Optimized and improved block chain PBFT consensus method
A block chain and consensus technology, applied in the field of block chain, can solve the problem of high communication complexity of PBFT algorithm, and achieve the effect of reducing communication complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
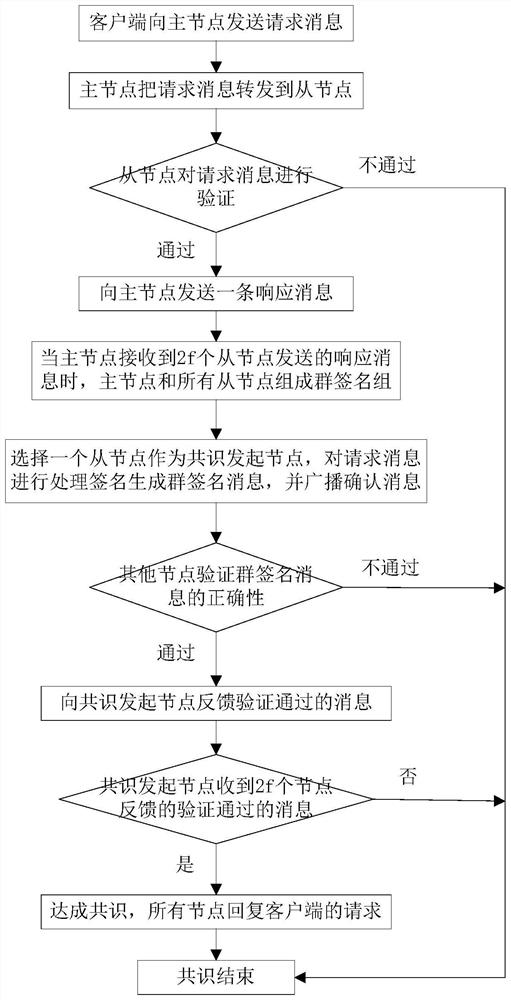
[0066] Such as figure 1 As shown, an optimized and improved blockchain PBFT consensus method includes the following steps:
[0067] S1: The client sends a request message to the master node of the blockchain network;
[0068] S2: The master node forwards the request message to the slave nodes of the blockchain network;
[0069] S3: The slave node verifies the request message; if the verification is passed, a response message is sent to the master node; if the verification fails, the consensus ends;
[0070] S4: When the master node receives the response message sent by 2f slave nodes, the master node and all slave nodes form a group signature group, and the master node acts as the group administrator; where, f is the number of error nodes;
[0071] S5: Select a slave node from all slave nodes as the consensus initiation node, process and sign the request message to generate a group signature message, and broadcast a confirmation message;
[0072] S6: Other nodes verify the ...
Embodiment 2
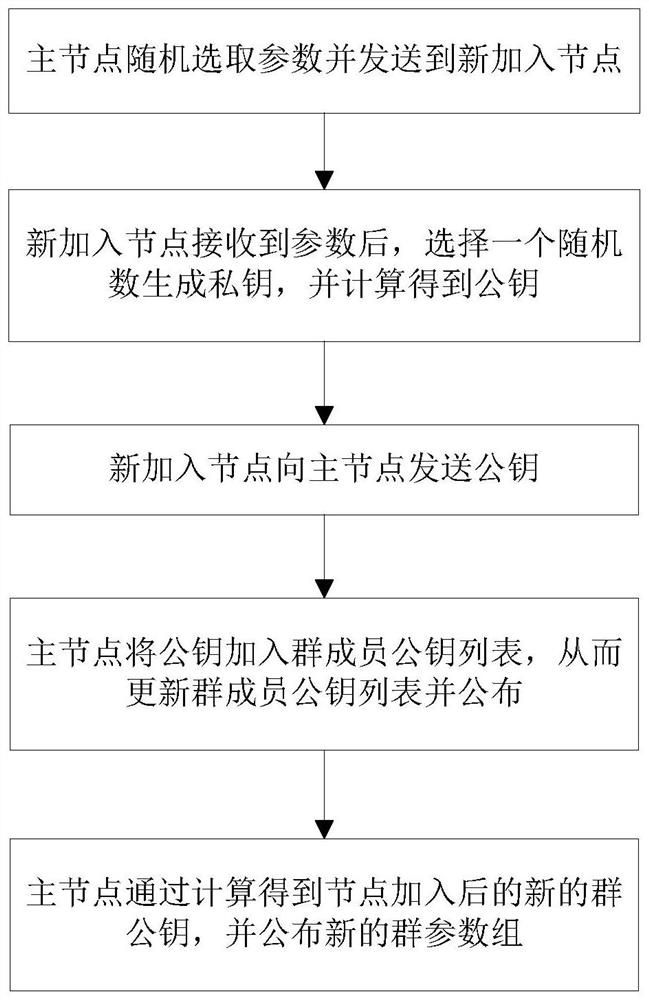
[0104] More specifically, such as figure 2 As shown, when a node joins the blockchain network, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0105] S8.1: The master node randomly selects the parameter p k+1 ,q k+1 and g k+1 , and the parameter p k+1 ,q k+1 and g k+1 Sent to the newly joined node ID k+1 ;
[0106] S8.2: Newly added node ID k+1 Received parameter p k+1 ,q k+1 and g k+1 After that, choose a random number x k+1 Generate a private key and pass the formula Calculate the public key y k+1 ;
[0107] S8.3: Newly added node ID k+1Send the public key y to the master node k+1 ;
[0108] S8.4: The master node sends the public key y k+1 Join the group member public key list, thereby updating the group member public key list and publishing it;
[0109] S8.5: The master node obtains the new group public key c after the node joins through calculation new , and announce the new group parameter set (y m ,c new ,H), calculate c new The formula is:
[0...
Embodiment 3
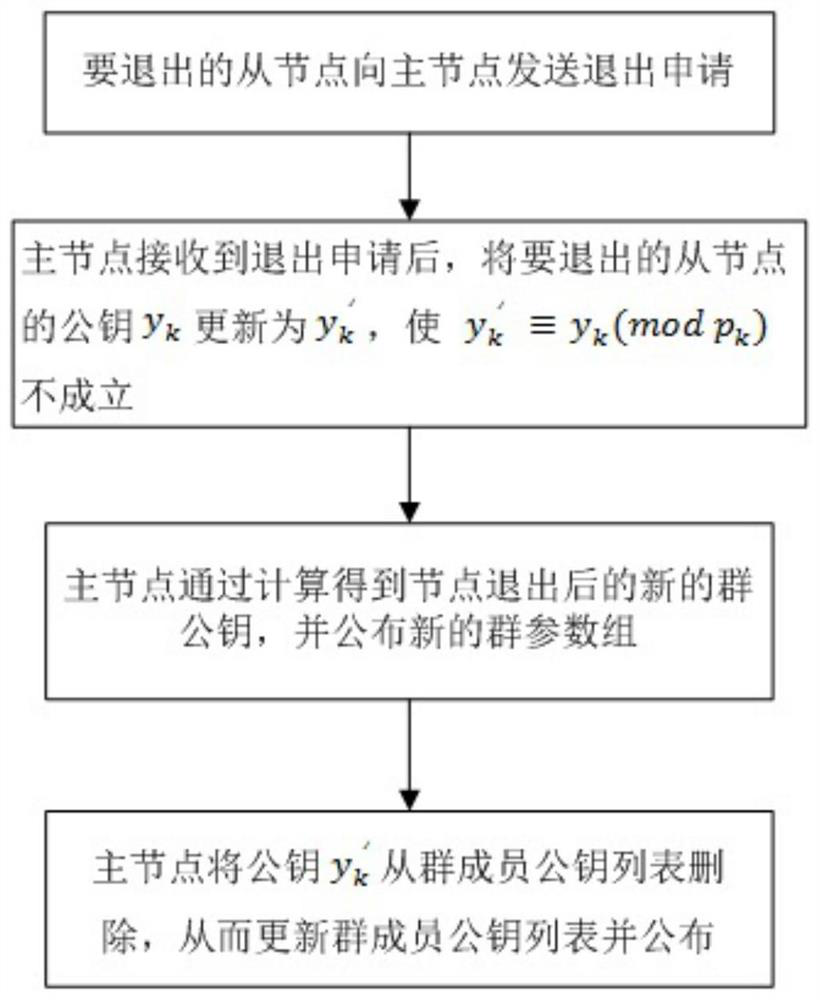
[0113] More specifically, such as image 3 As shown, when a node exits the network, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0114] S9.1: The ID of the slave node that wants to withdraw from the blockchain network and no longer participate in the consensus k Send an exit application to the master node;
[0115] S9.2: After receiving the exit application, the master node will send the ID k public key y k update to y k ', so that y k '≡y k (mod p k )invalid;
[0116] S9.3: The master node obtains the new group public key c′ after the node exits through calculation, and announces the new group parameter set (y m ,c′,H), the formula for calculating c′ is:
[0117]
[0118] S9.4: The master node sends the public key y k 'Delete from the group member public key list, thereby updating the group member public key list and publishing it.
[0119] During implementation, the congruence equations The solution is:
[0120]
[0121] in, P k ′ is to satisfy the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com