellite is taken as an example, and its moment of inertia matrix is as follows:
[0058]
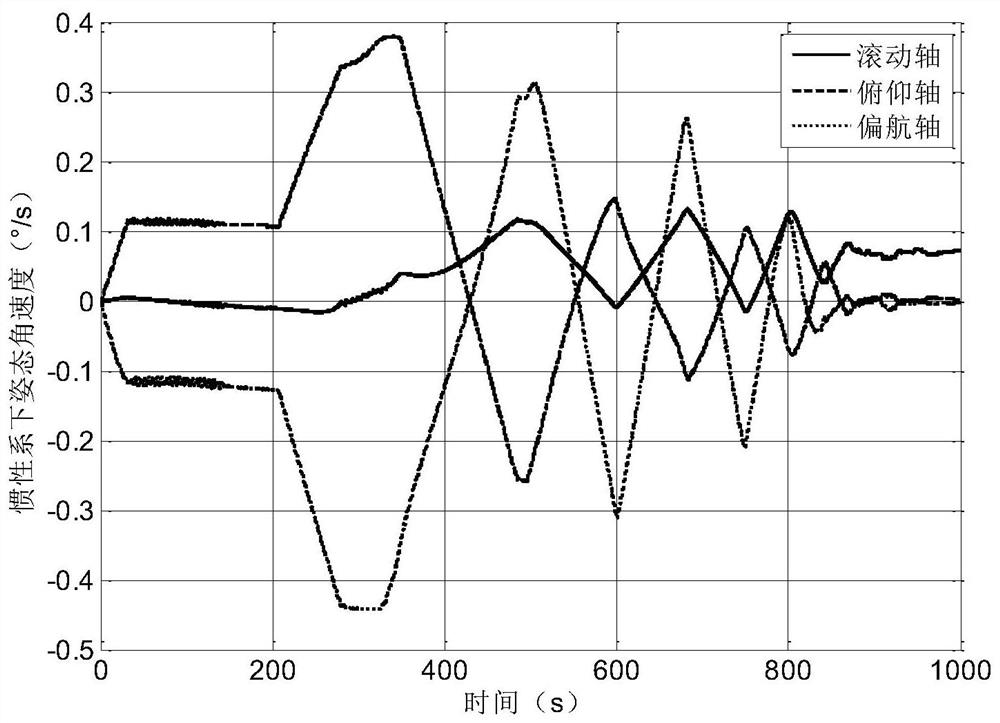
[0059] Set the maximum magnetic moment of the magnetic coil to 7Am 2 , and the attitude angular velocity at the initial moment of the simulation is [0,0,0]° / s. At the initial moment of the simulation, the sun is visible on the -Z and -Y planes of the satellite. During the sun-seeking and sun-aligning process of the satellite’s largest sail surface, the attitude angular velocity, magnetic control torque and output angle change curve of the digital sun sensor in the inertial system are as follows: image 3 , Figure 4 with Figure 5 shown. In the simulation time of about 207.5s, the satellite can rotate around the +Y axis and the -Z axis according to the set attitude angular ve...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com