Including transactional commit timestamps in the primary keys of relational databases
A timestamp, database technology applied in the primary key of a relational database that includes the transaction commit timestamp field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
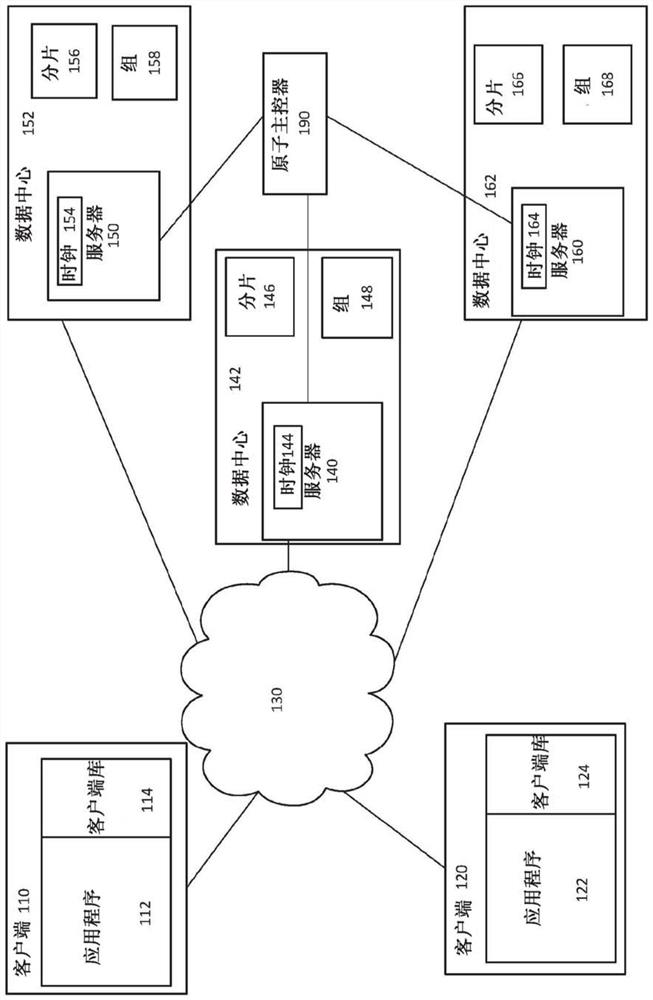
[0023] The technique generally involves a method of determining a commit timestamp and providing the commit timestamp to users of the distributed database. For example, a user can use commit timestamps to view snapshots of the database at various points in time, or build a transaction log for changes made to the database. In order to provide users with meaningful commit timestamps, each transaction for the same data item must correspond to a unique commit timestamp. This way, users can use these commit timestamps to read different versions of the data at different specific timestamps, or to see all changes made to a data item. Additionally, efficient methods for determining meaningful commit timestamps are provided to ensure that the throughput of the database is not compromised.
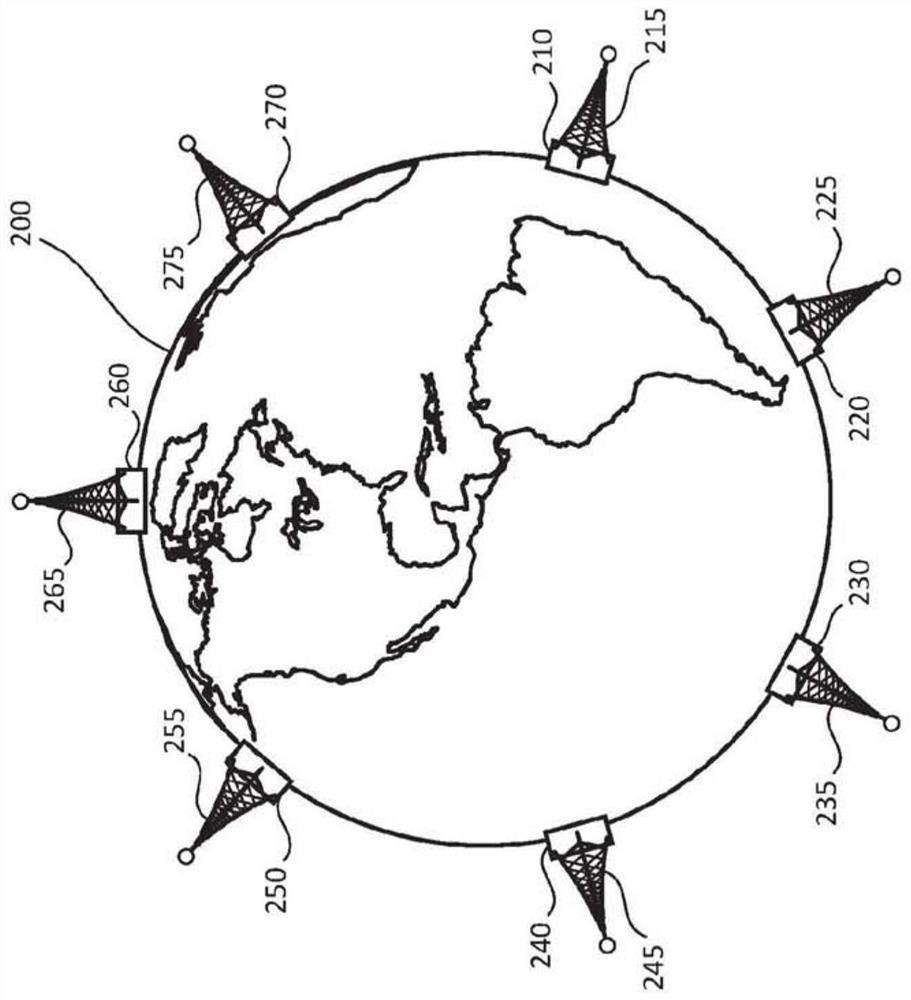
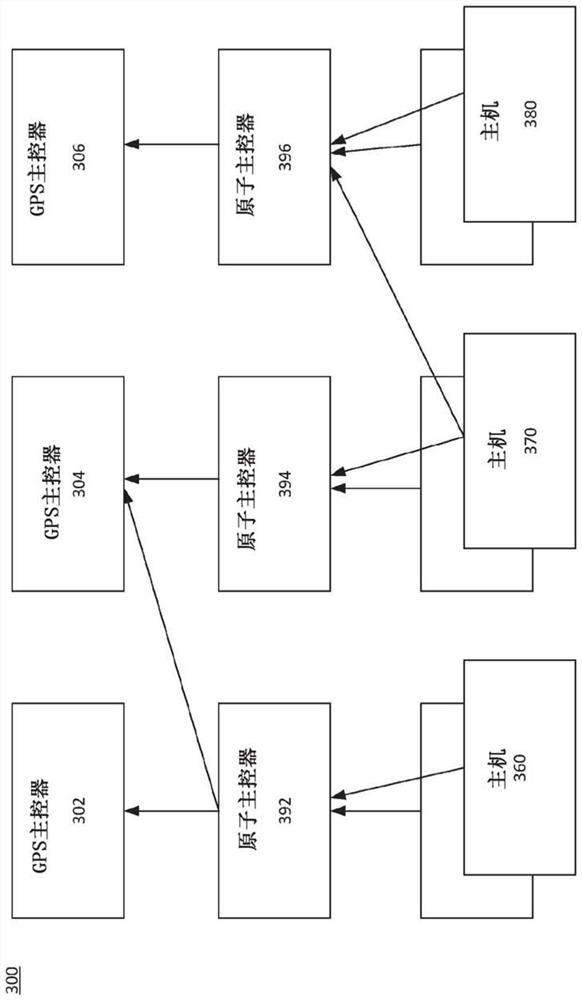
[0024] In a distributed database, transactions will be committed at a first coordinator server and one or more participant servers. The first coordinator server is configured to receive notificati...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com