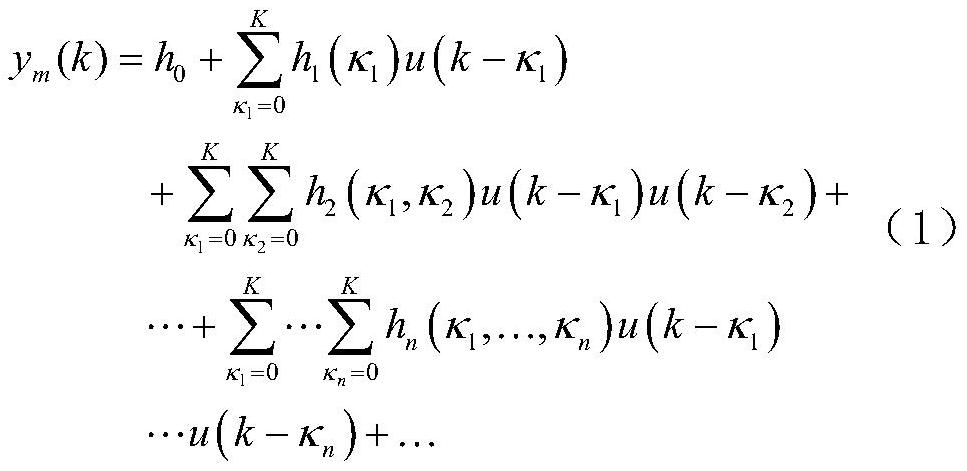Displacement Control Method of Magnetically Controlled Shape Memory Alloy Actuator
A memory alloy, displacement control technology, applied in the direction of adaptive control, general control system, control/regulation system, etc., can solve the problems of unknown system parameters, complex hysteresis dynamic characteristics of magnetic control shape memory alloy actuators, and restricted application.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
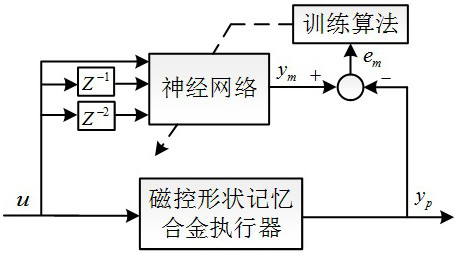
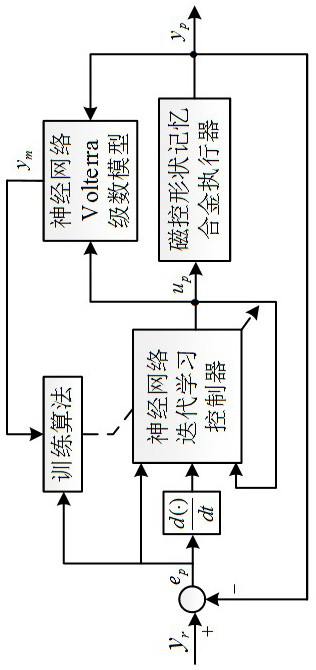
[0050]A method for controlling the displacement of a magnetically controlled shape memory alloy actuator based on neural network iterative learning control provided by the present invention is characterized in that it comprises the following steps:
[0051] Step 1: Establish a Volterra series model that can describe the rate-dependent hysteresis nonlinearity of the magnetically controlled shape memory alloy actuator, and use the neural network to construct the kernel function of the Volterra series;
[0052] The expression of the Volterra series model is:
[0053]
[0054] Among them, k=0,1,...,N-1 is the discrete time, N is the expected time length and is a positive integer, n is the order of the model, p is the number of iterations, u p (k) and is the input and output values of the model at the pth iteration, h n (κ 1 ,...,κ n ) and K is the nth order kernel function and memory length of the model, κ n is the memory delay corresponding to the nth item.
[0055] C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com